Abstract
Abstract 2275
Apixaban is direct factor-Xa inhibitor that reached the market for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in patients undergoing major orthopaedic surgery. It is also being evaluated in the reduction of recurrent ischemic events when added to antiplatelet therapy after an acute coronary syndrome and in the prevention of stroke in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation.
Thanks to its predictable pharmacokinetic profile, biological monitoring is not required. Nevertheless, evaluation of plasma drug concentration may be valuable in specific situations such as recurrent thrombosis, bleedings, before urgent surgery, in case of bridging and in case of at least two risk factors among the following ones: drug interactions with caution, moderate renal impairment and moderate hepatic impairment; Monitoring may also be useful in infants, pregnant women or in extreme body weights, although no relevant data on drug levels associated with approximate therapeutic and harmful ranges are currently available.
Apixaban was spiked at increasing concentrations (0, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200 and 500 ng/mL) in pooled citrated normal human platelet poor plasma (PPP) to measure Prothrombin Time (PT) and dilute PT with different thromboplastin, Thrombin Generation Assay (TGA) with different inducers and activity on different anti-Xa chromogenic assays. Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time with different reagents, Thrombin Time (TT), Ecarin Clotting Time (ECT) and Reptilase Time (RT), measurement of fibrinogen (Clauss method and PT-derived method) and antithrombin (anti-IIa and anti-Xa based chromogenic assays) were also tested. We also evaluated the impact of apixaban on assays used for the determination of lupus anticoagulant such as the DRVV-T.. (Screen and Confirm) as well as the PTT-LA.. and the Staclot-LA.. .
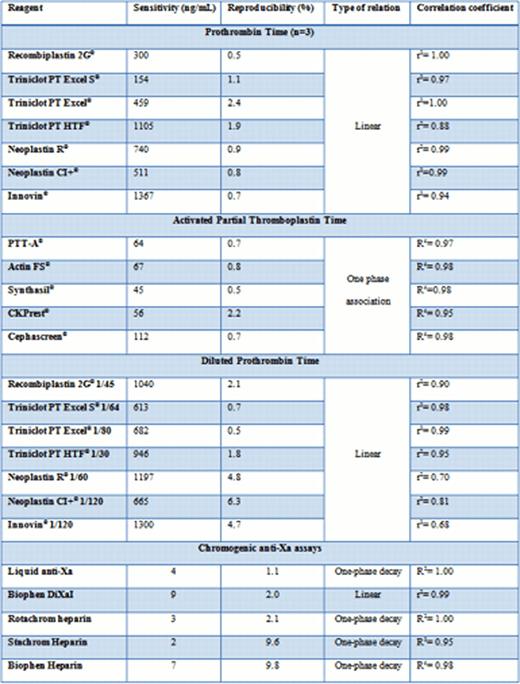
As mentioned in previous studies, PT showed a weak sensitivity towards apixaban in comparison with the plasma range obtained in short pharmacokinetic studies. Indeed, the concentration needed to double the clotting time was 154 ng/mL with the most sensitive reagent while the mean Cmax obtained in a short PK study after one oral intake of 5 mg apixaban (dose given in atrial fibrillation) was 96 ng/mL. Therefore, the sensitivity of PT is not strong enough to allow accurate quantitative measurement of the plasma drug concentration (Table 1). Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time presented a better sensitivity but showed a plateau after 100 ng/mL reflecting the uselessness of this test for the quantification of apixaban. Thrombin Time, ECT and RT were logically not affected while DRVV-T.. showed a sensitivity of 205 ng/mL (Screen), which is once again not enough sensitive.
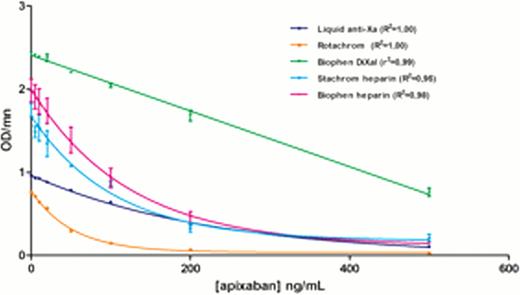
On the opposite, chromogenic anti-Xa assays seemed to be very sensitive (Figure 2 and Table 1). Nevertheless, the relation was not always linear and some methodologies needed to be adapted to ensure a broader range of application.
TGA (Figure 1) may be useful to assess the pharmacodynamics effects of apixaban on the coagulation process. Nevertheless, the turn around time and the lack of standardisation are currently limitations that restrict the use of this method.
In the case of the exploration of an haemorrhagic event, specific tests such as RT, fibrinogen (Clauss and PT-derived method (dFib)), TT and clotting factor activity may be used. Apixaban did not interfere with these tests. Antithrombin determination if also of importance and chromogenic anti-IIa based assays should be used in face of patients treated with apixaban to avoid misdiagnosis since an overvaluation of 12% by 100 ng/mL was shown using one chromogenic anti-Xa based assay.
PT may not be used as screening test to assess the risk of bleedings. A more specific and sensitive assay such as chromogenic anti-Xa assays using calibrators should be used to correctly assess the concentration of apixaban. Determination of lupus anticoagulant using DRVV-T.. and PTT-LA.. or Staclot LA.. as well as the determination of antithrombin using factor-Xa based chromogenic assays, were influenced by apixaban. Finally, standardization of the time between the last intake of apixaban and the sampling is mandatory.
Figures:
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal