Abstract
The genetic lesions identified to date do not fully recapitulate the molecular pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and do not entirely explain the development of severe complications such as chemorefractoriness. In the present study, BIRC3, a negative regulator of noncanonical NF-κB signaling, was investigated in different CLL clinical phases. BIRC3 lesions were absent in monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis (0 of 63) and were rare in CLL at diagnosis (13 of 306, 4%). Conversely, BIRC3 disruption selectively affected 12 of 49 (24%) fludarabine-refractory CLL cases by inactivating mutations and/or gene deletions that distributed in a mutually exclusive fashion with TP53 abnormalities. In contrast to fludarabine-refractory CLL, progressive but fludarabine-sensitive patients were consistently devoid of BIRC3 abnormalities, suggesting that BIRC3 genetic lesions associate specifically with a chemorefractory phenotype. By actuarial analysis in newly diagnosed CLL (n = 306), BIRC3 disruption identified patients with a poor outcome similar to that associated with TP53 abnormalities and exerted a prognostic role that was independent of widely accepted clinical and genetic risk factors. Consistent with the role of BIRC3 as a negative regulator of NF-κB, biochemical studies revealed the presence of constitutive noncanonical NF-κB activation in fludarabine-refractory CLL patients harboring molecular lesions of BIRC3. These data identify BIRC3 disruption as a recurrent genetic lesion of high-risk CLL devoid of TP53 abnormalities.
Introduction
The clinical course of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) ranges from a very indolent disorder with a normal lifespan to a rapidly progressive disease leading to death.1-3 Occasionally, CLL undergoes histological transformation to Richter syndrome (RS).4-6 The variable clinical course of CLL is driven, at least in part, by the immunogenetic and molecular heterogeneity of the disease.7,8
The genetic lesions identified to date in CLL do not fully recapitulate the molecular pathogenesis of the disease and do not entirely explain the development of severe complications such as chemorefractoriness that still represent a major unmet clinical need.9-16 In clinical trials, fludarabine refractoriness is due to TP53 disruption in approximately 40% of CLL patients failing treatment, but in a sizeable fraction of patients, the molecular basis of this aggressive clinical phenotype remains unclear.17-19 Recently, whole-exome sequencing studies have revealed novel genetic alterations such as NOTCH1 and SF3B1 mutations that might potentially contribute to high-risk CLL, although the precise clinical impact of these molecular lesions is still under scrutiny.20-23
In CLL, activation of the NF-κB pathway is regarded as a mechanism of resistance to disease eradication.24-28 Specific interactions between protective microenvironmental niches and CLL cells activate NF-κB signaling, which in turn provides prosurvival signals to the leukemic clone through the up-regulation of several antiapoptotic genes. NF-κB activation is correlated with CLL outcome and enhanced resistance to fludarabine.25,27,28 In addition to microenvironmental interactions, NF-κB signaling may also be activated in B-cell neoplasia through an array of molecular lesions affecting genes at different levels of the pathway.29,30 The Baculoviral IAP Repeat Containing 3 (BIRC3) gene, along with TRAF2 and TRAF3, cooperates in the same protein complex that negatively regulates the MAP3K14 serine-threonine kinase, the central activator of noncanonical NF-κB signaling.31-34
After our initial observation of recurrent mutations of BIRC3 in splenic marginal zone lymphoma,35 we performed targeted resequencing studies of the BIRC3 coding sequence and splicing sites across the spectrum of B-cell neoplasia. In the present study, we report that BIRC3-disrupting mutations and deletions recurrently and selectively associate with TP53 wild-type, fludarabine-refractory CLL and predict a dismal clinical outcome in consecutive CLL series.
Methods
Patients
The study population comprised 4 clinical CLL panels representative of different disease phases, including: (1) a consecutive series of newly diagnosed and previously untreated CLL (n = 306; Table 1; median survival from diagnosis, 12.5 years); (2) a cohort of fludarabine-refractory CLL (n = 49; Table 2; median survival from fludarabine-based treatment, 1.8 years); (3) a cohort of fludarabine-sensitive CLL (n = 68; supplemental Table 1 [available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article]; median survival from fludarabine-based treatment, 5.1 years); and (4) a cohort of clonally related RS (n = 33; all diffuse large B-cell lymphomas; supplemental Table 2; median survival from RS transformation, 1.1 year). A consecutive series of clinical monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis (MBL) with a CLL-like phenotype was also investigated (supplemental Table 3). Diagnosis of MBL, CLL, and fludarabine refractoriness was based on the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia-National Cancer Institute criteria.2 Diagnosis of RS was based on histological criteria.1
Clinical and genetic characteristics of the consecutive series of newly diagnosed and previously untreated CLL patients
| . | All (N = 306) . | BIRC3 disrupted (n = 13) . | BIRC3 WT (n = 293) . | P . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n . | % . | n . | % . | n . | % . | ||
| Age > 65 y | 200 | 65 | 10 | 77 | 190 | 65 | .553 |
| Male | 169 | 55 | 8 | 61 | 161 | 55 | .779 |
| CLL phenotypic score > 3 | 306 | 100 | 13 | 100 | 293 | 100 | 1.000 |
| Rai stage III-IV | 33 | 11 | 4 | 31 | 29 | 10 | .040 |
| IGHV identity ≥ 98% | 98 | 32 | 10 | 77 | 88 | 30 | .001 |
| TP53 disruption | 31 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 11 | .376 |
| NOTCH1 mutations | 33 | 11 | 2 | 15 | 31 | 11 | .641 |
| SF3B1 mutations | 13 | 4 | 2 | 15 | 16 | 5 | .173 |
| 11q22-q23 deletion | 18 | 6 | 9 | 69 | 9 | 3 | < .001 |
| Trisomy 12 | 59 | 19 | 4 | 31 | 55 | 19 | .285 |
| 13q14 deletion | 160 | 52 | 9 | 69 | 151 | 293 | .263 |
| Normal FISH | 91 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 91 | 31 | .012 |
| . | All (N = 306) . | BIRC3 disrupted (n = 13) . | BIRC3 WT (n = 293) . | P . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n . | % . | n . | % . | n . | % . | ||
| Age > 65 y | 200 | 65 | 10 | 77 | 190 | 65 | .553 |
| Male | 169 | 55 | 8 | 61 | 161 | 55 | .779 |
| CLL phenotypic score > 3 | 306 | 100 | 13 | 100 | 293 | 100 | 1.000 |
| Rai stage III-IV | 33 | 11 | 4 | 31 | 29 | 10 | .040 |
| IGHV identity ≥ 98% | 98 | 32 | 10 | 77 | 88 | 30 | .001 |
| TP53 disruption | 31 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 11 | .376 |
| NOTCH1 mutations | 33 | 11 | 2 | 15 | 31 | 11 | .641 |
| SF3B1 mutations | 13 | 4 | 2 | 15 | 16 | 5 | .173 |
| 11q22-q23 deletion | 18 | 6 | 9 | 69 | 9 | 3 | < .001 |
| Trisomy 12 | 59 | 19 | 4 | 31 | 55 | 19 | .285 |
| 13q14 deletion | 160 | 52 | 9 | 69 | 151 | 293 | .263 |
| Normal FISH | 91 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 91 | 31 | .012 |
WT indicates wild-type.
Clinical and genetic characteristics of the fludarabine-refractory CLL cohort
| . | All (N = 49) . | BIRC3 disrupted (n = 12) . | BIRC3 WT (n = 37) . | P . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N . | % . | N . | % . | N . | % . | ||
| Age > 65 y | 36 | 73 | 8 | 67 | 28 | 75 | .708 |
| Male | 31 | 63 | 7 | 58 | 24 | 65 | .738 |
| CLL phenotypic score > 3 | 49 | 100 | 12 | 100 | 37 | 100 | 1.000 |
| Rai stage III-IV | 28 | 57 | 8 | 67 | 20 | 54 | .443 |
| Treatment regimen at refractoriness | .499 | ||||||
| FCR | 17 | 35 | 5 | 42 | 12 | 32 | |
| FR | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | |
| FC | 14 | 29 | 2 | 17 | 12 | 32 | |
| F | 16 | 33 | 5 | 42 | 11 | 30 | |
| IGHV identity ≥ 98% | 39 | 80 | 10 | 82 | 29 | 78 | 1.000 |
| TP53 disruption | 17 | 35 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 37 | .004 |
| NOTCH1 mutations | 12 | 24 | 3 | 25 | 9 | 24 | 1.000 |
| SF3B1 mutations | 12 | 24 | 2 | 17 | 7 | 19 | 1.000 |
| 11q22-q23 deletion | 13 | 26 | 7 | 53 | 6 | 16 | .008 |
| Trisomy 12 | 14 | 29 | 3 | 25 | 11 | 30 | 1.000 |
| 13q14 deletion | 28 | 57 | 7 | 58 | 21 | 57 | 1.000 |
| Normal FISH | 6 | 12 | 1 | 8 | 5 | 13 | 1.000 |
| . | All (N = 49) . | BIRC3 disrupted (n = 12) . | BIRC3 WT (n = 37) . | P . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N . | % . | N . | % . | N . | % . | ||
| Age > 65 y | 36 | 73 | 8 | 67 | 28 | 75 | .708 |
| Male | 31 | 63 | 7 | 58 | 24 | 65 | .738 |
| CLL phenotypic score > 3 | 49 | 100 | 12 | 100 | 37 | 100 | 1.000 |
| Rai stage III-IV | 28 | 57 | 8 | 67 | 20 | 54 | .443 |
| Treatment regimen at refractoriness | .499 | ||||||
| FCR | 17 | 35 | 5 | 42 | 12 | 32 | |
| FR | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | |
| FC | 14 | 29 | 2 | 17 | 12 | 32 | |
| F | 16 | 33 | 5 | 42 | 11 | 30 | |
| IGHV identity ≥ 98% | 39 | 80 | 10 | 82 | 29 | 78 | 1.000 |
| TP53 disruption | 17 | 35 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 37 | .004 |
| NOTCH1 mutations | 12 | 24 | 3 | 25 | 9 | 24 | 1.000 |
| SF3B1 mutations | 12 | 24 | 2 | 17 | 7 | 19 | 1.000 |
| 11q22-q23 deletion | 13 | 26 | 7 | 53 | 6 | 16 | .008 |
| Trisomy 12 | 14 | 29 | 3 | 25 | 11 | 30 | 1.000 |
| 13q14 deletion | 28 | 57 | 7 | 58 | 21 | 57 | 1.000 |
| Normal FISH | 6 | 12 | 1 | 8 | 5 | 13 | 1.000 |
WT indicates wild-type; FCR, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, rituximab; FR, fludarabine, rituximab; FC, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide; and F, fludarabine.
In addition to CLL, RS, and MBL, we also investigated a cohort of 194 lymphoid tumors representative of the main categories of mature B-cell neoplasms (follicular lymphoma, n = 20; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.=, n = 30; Burkitt lymphoma, n = 38; extranodal marginal zone lymphoma, n = 65; hairy-cell leukemia, n = 19; and multiple myeloma, n = 22). The number of the mature B-cell neoplasms included in each panel allows a 90% probability of identifying genes that are mutated in at least 10% of patients.
CLL and clinical MBL samples were extracted from fresh or frozen PBMCs isolated by Ficoll-Paque gradient centrifugation. PBMCs were obtained at the following times: (1) for clinical MBL and for the consecutive series of newly diagnosed and previously untreated CLL, at disease presentation; (2) for the fludarabine-refractory CLL cohort, immediately before starting treatment to which the patient failed to respond because of stable/progressive disease; and (3) for the fludarabine-sensitive CLL cohort, at the time of progression immediately before starting the treatment to which the patient responded. All RS studies were performed on RS diagnostic biopsies. Samples of the other lymphoid neoplasms were obtained at diagnosis from the involved site (lymph nodes or extranodal sites in the case of lymphoma; CD138+ cells purified from BM aspirate in the case of multiple myeloma; and peripheral blood purified B cells in the case of hairy-cell leukemia). In all samples, the fraction of tumor cells corresponded to > 70% as assessed by flow cytometry and/or immunohistochemistry. Matched normal DNAs from the same patients were obtained from saliva or from purified granulocytes and confirmed to be tumor-free by PCR of tumor-specific IGHV-D-J rearrangements.36
Patients provided informed consent in accordance with local institutional review board requirements and the Declaration of Helsinki. The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Ospedale Maggiore della Carità di Novara affiliated with the Amedeo Avogadro University of Eastern Piedmont (protocol code 59/CE; study number CE 8/11).
Mutation analysis of BIRC3 and TP53
The BIRC3 (exons 2-9, including splicing sites; RefSeq NM_001165.3), TRAF2 (exons 2-11, including splicing sites; RefSeq NM_021138.3), TRAF3 (exons 3-12, including splicing sites; RefSeq NM_145725.2), MAP3K14 (exons 1-17, including splicing sites; RefSeq NM_003954.2), TP53 (exons 4-8, including splicing sites; RefSeq NM_000546.4), NOTCH1 (exons 26, 27 and 34; RefSeq NM_017617.2), and SF3B1 (exons 1-25, including splice sites; RefSeq NM_012433.2) genes were analyzed by PCR amplification and DNA direct sequencing of high-molecular-weight genomic DNA.11,20,22,23,35 Purified amplicons were subjected to conventional DNA Sanger sequences using the ABI PRISM 3100 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems). Sequences were compared with the corresponding germline RefSeq sequences using the Mutation Surveyor Version 2.41 software package (SoftGenetics) after both automated and manual curation. All variants were sequenced from both strands on independent PCR products. Synonymous mutations, previously reported polymorphisms (dbSNP135, Ensembl Database, UCSC Genome Browser, or the 1000 Genome Project) and changes present in the matched normal DNA were removed from the analysis. In patients displaying more than one mutational event within the BIRC3 gene, the allelic distribution of the mutations was determined by cloning and sequencing full-length PCR products obtained from cDNA (n = 20 clones). Molecular studies were performed blindly with respect to clinical data. All PCR primers and conditions are available on request.
IGHV mutation status
Interphase FISH
Probes used for FISH analysis were: LSI13 and LSID13S319 (13q14 deletion), CEP12 (trisomy 12), LSIp53 (17p13/TP53 deletion), and LSIATM (11q2-q23/ATM deletion; all from Abbott Laboratories) and the RP11-177O8 (BIRC3), RP11-769N4 (TRAF2), RP11-676M2 (TRAF3), and RP11-666C2 (MAP3K14) BAC clones. For each probe, at least 400 interphase cells with well-delineated fluorescent spots were examined. The presence of 13q14 deletion, trisomy 12, 11q22-q23 deletion, 17p13 deletion, BIRC3 deletion, TRAF3 deletion, MAP3K14 gain, and TRAF2 abnormalities was scored when the percentage of nuclei with the abnormality was above our internal cutoff (5%, 5%, 7%, 10%, 10%, 10%, 10%, and 10%, respectively), defined as the means plus 3 SDs of the frequency of normal control cells exhibiting the abnormality.6,35
Copy-number analysis
Copy-number data were derived from a previously reported dataset.39 Genome-wide DNA profiles were obtained from high-molecular-weight genomic DNA of CLL patients using the Genome-Wide Human SNP Array Version 6.0 (Affymetrix) following the manufacturer's instructions. The bioinformatics pipeline used for the identification of copy-number alterations is described in detail in Rinaldi et al.39
Western blot studies
CLL cells were purified by negative selection using anti-CD3, anti-CD14, and anti-CD16 mAbs and Dynal magnetic beads (Invitrogen). Proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blot. Abs were anti-NFKB2 (#4882; Cell Signaling Technology), anti-BIRC3 (#3130; Cell Signaling Technology), and anti-actin (#sc-1615; Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Image acquisition and densitometric analyses were performed using ImageQuant LAS4000 and TL Version 7.0 software (GE Healthcare). Band intensities were calculated by standardizing over actin and using the JJN3 cell line as an internal loading control in different gels.35
Statistical analysis
Overall survival (OS) was measured from date of initial presentation to date of death (event) or last follow-up (censoring).2 Survival analysis was performed by the Kaplan-Meier method.40 The crude association between exposure variables and outcome was estimated by univariate Cox regression analysis.41 The independence of BIRC3 disruption as a predictor of OS for CLL was estimated after controlling for confounding variables by multivariate Cox regression analysis.41 The following variables were included in multivariate analysis: BIRC3 disruption by mutation and/or deletion (present vs absent), age (> 65 years vs ≤ 65 years), Rai stage (III-IV vs 0-II), IGHV identity ≥ 98% (present vs absent), 11q22-q23 deletion (present vs absent), TP53 disruption by mutation and/or deletion (present vs absent), NOTCH1 mutations (present vs absent), and SF3B1 mutations (present vs absent). None of the covariates violated the proportional hazard assumption as documented by plotting the smoothed Schoenfeld residuals and by performing a correlation test between time and residuals.42,43 The assumption of effect additivity of predictors was not violated, as documented by a global test of additivity including interactions between BIRC3 disruption and other covariates. None of the covariates showed colinearity.42
The prediction accuracy of the multivariate survival model was verified by assessing model discrimination and calibration.42 Discrimination indicates how well the model separates patients who experienced the event of interest from patients who did not, and was measured by calculating the c-index (where 1 is perfect discrimination and 0.5 is equivalent to chance).42 Calibration describes how well the survival probability from the model corresponds to the survival probability from the observed data and was assessed graphically by plotting the predicted probability of survival against the actual probability of survival.42 The heuristic shrinkage estimator, which quantifies model overfitting, was calculated using the formula (model likelihood ratio χ2) − (number of degree of freedom in the model)/(model likelihood ratio χ2). According to this formula, the more the shrinkage approximates 1, the lower the overfitting of the model.42 A bootstrap resampling (with 1000 resamples) was used to calculate the bias-corrected c-index and to construct a bias-corrected calibration curve and slope.42 This approach provides a bias-corrected estimate of prediction accuracy of the model to protect against overfitting.
The stability and predictive performance of BIRC3 disruption as an independent predictor of OS from CLL was validated internally using a bootstrapping resampling procedure.42,44 In the first step, 1000 bootstrap samples were generated randomly with replacement from the original CLL population. Cox regression was applied to each bootstrap sample with the same covariates as the original modeling. The percentage of bootstrap samples for which each covariate was selected as significant in the model was then calculated. The percentage of selection reflects the prognostic importance of a covariate, because it is expected that an important covariate will be selected for the majority of bootstrap samples. In the second step, 1000 additional bootstrap samples were generated randomly with replacement from the original CLL population. Cox regression was applied to each bootstrap sample with the same covariates as the original modeling. For each covariate, the mean SD and confidence intervals were computed for the 1000 bootstrap replications.42,44
Categorical variables were compared by χ2 test and Fisher exact test when appropriate. Continuous variables were compared by the Mann-Whitney test. All statistical tests were 2-sided. Statistical significance was defined as P < .05. The analysis was performed with the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) Version 18.0 software and with R statistical package Version 2.13.0 (http://www.r-project.org).
Results
BIRC3 mutations across the spectrum of B-cell neoplasia
After the initial observation of recurrent BIRC3 mutations in splenic marginal zone lymphoma,35 we performed targeted resequencing of the BIRC3 coding sequence and splicing sites across the spectrum of B-cell neoplasias. This initial screening revealed that BIRC3 mutations are selectively restricted to CLL (2 of 20; both cases were primary fludarabine refractory), whereas they are absent in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (0 of 30), Burkitt lymphoma (0 of 38), follicular lymphoma (0 of 20), extranodal marginal zone lymphoma (0 of 65), hairy-cell leukemia (0 of 19), and multiple myeloma (0 of 22). These results prompted the investigation of the prevalence and clinical impact of BIRC3 genetic lesions in different clinical phases of CLL.
BIRC3 is frequently targeted by inactivating lesions in fludarabine-refractory CLL
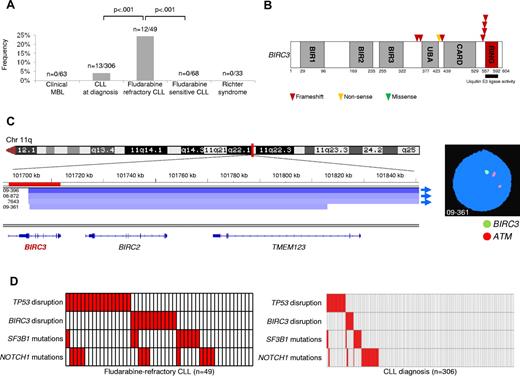
BIRC3 lesions were absent in MBL with a CLL-like phenotype (0 of 63) and were rare in CLL at diagnosis (13 of 306, 4%; n = 3 monoallelic truncating mutations, n = 8 monoallelic deletions, and n = 2 biallelic disruptions by truncating mutation coupling with a deletion; Figure 1A-B and supplemental Tables 3 and 4). Conversely, BIRC3 was affected in 12 of 49 (24%) fludarabine-refractory CLL patients by inactivating mutations (7 frameshift and 1 nonsense) and/or gene deletions (n = 7; nuclei harboring BIRC3 deletion: 20%-91%; Figure 1A-B and supplemental Tables 3 and 4). BIRC3 lesions were similarly represented among patients who received fludarabine-cyclophosphamide-rituximab (FCR) or other fludarabine-based regimens (Table 2). All inactivating mutations were somatically acquired, were predicted to generate aberrant transcripts carrying premature stop codons, and caused elimination or truncation of the C-terminal RING domain, the E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of which is essential for proteasomal degradation of MAP3K14 (Figure 1B).31-34
BIRC3 disruption in CLL. (A) prevalence of BIRC3 disruption in clinical MBL, in CLL at diagnosis, in fludarabine-refractory CLL, in fludarabine-sensitive CLL, and in RS. Numbers on top indicate the actual number of mutated samples over the total number analyzed. (B) Schematic diagram of the BIRC3 protein with its key functional domains. Color-coded symbols indicate the type and position of the mutations in BIRC3. (C) Graphic representation of segmentation data from 4 CLL patients carrying BIRC3 deletion. Deletions start from a centromeric break that truncates BIRC3 and removes its terminal exons, including exon 9, which encodes the RING domain. Sample 09-361 harbors a focal loss of 411 kb on 11q22 involving BIRC3 and its homolog, BIRC2. Each track represents one sample; white denotes a normal (diploid) copy number and blue indicates region of a copy number loss (Integrative Genomics Viewer software; http//www.broadinstitute.org/igv; assembly NCBI36/hg18). Individual genes in the region are aligned in the bottom panel. Dual-color FISH validates the occurrence of 11q22 deletion involving BIRC3 but sparing ATM in sample 09-361 (RP11-177O8-BIRC3 specific probe in green and LSIATM probe in orange). (D) Mutual relationship of the BIRC3 disruption with other genetic lesions in CLL at diagnosis and in fludarabine-refractory CLL. In the heat map, rows correspond to identical genes and columns represent individual patients color-coded based on the gene status (white indicates wild-type and red, mutations and/or deletion of TP53, mutations and/or deletion of BIRC3, mutations of SF3B1, and mutations of NOTCH1).
BIRC3 disruption in CLL. (A) prevalence of BIRC3 disruption in clinical MBL, in CLL at diagnosis, in fludarabine-refractory CLL, in fludarabine-sensitive CLL, and in RS. Numbers on top indicate the actual number of mutated samples over the total number analyzed. (B) Schematic diagram of the BIRC3 protein with its key functional domains. Color-coded symbols indicate the type and position of the mutations in BIRC3. (C) Graphic representation of segmentation data from 4 CLL patients carrying BIRC3 deletion. Deletions start from a centromeric break that truncates BIRC3 and removes its terminal exons, including exon 9, which encodes the RING domain. Sample 09-361 harbors a focal loss of 411 kb on 11q22 involving BIRC3 and its homolog, BIRC2. Each track represents one sample; white denotes a normal (diploid) copy number and blue indicates region of a copy number loss (Integrative Genomics Viewer software; http//www.broadinstitute.org/igv; assembly NCBI36/hg18). Individual genes in the region are aligned in the bottom panel. Dual-color FISH validates the occurrence of 11q22 deletion involving BIRC3 but sparing ATM in sample 09-361 (RP11-177O8-BIRC3 specific probe in green and LSIATM probe in orange). (D) Mutual relationship of the BIRC3 disruption with other genetic lesions in CLL at diagnosis and in fludarabine-refractory CLL. In the heat map, rows correspond to identical genes and columns represent individual patients color-coded based on the gene status (white indicates wild-type and red, mutations and/or deletion of TP53, mutations and/or deletion of BIRC3, mutations of SF3B1, and mutations of NOTCH1).
BIRC3 lesions were monoallelic in all but 2 CLL patients (patients 5977 and 6550) who carried inactivation of both BIRC3 alleles (Table 3 and supplemental Table 4). In patient 5977, a frameshift mutation of one allele was coupled with a deletion of the second allele. Patient 6550 harbored 3 distinct genetic events on BIRC3, including: (1) a monoallelic deletion of the entire BIRC3 locus in 84% of the nuclei; (2) a large intragenic deletion of 4894 bp that removed the last 142 bp of exon 6, the entire intron 6-7, and the first 285 bp of exon 7 and caused a frameshift mutation (c.1183_1352del, p.V395fs*78) in the gene-coding sequence; and (3) a nonsense truncating mutation (c.1270G > T, p.E424*). In patient 6550, sequencing analysis of BIRC3 transcripts after cDNA amplification and subcloning demonstrated that the c.1183_1352del intragenic deletion and the c.1270G > T nonsense mutation were located on separate alleles and that the c.1183_1352del intragenic deletion was represented in the majority of the clones, whereas the c.1270G > T nonsense mutation was restricted to 15% of the clones. These data suggest a tumor mosaicism for BIRC3 in patient 6550.
BIRC3 mutations in CLL
| Sample ID . | Nucleotide change‡ . | Amino acid change§ . | Predicted functional consequence . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5977*† | c.1101_1132del32 | p.G367fs*6 | Truncated protein |
| 6550*† | c.1270G > T | p.E424* | Truncated protein |
| 6550*† | c.1183_1352del4894 | p.V395fs*78 | Truncated protein |
| 3878*† | c.1279_1280insA | p.I427fs*11 | Truncated protein |
| 5610*† | c.1638_1639insA | p.Q547fs*12 | Truncated protein |
| 5889*† | c.1663_1666delAGAA | p.R555fs*12 | Truncated protein |
| 12632* | c.4388delA | p.E553fs*22 | Truncated protein |
| 12534* | c.4441_4444delAGAA | p.E553fs*14 | Truncated protein |
| Sample ID . | Nucleotide change‡ . | Amino acid change§ . | Predicted functional consequence . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5977*† | c.1101_1132del32 | p.G367fs*6 | Truncated protein |
| 6550*† | c.1270G > T | p.E424* | Truncated protein |
| 6550*† | c.1183_1352del4894 | p.V395fs*78 | Truncated protein |
| 3878*† | c.1279_1280insA | p.I427fs*11 | Truncated protein |
| 5610*† | c.1638_1639insA | p.Q547fs*12 | Truncated protein |
| 5889*† | c.1663_1666delAGAA | p.R555fs*12 | Truncated protein |
| 12632* | c.4388delA | p.E553fs*22 | Truncated protein |
| 12534* | c.4441_4444delAGAA | p.E553fs*14 | Truncated protein |
For these patients, paired normal DNA was available and confirmed the somatic origin of the mutation.
These patients were treated at diagnosis with fludarabine-based regimens to which they failed to respond; therefore, they are included both in the fludarabine-refractory CLL cohort and in the consecutive series of newly diagnosed CLL patients.
Numbering according to GenBank accession number NM_001165.3.
Numbering according to GenBank accession number NP_001156.1.
SNP array analysis of a large CLL dataset (n = 339, including 158 newly diagnosed CLL investigated in this study) identified a focal loss of 411 kb involving BIRC3 and its homolog BIRC2 in one CLL (case 09-361; Figure 1C and supplemental Table 4). This deletion truncated BIRC3 and removed its terminal exons, including exon 9 that encodes the RING domain. Three additional CLL harbored large 11q22 deletions starting from a centromeric break that truncated BIRC3 and removed its terminal exons, including exon 9 (Figure 1C and supplemental Table 4).
Overall, these data document that BIRC3 disruption by mutation and/or deletion occurs frequently in fludarabine-refractory CLL, and point to removal of the C-terminal RING domain as a common mechanism altering BIRC3 function in this context.
Genetic lesions of BIRC3 cause the formation of truncated BIRC3 proteins and associate with activated NF-κB signaling
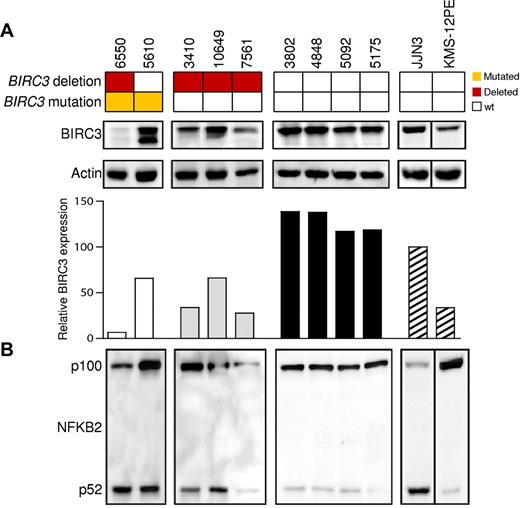
Among cases carrying truncating gene mutations, Western blot analysis using Abs directed against the N-terminus of the BIRC3 protein revealed the expression of an aberrant band of lower molecular weight corresponding in size to the predicted truncated BIRC3 (Figure 2). A full-length BIRC3 protein, corresponding to the wild-type allele, was also present. Patient 6550, who carried 3 genetic events, expressed very low levels of both the wild-type and the truncated BIRC3 proteins, with a pattern that is consistent with the occurrence of 2 clonal disrupting deletions and a subclonal truncating mutation in this patient. Patients carrying a monoallelic BIRC3 deletion displayed reduced levels of BIRC3 protein that were consistent with a residual expression of the wild-type allele (Figure 2).
The NF-κB pathway is activated in CLL patients harboring BIRC3 disruption. Western blot analysis showing BIRC3 expression and NFKB2 processing in purified primary tumor cells from 9 CLL patients carrying wild-type or disrupted BIRC3. The JJN3 (plasma cell leukemia) cell line was used as a positive control for NFKB2 processing and BIRC3 expression. The KMS-12PE cell line (a multiple myeloma cell line) was used as a negative control for NFKB2 processing. Actin was used as a loading control. The histogram shows the relative fold change of BIRC3 expression compared with the BIRC3 expression level observed in the JJN3 cell line (arbitrarily set as 100). The aberrant BIRC3 bands in patients 6550 and 5610 correspond in size to the predicted BIRC3-truncated protein.
The NF-κB pathway is activated in CLL patients harboring BIRC3 disruption. Western blot analysis showing BIRC3 expression and NFKB2 processing in purified primary tumor cells from 9 CLL patients carrying wild-type or disrupted BIRC3. The JJN3 (plasma cell leukemia) cell line was used as a positive control for NFKB2 processing and BIRC3 expression. The KMS-12PE cell line (a multiple myeloma cell line) was used as a negative control for NFKB2 processing. Actin was used as a loading control. The histogram shows the relative fold change of BIRC3 expression compared with the BIRC3 expression level observed in the JJN3 cell line (arbitrarily set as 100). The aberrant BIRC3 bands in patients 6550 and 5610 correspond in size to the predicted BIRC3-truncated protein.
Western blot analysis of NFKB2 processing from p100 to p52 revealed a constitutive noncanonical NF-κB activation in CLL harboring BIRC3 disruption by mutations or deletion (Figure 2; mean p52/p100 ratio, 0.565). In contrast, noncanonical NF-κB activation was not observed in patients devoid of BIRC3 abnormalities, as documented by the predominant expression of p100 over p52 (mean p52/p100 ratio, 0.138) in these patients.
BIRC3-inactivating lesions are specific for fludarabine-refractory CLL and are mutually exclusive with TP53 disruption
To investigate whether BIRC3 genetic lesions were restricted to chemorefractory cases in progressive CLL patients, we analyzed BIRC3 for mutations and deletions in progressive but fludarabine-sensitive CLL and in RS (supplemental Tables 1-3).
Fludarabine-sensitive CLL patients were consistently devoid of BIRC3 disruption in all cases (n = 68), suggesting that BIRC3 genetic lesions specifically associate with a chemorefractory phenotype among progressive CLL cases requiring treatment (Figure 1A). BIRC3 genetic lesions were absent in clonally related RS (0 of 33; Figure 1A and supplemental Table 2), thus strengthening the notion that RS is molecularly distinct from chemorefractory progression without transformation.6,22
We then tested the relationship between disruption of BIRC3 and TP53 in fludarabine-refractory CLL. In the current series of fludarabine-refractory patients, TP53 was disrupted by mutations (n = 10) and/or deletions (n = 14) in 17 of 49 (35%) patients. BIRC3 lesions distributed in a mutually exclusive fashion with TP53 disruption (Figure 1D). BIRC3 lesions segregated with TP53 wild-type, fludarabine-refractory CLL patients (12 of 32, 37%), whereas they were consistently absent among TP53-disrupted patients (0 of 17; P = .004). These data show that BIRC3 lesions selectively associate with fludarabine-refractory but TP53 wild-type CLL across the clinical spectrum of the disease.
By combining BIRC3 disruption with other genetic lesions enriched in chemorefractory patients (ie, TP53 disruption, NOTCH1 mutations, and SF3B1 mutations), fludarabine-refractory CLL appeared to be characterized by multiple molecular alterations that to some extent are mutually exclusive and account for approximately 80% of cases.
BIRC3 disruption identifies CLL patients whose survival is similar to that associated with TP53 abnormalities
In a consecutive CLL series evaluated at diagnosis, BIRC3 disruption (13 of 306, 4%) was associated with unfavorable clinical and genetic features (Table 1) and predicted poor outcome because of primary chemorefractoriness among patients requiring treatment. As shown by univariate analysis, the crude impact of BIRC3 disruption on survival was an approximately 5-fold increase in the hazard of death (hazard ratio = 5.09; 95% confidence interval, 2.52-10.28; P < .001) and a shortening of OS (median OS in BIRC3-disrupted patients, 3.1 years vs not reached in BIRC3 wild-type patients; P < .001; Figure 3A and Table 4), which occurred irrespective of the type of BIRC3 lesion (for mutations, P = .001; for deletions, P = .001; supplemental Figure 1).
Kaplan-Meier estimates of OS according to BIRC3 disruption. (A) Kaplan-Meier estimates of OS according to BIRC3 disruption in newly diagnosed CLL patients (n = 306). BIRC3 wild-type (WT) patients are represented by the blue line. Patients with BIRC3 disruption by mutations and/or deletions (BIRC3 dis) are represented by the red line. (B) Kaplan-Meier estimates of OS according to BIRC3 and TP53 disruption in newly diagnosed CLL patients (n = 306). BIRC3 and TP53 wild-type patients are represented by the blue line. Patients harboring BIRC3 disruption but who are wild-type on the TP53 gene (BIRC3 dis) are represented by the red line. Patients harboring TP53 disruption but who are wild-type on the BIRC3 gene (TP53 dis) are represented by the yellow line.
Kaplan-Meier estimates of OS according to BIRC3 disruption. (A) Kaplan-Meier estimates of OS according to BIRC3 disruption in newly diagnosed CLL patients (n = 306). BIRC3 wild-type (WT) patients are represented by the blue line. Patients with BIRC3 disruption by mutations and/or deletions (BIRC3 dis) are represented by the red line. (B) Kaplan-Meier estimates of OS according to BIRC3 and TP53 disruption in newly diagnosed CLL patients (n = 306). BIRC3 and TP53 wild-type patients are represented by the blue line. Patients harboring BIRC3 disruption but who are wild-type on the TP53 gene (BIRC3 dis) are represented by the red line. Patients harboring TP53 disruption but who are wild-type on the BIRC3 gene (TP53 dis) are represented by the yellow line.
Univariate and multivariate analysis for OS in newly diagnosed and previously untreated CLL patients
| Characteristic . | Events . | Total . | OS, y . | Univariate analysis . | Multivariate analysis*†‡ . | Internal bootstrapping validation . | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bootstrap parameters, mean . | Bootstrap selection, % . | ||||||||||||||||
| Median . | LCI . | UCI . | HR . | LCI . | UCI . | P . | HR . | LCI . | UCI . | P . | HR . | LCI . | UCI . | ||||
| BIRC3 WT | 69 | 293 | NR | 85% | |||||||||||||
| BIRC3 disruption | 9 | 13 | 3.1 | 0 | 6.7 | 5.09 | 2.52 | 10.28 | < .001 | 3.04 | 1.21 | 7.61 | .017 | 3.90 | 1.32 | 13.17 | |
| Age ≤ 65 y | 13 | 106 | NR | 100% | |||||||||||||
| Age > 65 y | 65 | 200 | 8.5 | 4.6 | 12.4 | 3.57 | 1.95 | 6.52 | < .001 | 3.88 | 2.08 | 7.22 | < .001 | 4.41 | 2.21 | 8.87 | |
| Rai stage 0-II | 56 | 273 | NR | 97% | |||||||||||||
| Rai stage III-IV | 22 | 33 | 2.7 | 0.6 | 4.9 | 5.44 | 3.31 | 8.97 | < .001 | 3.10 | 1.72 | 5.59 | < .001 | 3.44 | 1.83 | 6.47 | |
| IGHV identity < 98% | 42 | 208 | NR | 33% | |||||||||||||
| IGHV identity ≥ 98% | 36 | 98 | 11.7 | 3.0 | 20.4 | 2.03 | 1.29 | 3.18 | .002 | 1.24 | 0.72 | 2.12 | .426 | 1.31 | 0.75 | 2.28 | |
| No 11q22-q23 deletion | 67 | 288 | NR | 57% | |||||||||||||
| 11q22-q23 deletion | 11 | 18 | 3.1 | 0.8 | 5.4 | 4.08 | 2.14 | 7.77 | < .001 | 2.18 | 0.85 | 5.62 | .105 | 2.51 | 0.85 | 5.64 | |
| TP53 WT | 61 | 275 | NR | 99% | |||||||||||||
| TP53 disruption | 17 | 31 | 2.9 | 0.6 | 5.3 | 3.85 | 2.23 | 6.65 | < .001 | 4.97 | 2.75 | 8.97 | < .001 | 5.30 | 2.84 | 9.92 | |
| NOTCH1 WT | 63 | 273 | NR | 74% | |||||||||||||
| NOTCH1 mutated | 15 | 33 | 3.3 | 1.2 | 14.3 | 2.15 | 1.22 | 3.79 | .007 | 2.08 | 1.04 | 4.16 | .038 | 2.31 | 1.13 | 4.76 | |
| SF3B1 WT | 71 | 288 | NR | 71% | |||||||||||||
| SF3B1 mutated | 7 | 18 | 2.5 | 1.7 | 3.3 | 3.29 | 1.50 | 7.21 | .003 | 2.49 | 1.08 | 5.72 | .032 | 2.94 | 1.20 | 7.35 | |
| Characteristic . | Events . | Total . | OS, y . | Univariate analysis . | Multivariate analysis*†‡ . | Internal bootstrapping validation . | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bootstrap parameters, mean . | Bootstrap selection, % . | ||||||||||||||||
| Median . | LCI . | UCI . | HR . | LCI . | UCI . | P . | HR . | LCI . | UCI . | P . | HR . | LCI . | UCI . | ||||
| BIRC3 WT | 69 | 293 | NR | 85% | |||||||||||||
| BIRC3 disruption | 9 | 13 | 3.1 | 0 | 6.7 | 5.09 | 2.52 | 10.28 | < .001 | 3.04 | 1.21 | 7.61 | .017 | 3.90 | 1.32 | 13.17 | |
| Age ≤ 65 y | 13 | 106 | NR | 100% | |||||||||||||
| Age > 65 y | 65 | 200 | 8.5 | 4.6 | 12.4 | 3.57 | 1.95 | 6.52 | < .001 | 3.88 | 2.08 | 7.22 | < .001 | 4.41 | 2.21 | 8.87 | |
| Rai stage 0-II | 56 | 273 | NR | 97% | |||||||||||||
| Rai stage III-IV | 22 | 33 | 2.7 | 0.6 | 4.9 | 5.44 | 3.31 | 8.97 | < .001 | 3.10 | 1.72 | 5.59 | < .001 | 3.44 | 1.83 | 6.47 | |
| IGHV identity < 98% | 42 | 208 | NR | 33% | |||||||||||||
| IGHV identity ≥ 98% | 36 | 98 | 11.7 | 3.0 | 20.4 | 2.03 | 1.29 | 3.18 | .002 | 1.24 | 0.72 | 2.12 | .426 | 1.31 | 0.75 | 2.28 | |
| No 11q22-q23 deletion | 67 | 288 | NR | 57% | |||||||||||||
| 11q22-q23 deletion | 11 | 18 | 3.1 | 0.8 | 5.4 | 4.08 | 2.14 | 7.77 | < .001 | 2.18 | 0.85 | 5.62 | .105 | 2.51 | 0.85 | 5.64 | |
| TP53 WT | 61 | 275 | NR | 99% | |||||||||||||
| TP53 disruption | 17 | 31 | 2.9 | 0.6 | 5.3 | 3.85 | 2.23 | 6.65 | < .001 | 4.97 | 2.75 | 8.97 | < .001 | 5.30 | 2.84 | 9.92 | |
| NOTCH1 WT | 63 | 273 | NR | 74% | |||||||||||||
| NOTCH1 mutated | 15 | 33 | 3.3 | 1.2 | 14.3 | 2.15 | 1.22 | 3.79 | .007 | 2.08 | 1.04 | 4.16 | .038 | 2.31 | 1.13 | 4.76 | |
| SF3B1 WT | 71 | 288 | NR | 71% | |||||||||||||
| SF3B1 mutated | 7 | 18 | 2.5 | 1.7 | 3.3 | 3.29 | 1.50 | 7.21 | .003 | 2.49 | 1.08 | 5.72 | .032 | 2.94 | 1.20 | 7.35 | |
WT indicates wild-type; HR, hazard ratio; LCI, 95% lower confidence interval; UCI, 95% upper confidence interval; and NR, not reached.
Shrinkage coefficient, 0.91.
Discrimination: c-index of the original model, 0.788; bias-corrected c-index, 0.776; optimism, 0.012.
Calibration: calibration slope of the original model, 1.000; bias-corrected calibration slope, 0.894; optimism, 0.106.
As shown by multivariate analysis, the increased risk of death predicted by BIRC3 disruption (hazard ratio = 3.04; 95% confidence interval, 1.21-7.61; P = .017) was independent of confounding clinical (ie, age and Rai stage) and genetic (ie, IGHV mutation status, 11q22-q23 deletion, TP53 abnormalities, NOTCH1 mutations, and SF3B1 mutations) variables at diagnosis (Table 4).
Analogous to CLL analyzed at the time of chemorefractoriness, BIRC3 disruption and TP53 abnormalities were also distributed in a mutually exclusive fashion at CLL presentation (mutual information = 0.004; Figure 1D). Because TP53 abnormalities identify patients with the shortest survival in CLL, the outcome of BIRC3-disrupted cases was compared with that of patients with TP53 abnormalities. As shown by survival analysis, CLL patients harboring BIRC3 disruption displayed an OS (median, 3.1 year) similar to that of CLL patients harboring TP53 abnormalities (median, 2.9 years; P = .543; Figure 3B).
BIRC3 is the sole noncanonical NF-κB pathway gene mutated in fludarabine-refractory CLL
To determine the occurrence of genetic lesions of other members of the BIRC3 protein complex,33 we performed an extensive mutation and FISH analysis of the TRAF2, TRAF3, and MAP3K14 genes in fludarabine-refractory CLL patients (n = 49). This analysis did not reveal alterations of TRAF2, TRAF3, or MAP3K14, documenting that BIRC3 is the sole gene targeted by molecular lesions across all members of the BIRC3 complex.
Discussion
The results of the present study document that BIRC3 genetic lesions: (1) recurrently and selectively associate with fludarabine-refractory but TP53 wild-type CLL; (2) at diagnosis, identify patients with a poor outcome similar to that associated with TP53 abnormalities; (3) exert a prognostic role independent of widely accepted clinical and genetic risk factors; and (4) activate NF-κB signaling.
Fludarabine refractoriness in CLL may be explained by TP53 disruption in approximately 40% of patients, whereas approximately 60% of high-risk CLL patients are devoid of TP53 abnormalities.8,17 This observation prompted the search for other markers of fludarabine refractoriness. Although next-generation sequencing studies have allowed the identification of several previously unrecognized mutated genes in chemorefractory CLL, including NOTCH1 and SF3B1,20-22 at present, these novel mutations are not numerically sufficient to fully recapitulate the genetics of fludarabine-refractory CLL patients who are wild-type on the TP53 gene.20,22
The candidate gene approach used in this study revealed that genetic lesions of BIRC3 contribute to clinical aggressiveness and chemorefractoriness in TP53 wild-type CLL. BIRC3 disruption selectively occurs in approximately 40% of fludarabine-refractory CLL patients harboring a wild-type TP53, whereas it is consistently absent in progressive CLL patients who require treatment but prove to be sensitive to fludarabine-based regimens. At diagnosis, BIRC3 disruption is rare, but identifies a subgroup of high-risk patients displaying poor survival similar to that associated with TP53 abnormalities. Confirmation within the frame of prospective clinical trials will be helpful to fully assess the generalization of BIRC3 disruption as a CLL prognostic marker and as a tool for the early identification of chemorefractory cases.
BIRC3 genetic lesions were absent among clinical MBL cases with a CLL-like phenotype. This observation is consistent with the low frequency in clinical MBL of genetic lesions that are otherwise associated with high-risk CLL, namely NOTCH1 mutations and TP53 or ATM disruption, and corroborates the notion that clinical MBL is characterized by an indolent biologic phenotype.45
BIRC3, along with TRAF2 and TRAF3, cooperates in the same protein complex that negatively regulates MAP3K14, the central activator of noncanonical NF-κB signaling.31-34 All inactivating mutations of BIRC3 detected in CLL are predicted to cause the elimination or truncation of the C-terminal RING domain, the E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of which is essential for MAP3K14 proteasomal degradation by BIRC3.31-34 Consistently, fludarabine-refractory CLL patients harboring BIRC3 disruption by either mutation and/or deletion display constitutive NF-κB activation.
NF-κB activation is known to provide prosurvival signals to leukemic cells through the up-regulation of several antiapoptotic genes, including members of the BCL-2 family, and to be correlated with both survival and enhanced fludarabine resistance of CLL cells.24-28 In CLL, NF-κB activation is generally viewed as a consequence of specific interactions between leukemic cells and the microenvironment.24-28 The present study expands the mechanisms that may sustain NF-κB activation in CLL. In fact, our data suggest that, at least in a fraction of high-risk CLL patients, leukemic cells might become independent from microenvironmental interactions and may gain active NF-κB signaling through the acquisition of functionally active mutations targeting BIRC3. Genome-wide studies have pointed to the potential role of other NF-κB gene alterations, namely mutations of MYD88, in CLL development.20,21 On these bases, the poor prognosis and refractory phenotype associated with BIRC3 abnormalities might be a consequence of the constitutive NF-κB activation specifically observed among fludarabine-refractory CLL patients harboring BIRC3 disruption. NF-κB inhibitors are under development in CLL, and preclinical findings suggest that these compounds might be active against chemoresistant CLL clones.46-49 On these bases, our data might provide a molecular rationale for targeting NF-κB in poor-risk refractory CLL patients.
Identification of BIRC3 involvement in CLL may be important for elucidating the molecular genetics of 11q22-q23 deletion. In fact, although ATM has been regarded as the relevant gene of this chromosomal abnormality,9,12 biallelic inactivation of ATM does not exceed 30% in patients with 11q22-q23 deletion.13-16 On these bases, a second tumor suppressor in the 11q22-q23 region has been postulated along with ATM.50 BIRC3, which maps on 11q22.2 approximately 6 Mb centromeric to the ATM gene, might represent an attractive candidate, because: (1) the BIRC3 locus is included in focal deletions that affect the 11q22.2 band but spare ATM; (2) a fraction of 11q22-q23 deletions truncate BIRC3 and, similarly to BIRC3-disrupting mutations, remove its terminal exons encoding the RING domain; (3) analogous to BIRC3 mutations, BIRC3 deletions also activate NF-κB signaling; and (4) the poor prognosis marked by BIRC3 disruption is independent of ATM deletion in multivariate analysis.
The identification of BIRC3 disruption elucidates the molecular basis of a fraction of high-risk CLL cases and expands knowledge of the molecular mechanisms activating NF-κB in this leukemia. In addition to its pathogenetic relevance, BIRC3 disruption might represent a molecular marker for the early identification of chemorefractoriness among CLL patients who are wild-type on TP53, and may provide the rationale for targeted anti–NF-κB therapeutic approaches in this unfavorable clinical setting.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Italian Association for Cancer Research Special Program in Molecular Clinical Oncology (5 × 1000, no. 10007, Milan, Italy, to G.G. and R.F.); Futuro in Ricerca 2008 (to D.R. and S.D.); Programma di ricerca di Rilevante Interesse Nazionale (PRIN) 2008 (to G.G. and R.M.) and PRIN 2009 (to D.R.); Ministero dell'Istruzione, dell'Universitáe della Ricerca, Rome, Italy; Progetto Giovani Ricercatori 2008 (to D.R. and S.D.); Ricerca Sanitaria Finalizzata 2008 (to G.G.); Ministero della Salute, Rome, Italy; Novara–Associazione Italiana contro le Leucemie, linfomi e i mieloma (AIL) Onlus, Novara, Italy (to G.G. and D.R.); Compagnia di San Paolo, Turin, Italy (to R.F.); and the Helmut Horten Foundation and the San Salvatore Foundation (to F.B.). S.M. and S.C. are supported by fellowships from Novara-AIL Onlus, Novara. L.P. is on leave from the University of Perugia Medical School, Perugia, Italy.
Authorship
Contribution: D.R., R. Foà, and G.G. designed the study, interpreted the data, and wrote the manuscript; D.R. and M.F. performed the statistical analysis; M.F., S.R., S. Cresta, A.B., V.S., R. Famà, and M.G. performed the molecular analysis; S.M., C.D., and G.D. performed the FISH analysis; T.V. and S.D. performed and interpreted the biochemical assays; F.B. provided the SNP array data; S. Chiaretti, I.D.G., M.M., and F.F. provided well-characterized biological samples and clinical data; and G.F., V.G., L.P., A.G., and R.D.-F. contributed to data interpretation.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Davide Rossi, MD, PhD, Division of Hematology, Department of Translational Medicine, Amedeo Avogadro University of Eastern Piedmont, Via Solaroli 17, 28100 Novara, Italy; e-mail: rossidav@med.unipmn.it.
References
Author notes
D.R., M.F., and S.R. contributed equally to this study.
R.F. and G.G. contributed equally to this study.