Abstract
Abstract 623
The IgVH/IgVL repertoire of the leukemic clones in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) patients is biased as compared to the repertoire of various B-cell subsets in healthy donors. Approximately, 30% of B-CLL patients can be classified in homology subsets based on the B-cell receptor (BCR) heavy chain complementary determining region 3 (CDR3) amino acid sequence of their leukemic clone. Interestingly, within these homology subsets, recurrent somatic hypermutations have been identified and heavy chains are paired to characteristic light chains. The occurrence of B-CLL groups expressing highly similar BCRs strongly suggests a shared specificity and involvement of recurrent antigens in the development of B-CLL.
We have identified a novel B-CLL homology subset of four patients with a leukemic clone expressing highly similar mutated IgVH coupled to nearly identical IgVL rearrangements. Interestingly, all four patients had subset-biased somatic replacement mutations at two positions in IgVH. We produced the BCR of three patients belonging to this homology subset as recombinant soluble IgM (Subset-IgM) as well as BCRs of twenty-six cases expressing other rearrangements (Control-IgM).
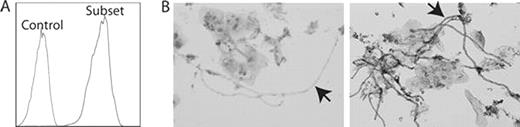
The Subset-IgM did not show any signs of autoreactivity in tissue arrays and were not found polyreactive by ELISAs for various well-known autoantigens. Therefore, we tested for reactivity with common pathogens by flow cytometry. The Subset IgM did not stain any of 20 bacterial strains. Interestingly, the yeast Candida Albicans stained brightly with Subset-IgM, as well as two other Candida strains and zymosan (cell wall of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae) (Figure 1A). None of the twenty-six Control-IgM showed this specificity. The Subset-IgM also stained yeast-infected hair-follicles and cervical smears by immunohistochemistry (Figure 1B). By ELISA, the antigen was found to be mannan, a main constituent of the yeast cell wall. Preincubation of Subset-IgM with mannan abolished the reactivity to Zymosan. Furthermore, B-CLL cells of subset patients bound zymosan ex-vivo. Of note, when the subset characteristic light chain was replaced by light chains of control B-CLL, reactivity to mannan was abrogated. In addition, when cultured in vitro, mannan induced proliferation of B-CLL cells of this homology subset, whereas proliferation of control B-CLL cells was not induced.
In conclusion, we identified a novel B-CLL homology subset, expressing highly similar BCRs with specificity for yeast mannan. This study shows for the first time that a hypermutated B-CLL homology subset expresses functional BCRs with high-affinity towards a pathogen, which are able to transduce signals that support tumour cell growth.
Recombinant IgM of a novel B-CLL subset stain yeast
(A) Subset-IgM stain Zymosan by flow cytometry. (B) Staining of yeast in infected cervical smears. Left: Control-IgM. Right: Subset-IgM. Arrows indicate yeast (in hyphal form).
Recombinant IgM of a novel B-CLL subset stain yeast
(A) Subset-IgM stain Zymosan by flow cytometry. (B) Staining of yeast in infected cervical smears. Left: Control-IgM. Right: Subset-IgM. Arrows indicate yeast (in hyphal form).
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal