Abstract
Abstract 544
In patients with unprovoked venous thromboembolism (VTE) occurring in the absence of major provoking factors, the optimal duration of anticoagulation is anchored on estimating the risk for disease recurrence in the individual patient. Evidence from several studies suggests that, at least in selected patient subgroups, the risk for recurrence may approximates the annual risk for anticoagulant-related major hemorrhage, which is estimated at 1–3%, and a recent ISTH consensus considers an annual risk of recurrence below 5% as acceptable to justify stopping anticoagulant therapy.
To develop a clinical prediction guide that stratifies patients according to recurrence risk and, thereby, facilitate decisions about whether to continue or stop anticoagulation.
Individual patient data meta-analysis of 7 prospective studies enrolling patients with a first episode of objectively diagnosed VTE. Eligible VTE cases were those which occurred in the absence of surgery, trauma, active cancer, immobility, or pregnancy and the puerperium. Follow-up started when anticoagulant therapy was stopped and ended when one of the following occurred: symptomatic, objectively documented, recurrent VTE; death from another cause; resumption of anticoagulant therapy for another reason; or the study ended. Predictors were identified using stratified Cox regression, and the weight of predictors was obtained after model shrinkage to correct for over-optimism. The discriminative ability of the prediction rule was estimated using time-dependent c-statistics, and was internally validated by bootstrap analysis.
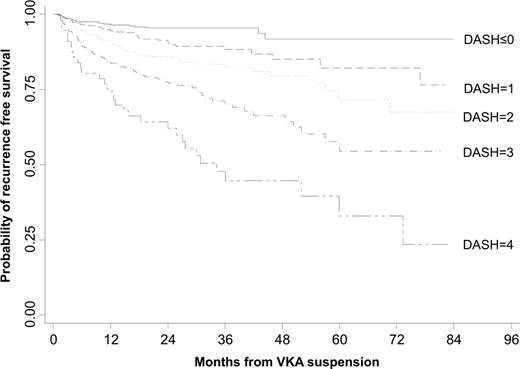
1818 consecutively referred cases with unprovoked VTE treated for at least three months with a vitamin K antagonist were eligible for analysis. Abnormal D-dimer after stopping anticoagulation, age < 50 years, male sex and VTE not associated with hormonal therapy (in women) were the main predictors of recurrence. Optimism-corrected regression coefficients were used to derive a prognostic recurrence score (DASH, D-dimer, Age, Sex, Hormonal therapy), that showed a good predicting capability (ROC area=0.71). The DASH score attributes the following points: +2 for positive (abnormal) post-anticoagulation D-dimer, +1 for age ≤ 50 years, +1 for male sex, −2 for hormone use at time of initial VTE (in women only). The annualized recurrence risk was 3.1% (95% confidence interval [CI] 2.3 – 3.9) in patients with a DASH score ≤ 1, 6.4% (95% CI 4.8–7.9) in patients with a DASH score 2, and 12.3% (95% CI, 9.9–14.7) in patients with a DASH score ≥ 3, as reported by the Kaplan-Meier recurrence-free survival plot. By considering at low recurrence risk those patients with a DASH score ≤ 1, life-long anticoagulation might be avoided in 51.6% of patients with unprovoked VTE.
The DASH score appears to reliably predict recurrence risk in patients with a first unprovoked VTE and may be used to decide whether anticoagulant therapy should be continued indefinitely or stopped after an initial treatment period of at last three months. Patients with a DASH score ≤ 1 appear to have an annual risk for recurrence (3.1%) that may be sufficiently low to justify stopping anticoagulation in an average patient after 3–6 months of anticoagulation, whereas a DASH score ≥ 2 appears to confer a risk of recurrent VTE that may warrant indefinite anticoagulation.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal