Abstract
Abstract 5108
Co-stimulatory signal is antigen non-specific and is provided by the interaction of costimulatory molecules expressed on the membranes of antigen presenting cells (APC) and T/NK cells. It plays as a complementary second signal to interaction of MHC molecules on APC and T cell receptors on T cells (first signal). Costimulatory molecules can be either inhibitory or stimulatory and may play a role in MM cell growth. Blockade of these pathways may provide a new therapeutic avenue.
Prior studies have shown up-regulation of inhibitory pathways such as CTLA-4 and down regulation of activating CD28 in MM patients, compared to healthy controls but there was no comprehensive characterization of costimulatory functions in MM patients. This is a pilot study assessing NK cell reconstitution and expression of inhibitory molecules (PD-1 and CTLA-4) and stimulatory molecules (ICOS, 4-1BB, CD28 and OX40) before and after autologous transplantation in MM patients.
Twelve adult patients with MM undergoing auto-transplant who are able to provide written informed consent are included in the study. Median age is 56.5 years (range 36 – 67). Peripheral blood samples were taken on 3–21 days prior to autologous HCT, 14, 30, 60, 90, 180 and 360 days after HCT. At the time of the current analysis, all patients were followed up to 90 days after autotransplant conditioned with high dose melphalan. Median length of follow up is 90 days post autologous HCT.
A Flowcytometry method was developed in 2 six color panels to identify NK & T cells (using antibodies to CD3, CD56 & CD16) and subsets of NK cells expressing different costimulatory molecules using specific antibodies to CD28, CD152(CTLA-4), CD278(ICOS), CD134 (OX-40), CD137 (4-1BB) and CD279 (PD-1). Each panel contained 200 ul of whole blood treated with RBC lysing buffer before staining with antibodies. Clinical data were collected for disease status before and after HCT as well as the presence of documented infections. One way ANOVA test and Kruskal-Wallis test (non-parametric) were used to analyze the data. Disease status for MM was defined as per International myeloma working group guidelines.
Very Good Partial Response or better (≥ VGPR) was seen in 5 patients before HCT and 8 patients after HCT (best response was taken if there are different disease status in a given patient after HCT). Partial Response or worse (≤ PR) was seen in 7 patients before HCT and 4 patients after HCT. One patient had a progressive disease.
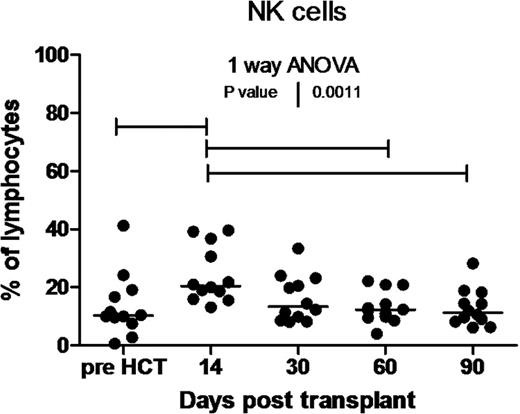
NK cell number was highest (20% of total lymphocytes) at d14 (p =0.011) compared to pre HCT, d60 and d90 levels and back to pre HCT level at d90 (Figure 1). No statistically significant difference in individual costimulatory molecule expression was noted between pre-HCT vs. post-HCT periods.
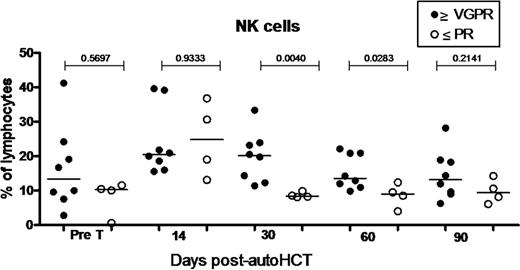
NK cell numbers were higher in patients with ≥VGPR compared to patients with ≤PR at d30 (p =0.004) and d60 (p =0.028) (Figure. 2). There was no significant difference in individual costimulatory molecule expression between ≥ VGPR vs. ≤ PR groups.
Higher number of NK cells were noted in patients with infections up to d90 (p=0.0081). In contrast, no significant difference in individual costimulatory molecule expression was seen between patients with infections vs. no infections.
At present analysis, we can determine that NK cell recovery is shorter (60–90 days) as opposed to CD 4 + T cells which have been shown to take about 12 months to recover after autologous HCT. Higher NK cell number were seen in patients with better disease response. There were no differences in costimulatory molecule profiles pre and post HCT based on early disease response. However, we plan long term follow up to see if this is a predictor of relapse.
Off Label Use: in administration of plerixafor. Krishnan:Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Millenium: Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal