Abstract
Abstract 4505
Patients with AML in 1st CR are frequently consolidated with an auto SCT but the role of this modality in the management of AML is still not fully defined.
Retrospective analysis was performed on all patients who underwent an auto SCT for AML in 1st CR at UMass Memorial Medical Center from January 2000 to December 2010. Data was analyzed as of August 2011. The study was approved by UMass Memorial Medical Center IRB.
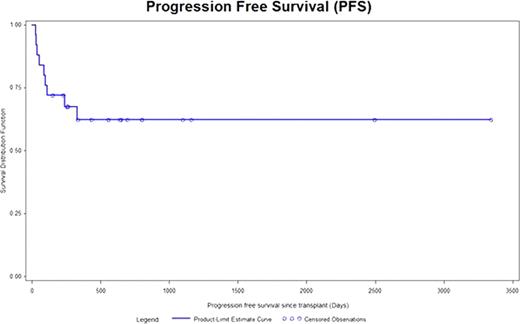
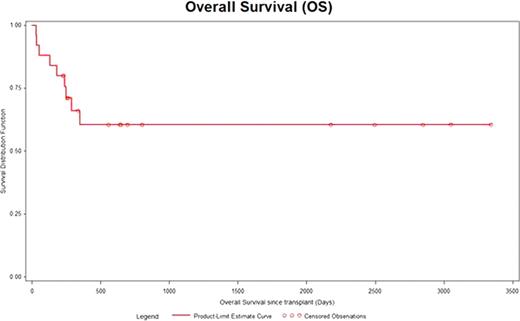
25 Patients were identified from the database. There were 13 males and 12 females. The median age was 46 years range (19–72). Cytogenetics was good risk in 6 patients, intermediate risk in 14, poor risk in 3 and unknown in 2 patients. Induction chemotherapy was standard dose Ara-C based in 13 patients and high dose Ara-C based regimen in 12 patients. Median time from diagnosis to transplant was 133 days range (107–362). Stem cell mobilization regimen consisted of Ara-C/Etoposide (E) in 21 (80%), Cyclophosphamide (Cy) in 3 (12%) and Mitoxantrone/Ara-C/E in 1 (4%). Preparative regimen included Busulfan (Bu) 4/ E in 17 (68%), Bu4/Cy in 5 (20%) and high dose Melphalan in 3 (12%). A median of 4.56 ×106 range (1.05 × 106 – 9.67 × 106 ) CD34 cells/kg were infused. 3 patients failed to engraft. Median time to neutrophil recovery was 11 days range (9 to 16) and platelet recovery was 20 days range (9 to 116). 100 day mortality was 12% (3/25). Median follow of the entire cohort is 6.5 years range (0.6 – 10.7). Total of 9 patients died. The cause of death included disease in 7, sepsis in 1 and unknown in 1 patient. Kaplan Meier estimate for progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) was 72% and 80% at 6 months and 62% and 61% at 3 years.
ASCT is an effective and safe intensive consolidation therapy for patients with AML in 1st CR.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal