Abstract
Abstract 4218
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) remains the most common cause of preventable death in hospitalized patients despite more than 25 guidelines and over 5 decades of data on VTE prevention. American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) and International Union of Angiology (IUA) guideline recommendations are primarily based off of risk factors utilized for entry into randomized controlled trials (RCT) or post-hoc analysis of these RCTs. These guidelines recommend a group-based, as opposed to an individualized risk assessment, approach. It is currently unknown how these risk factors interact in a quantitative manner.
There are currently no weighted, validated, VTE risk assessment models (RAM) that are data-derived in medical patients. A retrospective VTE RAM (IMPACT ILL) was recently derived from the multinational IMPROVE registry in hospitalized medical patients. (Table 1) The “VTE-VALOURR ” is a retrospective, multi-center, case control, validation study of this RAM. The VTE-VALOURR is also assessing other VTE and bleeding risk factors.
IMPROVE Risk Assessment Model
| VTE Risk Factor . | Points . |
|---|---|
| Previous VTE | 3 |
| Thrombophilia | 2 |
| Lower Limb Paralysis | 2 |
| Current Cancer | 2 |
| Immobilization ≥7 Days | 1 |
| ICU/CCU Stay | 1 |
| Age > 60 Years | 1 |
| VTE Risk Factor . | Points . |
|---|---|
| Previous VTE | 3 |
| Thrombophilia | 2 |
| Lower Limb Paralysis | 2 |
| Current Cancer | 2 |
| Immobilization ≥7 Days | 1 |
| ICU/CCU Stay | 1 |
| Age > 60 Years | 1 |
0–1 Points = Low Risk, 2–3 Points = Moderate Risk, ≥ 4 points = High Risk
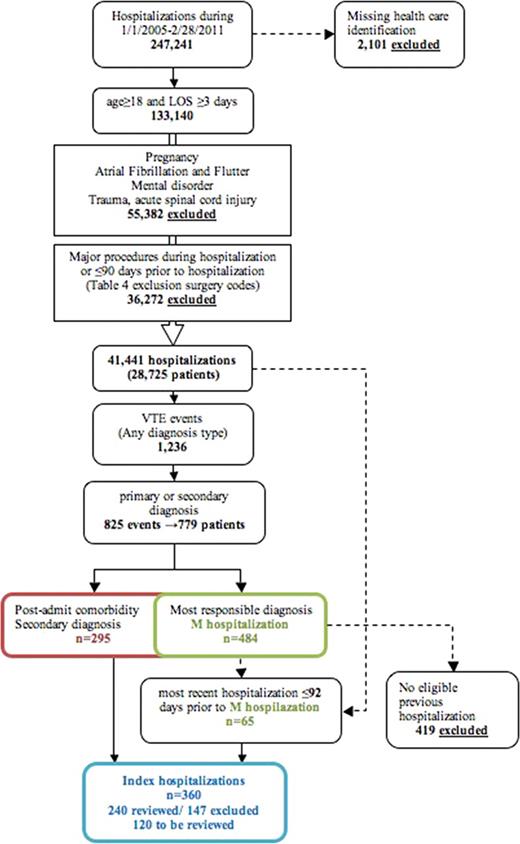
ICD-10 reports and the McMaster Transfusion Registry for Utilization Surveillance and Tracking (TRUST) database, which contains demographics, transfusion data, and approximately 50 clinical variables including thrombotic outcomes of inpatients, were used as the data source at 3 hospitals. Inclusion criteria were hospitalized medical patients ≥ 18 years with ≥ 3 days length of stay (LOS). Exclusion criteria were patients with pregnancy, mental health disorders, atrial fibrillation/ flutter, trauma, spinal cord injury, surgery within 90 days, VTE within 24 hours of admission, treatment dose anticoagulants (including warfarin) within 48 hours of admission, or transferred from a non-McMaster acute care facility. Lower extremity deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism out to 90 days post admission were the thrombotic outcomes of interest and verified by chart review. Upper extremity DVT was excluded. Descriptive statistics (proportions and frequencies) were used to summarize binary variables.
From January 1st, 2005 to February 28th, 2011, 247,241 hospitalizations occurred at 3 McMaster hospitals. After exclusionary criteria were applied, 779 VTE events were identified. (Figure 1) Of these, 419 were excluded because they were VTE events not related to a previous hospitalization (i.e. community-acquired). Of the remaining 360 patients, 240 have been reviewed with 93 confirmed, included, VTE events having occurred, 147 events being further excluded, and another 120 patients still requiring review.
We present an interim analysis of the 93 currently included patients. Of the included patients, 68 (73%) received some form of prophylaxis during their hospital stay while 35 (38%) received appropriate type, dose and duration of prophylaxis. Fifty-eight (62%) of VTE events were therefore “preventable.” Number of risk factors per patient and risk scores for the 93 patients are listed in tables 2 and 3.
Distribution of Risk Factors (N=93)
| VTE Risk Factor . | Points . | # of patients . | % . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Previous VTE | 3 | 15 | 16.1 |
| Thrombophilia | 2 | 2 | 2.2 |
| Lower Limb Paralysis | 2 | 8 | 8.6 |
| Current Cancer | 2 | 46 | 49.5 |
| Immobilization ≥7 Days | 1 | 40 | 43.0 |
| ICU/CCU Stay | 1 | 12 | 12.9 |
| Age > 60 Years | 1 | 71 | 76.3 |
| VTE Risk Factor . | Points . | # of patients . | % . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Previous VTE | 3 | 15 | 16.1 |
| Thrombophilia | 2 | 2 | 2.2 |
| Lower Limb Paralysis | 2 | 8 | 8.6 |
| Current Cancer | 2 | 46 | 49.5 |
| Immobilization ≥7 Days | 1 | 40 | 43.0 |
| ICU/CCU Stay | 1 | 12 | 12.9 |
| Age > 60 Years | 1 | 71 | 76.3 |
Risk Scores of the 93 Patients
| Score . | Frequency . | Percent Cum. . | Frequency . | Cum. Percent . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 5.38 | 5 | 5.38 |
| 1 | 14 | 15.06 | 19 | 20.43 |
| 2 | 15 | 16.13 | 34 | 36.56 |
| 3 | 27 | 29.03 | 61 | 65.59 |
| 4 | 17 | 18.28 | 78 | 83.87 |
| 5 | 7 | 7.53 | 85 | 91.40 |
| 6 | 4 | 4.30 | 89 | 95.70 |
| 7 | 4 | 4.30 | 93 | 100.00 |
| Score . | Frequency . | Percent Cum. . | Frequency . | Cum. Percent . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 5.38 | 5 | 5.38 |
| 1 | 14 | 15.06 | 19 | 20.43 |
| 2 | 15 | 16.13 | 34 | 36.56 |
| 3 | 27 | 29.03 | 61 | 65.59 |
| 4 | 17 | 18.28 | 78 | 83.87 |
| 5 | 7 | 7.53 | 85 | 91.40 |
| 6 | 4 | 4.30 | 89 | 95.70 |
| 7 | 4 | 4.30 | 93 | 100.00 |
Validation of this VTE RAM will identify medical patients at risk of VTE that do not readily fit into group-specific VTE risk categories. Additionally, validation will identify subsets of patients at especially high risk of VTE and focus future randomized controlled trials. Other VTE risk factors may be identified with the study. Review of the 120 VTE cohort patients needs to be completed as well as review of a comparator control cohort. Approximately 80% of the current VTE cohort appears to have a score of 2 or above and be at moderate to high risk of VTE. Final results of approximately 150 VTE patients will be presented along with the control cohort as well as if the model is valid.
Turpie:Astellas Pharma Europe: Consultancy; Bayer HealthCare AG: Consultancy; Portola Pharma: Consultancy; sanofi-aventis: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal