Abstract
Abstract 3914
Bendamustine is a unique, well-established alkylating agent with multifaceted actions leading to cancer cell death in several hematologic malignancies. In a phase 3 trial in treatment-naïve patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), rates of response and progression-free survival (PFS) were significantly superior to those for chlorambucil [Knauf WU et al. J Clin Oncol 2009;27:4378–84]. In vitro studies have found that the cytotoxic activity of bendamustine against CLL-derived cell lines is synergized by rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody [Demidem A et al. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 1997;12:177–86]. Older patients may demonstrate lower tolerance to chemoimmunotherapy [Foon KA & Hallek MJ. Leukemia 2010;24:500–11], and published clinical data on bendamustine-rituximab in CLL are scarce. Thus, this retrospective study sought to characterize a population of adults ≥70 years old with CLL receiving bendamustine with or without rituximab, describe patterns of care, assess data on real-world effectiveness outside of the controlled environment of clinical trials [Waldthaler C et al. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2011;123:269–275], and assess safety.
Records were extracted from US Oncology iKnowMed (iKM) record databases for all outpatients ≥70 years old with CLL (but no other tumor) and more than 1 visit recorded (but not enrolled in clinical trials) who received bendamustine between March 2008 and May 2010. Patients were classified as treatment-naïve or relapsed (including ≥ second-line therapy). To ascertain mortality, the iKM data were supplemented with vital-status data from the Social Security Administration Death Index. The overall response rate (ORR) included complete response (CR), nodal partial response (nPR), and partial response (PR). PFS was time from first bendamustine dose to progressive disease (change in line of therapy), relapse, or death from any cause. Data from patients who did not die, or had no progression and were lost to follow-up were censored.
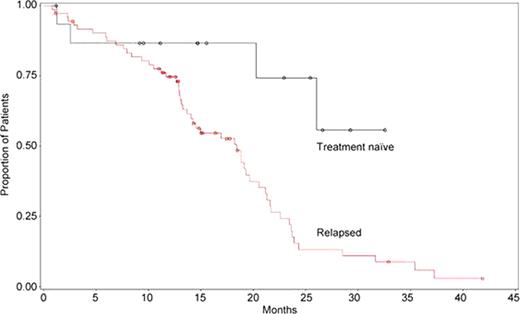
Among 91 patients, the mean (SD) initial age at beginning of first therapy was 77.4 (5.6) years, age at diagnosis was 70.3 (6.5) years, and 63.7% were male. Of the 16 (17.6%) treatment-naïve patients, 10 had received bendamustine monotherapy and 6 received bendamustine-rituximab. Of the 75 (82.4%) relapsed patients, 20 had received bendamustine monotherapy and 55 received bendamustine-rituximab. The observed ORR for treatment-naïve patients was 56.3% (n=9; 18.8% CR, 37.5% PR, and 0 nPR); 6.3% had progressive disease. For relapsed patients, the ORR was 58.7% (n=44; 13.3% CR, 44.0% PR, and 1.3% nPR); 24.0% had progressive disease. Among patients with data, median PFS for 16 treatment-naïve patients has not been reached (median follow-up 15.1 months); for 73 relapsed patients, PFS was 18.4 months. Kaplan-Meier estimates for PFS over time for each group are shown in the Figure. No unexpected toxicities were seen. The overall rate of blood/bone marrow toxicities (all grades) was 40.7%; grade 3/4 rates were 18.8% for treatment-naïve patients and 25.3% for relapsed patients. Other grade 3/4 adverse events (AEs) included upper respiratory infection and abdominal pain in the relapsed group as well as rash and sepsis in both groups (n=1 each). The most frequent nonhematologic AEs (≥5%, any grade) were fatigue (33.0%), weight loss (11.0%), infection (9.9%; herpes zoster [n=2]; cryptococcal sepsis, Klebsiella sepsis, and pneumonia [n=1 each]), gastrointestinal (8.8%), fever (8.8%), pulmonary (6.6%), and rash (5.5%).
o = data censored.
In this retrospective chart review of patients ≥70 years old with CLL, bendamustine, either alone or with rituximab, provided meaningful response rates and was generally well tolerated. The length of PFS of both treatment-naïve and relapsed patients was clinically meaningful.
This research was sponsored by and conducted in collaboration with Cephalon, Inc., Frazer, PA.
Sterchele:Cephalon, Inc.: Employment. Beygi:Cephalon, Inc.: Employment. Kennealey:Cephalon, Inc.: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal