Abstract
Abstract 2773
For patients with high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes an epigenetic therapy with hypomethylating agents is considered standard of care. Intensive chemotherapy can be offered to a subset of patients; however, data about the long-term outcome of MDS patients receiving intensive chemotherapy are scarce.
For this evaluation, 104 adult patients with IPSS intermediate-2 or high-risk MDS with at least 10% bone marrow blasts of all age groups treated within the AMLCG1999 trial were included. Patients were randomized upfront to receive 1. double induction therapy with either standard-dose containing TAD - versus high-dose containing HAM–HAM, 2. TAD consolidation therapy followed by either a monthly maintenance therapy for 3 years after achievement of CR or an autologous stem cell transplantation (patients aged ≥ 60 years were all assigned to maintenance therapy), and 3. blast priming with filgastrim starting on day -1 of chemotherapy in selected centers.
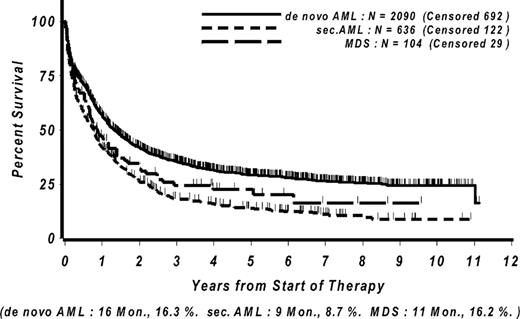
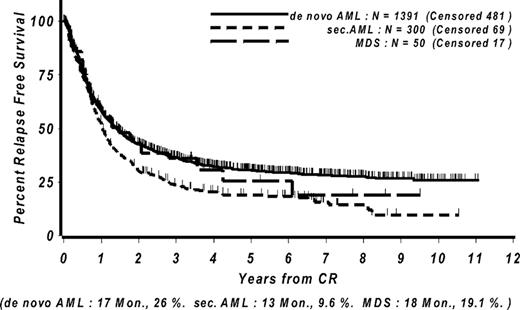
Fifty-four patients had IPSS Score intermediate-2 and 50 patients were IPSS high risk. Median bone marrow blast count at diagnosis was 15%. The median age was 63.5 years (range: 27–76 years), 39 patients (37.5 %) were female. Median lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) serum level was 296 U/l, median leukocyte count at diagnosis was 5,950 per μl. The cytogenetic risk groups were as follows: favorable 3, intermediate 57, unfavourable 37, missing 7. Among 38 patients with normal karyotype, NPM1/FLT3 mutational status was available for 22 with 5 patients having the combination NPM1 mutated/FLT3 wildtype. Comparison with 2051 patients with de novo AML within the same trial revealed the following significant differences: patients with MDS were older, had a higher male to female ratio, a lower LDH serum level at diagnosis, a lower leukocyte count at diagnosis and were more likely to have adverse cytogenetic risk. Compared to 636 patients with secondary AML after MDS, cytotoxic therapy or irradiation, the cohort of patients with MDS did not display any significant differences except the sex distribution. Patients with MDS displayed a CR rate of 48% (50/104 patients), which was significantly lower than de novo AML patients (67%) and not different to secondary AML patients (47%). Median overall survival in MDS patients was 320 (95% CI: 236 to 505) days with a 2-year and 5-year survival of 33.4% (95% CI: 23.6% to 43.2%) and 22.7% (95% CI: 13.5% to 31.9%), respective, which was significantly (p=0.03) lower than in patients with de novo AML (median 484, 95% CI 435 to 541 days) and comparable to patients with secondary AML (median 282, 95% CI 224 to 311 days, p=0.13). Median relapse-free survival in responding MDS patients was 536 (95% CI: 264 to 1299) days with no significant differences of RFS compared to de novo or secondary AML patients. In multivariate analyses, the diagnosis of MDS remained an independent prognostic factor for CR probability but had no independent influence on survival compared with de novo AML patients. Nine patients proceeded to allogeneic stem cell transplantation in first complete remission of whom six remain in first complete remission between 1354 and 1911 days after achievement of CR. In addition, 16 patients remained in CR for more than one year without allogeneic transplantation.
Taken together, outcome of patients with intermediate-2 or high-risk MDS after intensive chemotherapy is comparable to the outcome of patients with secondary AML. Adjustment for known risk factors such as age, cytogenetic risk and LDH revealed that inferior outcome of MDS patients compared to patients with de novo AML is attributable to the higher incidence of adverse risk factors. CR-rates appear to be higher compared to hypomethylating therapy and a fraction of MDS patients experiences long-term survival by intensive chemotherapy. Allogeneic transplantation can improve long-term survival for patients achieving remission.
Krug:MedA Pharma: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Alexion: Honoraria; Boehringer Ingelheim: Research Funding; Sunesis: Honoraria. Haferlach:MLL Munich Leukemia Laboratory: Employment, Equity Ownership. Schnittger:MLL Munich Leukemia Laboratory: Employment, Equity Ownership. Haferlach:MLL Munich Leukemia Laboratory: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal