Abstract
Abstract 2710
Introduction Recent refinement in B-cell lymphoma classification by the WHO in 2008 has defined an entity that exists in the gray zone between diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and Burkitt lymphoma (BL). Varying in morphology, immunohistochemical, or genetic features, B-cell lymphoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between DLBCL and BL (Intermediate DLBCL/BL) has been reported to have a poor clinical outcome. We aim to describe the clinical factors affecting outcomes and compare therapy response in a representative population.
Methods A retrospective search of the Nebraska Lymphoma Study Group Registry from 1983–2009 meeting the diagnostic criteria for Intermediate DLBCL/BL yielded clinical data at presentation, follow-up, and treatment information. Treatments were grouped as CHOP-like +/− Rituximab (R) vs. intensive regimens (e.g. CODOX-M +/− R, R-EPOCH). Diagnostic slides were re-reviewed to verify the diagnosis. Probabilities of progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were approximated using Kaplan-Meier method. Cox proportional regression analysis was used to evaluate the clinical variables associated with risk of treatment-failure and death.
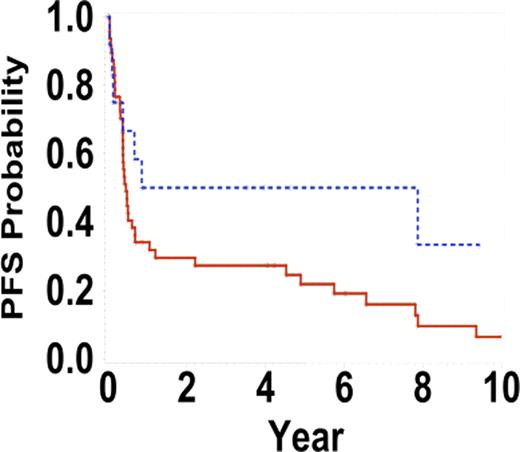
Progression free survival intensive versus CHOP/CHOP-like regimens +/− Rituximab, p=0.08
Progression free survival intensive versus CHOP/CHOP-like regimens +/− Rituximab, p=0.08
Summary Our analysis confirmed poor clinical outcome with stage IV disease, elevated serum LDH, at least 2 extra-nodal sites at presentation, or worse IPI score. There was a better outcome with intensive chemotherapy regimens. This study underscores the importance of early identification and proper treatment choice.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal