Abstract
Abstract 2685
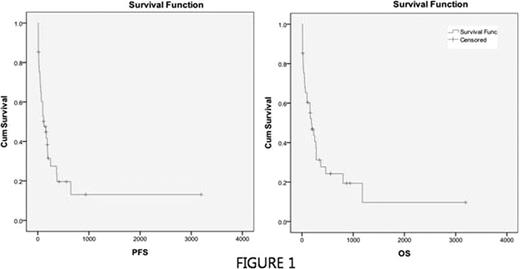
Although high dose chemotherapy with hematopoietic stem cell support is the current standard for patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL), all patients are not eligible for this strategy. A portion of this patients experiences refractory or relapsing disease after first salvage. However there are few data for treatment outcomes in this group of patients. In this retrospective analysis we evaluated the efficacy of ifosfamide, etoposide, cytarabine, methotrexate plus dexamethasone (IVAMdex) regimen in 2nd salvage (3rd line) setting and analyzed the pretreatment factors for patients who would be beneficial for this 2nd salvage regimen. A total of 41 patients with relapsed or refractory NHL after 1st salvage chemotherapy were analyzed. All patients were treated with IVAMdex regimen which consisted of ifosfamide (1500 mg/m2 daily from day 1 to day 5), mesna (1500 mg/m2 daily from day 1 to day 5), etoposide (150 mg/m2 daily from day 1 to day 3), cytarabine (100 mg/m2 daily from day 1 to day 3), methotrexate (3 g/m2 on day 5), leucovorin rescue (100 mg/m2 daily from day 5 to day 7), and dexamethasone (40mg on day 1 to day 3). The response rate was assessed after a minimum of two courses of chemotherapy. Toxicity and survival were analyzed in all patients. The median age was 51 years. Performance 0–1 and 2 was 56% and 44%, respectively. 28 evaluable patients completed more than 2 cycles. 13 patients were not evaluated due to early death (n=10), death without response evaluation (n=2), and follow-up loss (n=1), respectively. The overall response was as follows: 9 complete remission (32%), 4 partial remission (14%), 2 stable disease (8%), and 13 progressive disease (46%). The median overall and progression-free survival was 185 days (95% confidence interval, 84 days to 285 days) and 119 days (95% confidence interval, 30 days to 207 days), respectively (Figure 1). Univariate analysis of pretreatment factors for overall survival showed increased LDH (p=0.001), presence of B symptom (p=0.001), chemosensitive disease to prior regimen (p=0.044), performance status 0–1 (p=0.003), and low/low-intermediate IPI group (p=0.017) were significant. Multivariate analysis by Cox regression method showed that increased LDH (p=0.028, harad ratio 3.47, 95% confidence interval 1.147 to 10.526) and performance status 0–1 (p=0.041, hazard ratio 0.35, 95% confidence interval 0.13 to 0.96) were independently significant factor for overall survival. Treatment-related mortality (TRM) was reported in 16 patients (39%) and the cause of all TRMs was infection associated with febrile neutropenia. Of these, 10 deaths (63%) occurred within 30 days after initiation of chemotherapy (early death). Univariate analysis of pretreatment factors for early death showed increased LDH (p=0.011) and presence of B symptom (p=0.017) were significant. However multivariate analysis by log-rank test did not show any independently significant factors for early death. In this study salvage chemotherapy with IVAMdex regimen in 3rd line setting showed moderate response with high toxicities. However, we discovered that there might be subgroup of patients who can benefit from this regimen and serum LDH level and presence of B-symptoms may be useful indicators in differentiating these patients. However, considering high toxicities, the strategy to prevent early death associated with febrile neutropenia should be required. It might include prophylactic G-CSF and antimicrobial agent administration. To draw the conclusion, validation should be warranted in prospective trial with large scale.
Disclosures:
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
*
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
© 2011 by The American Society of Hematology
2011

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal