Abstract
Abstract 2127
Activation of the hemostatic cascade and platelet activation in particular, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of sickle cell disease (SCD). Prasugrel is a third generation thienopyridine antiplatelet agent, an oral P2Y12 ADP receptor antagonist that is FDA-approved for use in patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing percutaneous coronary revascularization. We evaluated serial biomarkers of hemostatic activation from a trial of prasugrel in adult patients with SCD.
This was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind phase 2 adaptive study design with a 2:1 prasugrel:placebo ratio. Study drug, prasugrel 5 mg or placebo, was given once daily for 30 days. The primary endpoint was safety as measured by hemorrhagic events requiring medical attention. Samples for biomarkers were collected prior to initiation of study drug, on day 10 ± 2, and on day 30 ± 3. Multi-color fluorescent activated cell sorting and monoclonal antibodies were used to determine platelet P-selectin expression, platelet-monocyte aggregates (PMA), and platelet-neutrophil aggregates (PNA) using previously published protocols. Soluble P-selectin (sP-selectin), soluble CD40 ligand (sCD40L), thromboxane B2 (serum TXB2), and prothrombin fragment F1.2 (F1.2) were determined using standard enzyme-linked immunoassays. Statistical comparison between prasugrel and placebo was performed using a mixed model with treatment, baseline measurement, genotype of SCD, visit and the interaction between visit and treatment as fixed effects and subjects as a random effect.
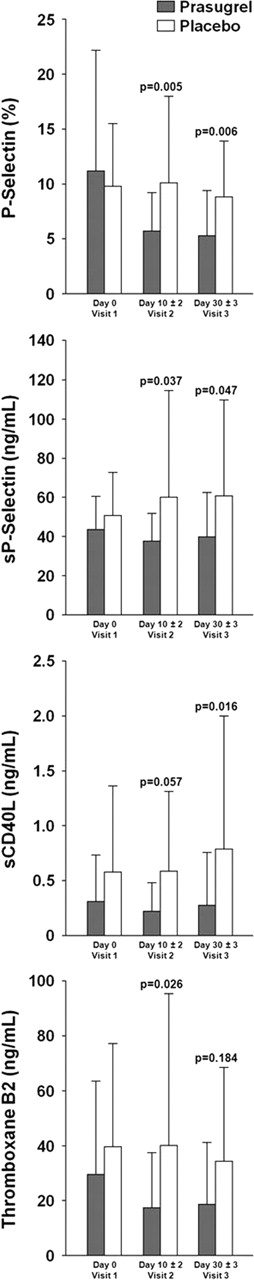
Forty-one patients were randomized to prasugrel 5 mg and 21 to placebo. Mean age was 32 years; 48% were female; 60% HbSS, 5% HbS/b0thalassemia, 10% HbS/b+thalassemia, and 24% HbSC (1 patient was found not to have SCD but to only have b-thalassemia trait). Eighteen patients in the prasugrel and 9 in the placebo arm were on hydroxyurea prior to study drug. Results are shown in the Figure. Compared to placebo, platelet P-selectin (unstimulated), sP-selectin, and sCD40L all achieved or approached significantly lower values in the prasugrel group on day 10 and 30, as did ADP-stimulated platelet P-selectin values (data not shown). TXB2 was significantly lower on day 10 but not on day 30 (Fig. 1), as were PMA/PNA unstimulated, and PMA/PNA in response to ADP ex vivo. F1.2 levels were not different between the groups at either day 10 or 30 (data not shown).
As would be predicted by the mechanism of action, prasugrel resulted in decreased cellular and soluble biomarkers of platelet activation. There was no effect on coagulation as assessed by F1.2, a marker of thrombin generation. Clinical results reported elsewhere suggest a decrease in pain rate. Prasugrel 5 mg po daily clearly decreases markers of platelet activation in adult SCD patients. These biomarkers can be incorporated in future studies of prasugrel in SCD to correlate with clinical outcomes.
Wun:Daiichi Sankyo Company, Ltd. and Eli Lilly and Company: Research Funding. Off Label Use: This abstract discusses prasugrel treatment in patients with sickle cell disease. Please see USPI for most up-to-date information. Knupp:Daiichi Sankyo Company, Ltd. and Eli Lilly and Company: Research Funding. McMahon:Daiichi Sankyo Company, Ltd. and Eli Lilly and Company: Research Funding. Strouse:Daiichi Sankyo Company, Ltd. and Eli Lilly and Company: Research Funding. Zhou:Eli Lilly and Company: Employment, Equity Ownership. Heath:Eli Lilly and Company: Employment, Equity Ownership. Nwachuku:Daiichi Sankyo, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Jakubowski:Eli Lilly and Company: Employment, Equity Ownership. Winters:Eli Lilly and Company: Employment, Equity Ownership. Riesmeyer:Eli Lilly and Company: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal