Abstract
Abstract 1618
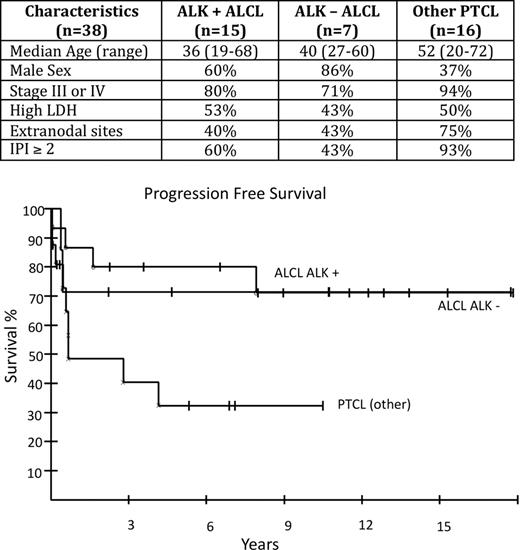
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) is a distinct type of peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) characterized histologically, by large anaplastic lymphoid cells that are CD30 positive. There is biologic heterogeneity within ALCL: ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) positive cases harbor a translocation usually involving chromosomes 2 and 5 resulting in over-expression of ALK (variant translocations also occur) whereas ALK negative cases do not. ALK positive ALCL is also clinically distinctive, with a younger age of onset and better treatment outcomes. In the recent International PTCL and Natural Killer (NK) T-Cell Lymphoma Study (Savage et al. Blood.2008: 111 (12)), the outcome for patients with ALK positive compared to ALK negative ALCL was significantly better (5-year failure-free survival (FFS) 60% versus 36%: p=0.15). Methods: We prospectively investigated the efficacy of 6 cycles of DA-EPOCH chemotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with both ALK positive and ALK negative ALCL and compared their outcome to other subtypes of PTCL. Results: Clinical characteristics of 38 enrolled patients are shown below. 22 patients had a diagnosis of ALCL and other diagnoses were PTCL-NOS (10), hepatosplenic gamma delta T-cell lymphoma (4), enteropathy associated T-cell lymphoma (1) and angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (1). Patients with ALK positive and ALK negative ALCL had similar characteristics. With a median potential follow-up time of 10.5 years, the 5 year progression-free survival (PFS) probability for ALK positive versus negative patients was 80% versus 71% (p=0.82); 5 year overall survival (OS) was 86% in both groups (p=0.95). For patients with other subtypes of PTCL, PFS and OS were 32% and 50% respectively, at 5-years. Conclusions: In contrast to other reports, patients with ALK negative ALCL had a very favorable outcome following DA-EPOCH chemotherapy that was no different from that of ALK positive cases. This regimen is highly effective in ALCL, independent of ALK expression. Accrual continues.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal