Abstract
Abstract 1526
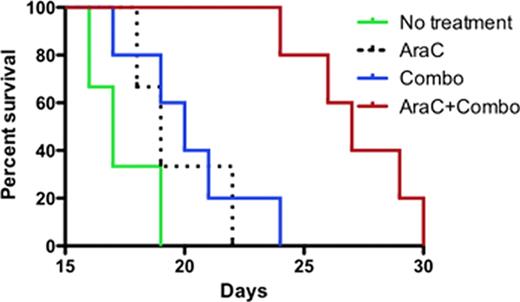
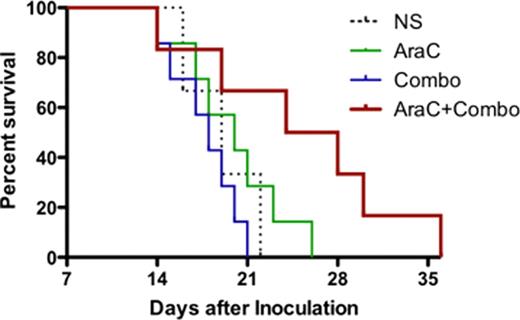
The immunotoxin combotox (1: 1 mixture of deglycosylated ricin-A chain (dgRTA)-containing anti-human CD19 and anti-CD22 monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) (Combotox) has demonstrated single agent activity in children (Herrera et al, 2009) and adults (Schindler et al, 2011) with relapsed/refractory B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Even though single agent Combotox is effective in reducing the number of blasts, relapses usually occur early on especially in advanced disease. We designed experiments to explore potential synergy of concurrent and sequential administration of Combotox and cytarabine (Ara-C) in a murine model of advanced human pre-B cell ALL. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A xenograft model of advanced ALL in NOD mice was established using the human pre-B lymphoblast cell line NAML/6 (Herrera et al 2009). 6–8 week old NOD mice (Cg-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ) were injected in the tail vein with 8–10×106 NALM/6 cells. The presence of leukemic blasts in the blood was confirmed microscopically 7, 14 and 18 days after inoculation. Drug administration was done after establishment of increased blast counts in order to mimic human advanced disease. In the first experiment (concurrent schedule) mice were treated daily on Days (d) 12–17 with either 1) Ara-C, 2) Combotox, 3) Ara-C concurrent with Combotox, or 4) normal saline (control), respectively. In a second experiment (sequential schedule), mice were treated with either 1) Ara-C on Days (d) 7–9 after inoculation, 2) Combotox on d14, d16 and d18, 3) Ara-C d7-9 followed by Combotox on d14, d16 and d18 or 4) normal saline (control) on d7-9, d14, d16 and d18. The doses were 200mg/kg daily x3 for Ara-C and 2.4mg/kg anti-CD19-dgRTA plus 1.5mg/kg anti-CD22-dgRTA per injection every other day x3 for Combotox The median survival time (MST) for each treatment group was calculated. Overall survival was plotted as Kaplan-Meier curve and a 2-sided log-rank test was performed. A p-value <0.05 indicated statistical significance. RESULTS: Both concurrent (Experiment #1) and sequential administration (Experiment #2) of Ara-C combined with Combotox resulted in statistically significantly improved overall survival (p-value <0.05 for both schedules). The median survival time (MST) was 27 and 28 days respectively for concurrent and sequential combined chemo-immunotherapy with Ara-C and Combotox as compared to control (MST 17 & 19 days) and/or each agent by itself (MST Ara-C 19 & 20 days; Combotox 20 and 18 days) as demonstrated in Figures 1 and 2. CONCLUSION: The combination of Ara-C and Combotox resulted in improved survival in mice xenografted with NALM/6 cells, which served as a model for advanced B-lineage ALL. Whether concurrent or sequential administration has superior efficacy is under current active investigation. These results influenced the design of a clinical trial that will explore the safety and efficacy of Ara-C combined with Combotox in adults with relapsed/refractory ALL (clinicaltrials.gov identifier NCT01408160).
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal