Abstract
Abstract 1087
No data are available in literature about possible different changes in cardiac and hepatic iron and in cardiac function in thalassemia major (TM) patients treated with sequential deferipron–desferrioxamine (DFP-DFO) versus deferasirox (DFX). Magnetic Resonance (MR) is the unique non invasive suitable technique to evaluated quantitatively this issue.Our aim was to prospectively assess the efficacy of the DFP-DFO vs DFX in a large cohort of TM patients by quantitative MR.
Among the first 1135 TM patients enrolled in the MIOT (Myocardial Iron Overload in Thalassemia) network, 392 patients performed a MR follow up study at 18 ± 3 months according to the protocol. We evaluated prospectively 35 patients treated with DFP-DFO versus 80 patients treated with DFX between the 2 MR scans. Cardiac iron was evaluated by T2* multiecho multislice technique. Biventricular function parameters were quantitatively evaluated by cine images. Liver iron was measured by T2* multiecho technique.
Excellent/good levels of compliance were similar in the two groups (DFP-DFO 97.1% vs DFX 98.8%; P=0.544).
Among the patients with no significant myocardial iron overload (MIO) at baseline (global heart T2*≥20 ms), there were no significant differences between groups to maintain the patients without myocardial iron overload (DFP-DFO 96% vs DFX 98%; P=0.536).
Among the patients with MIO at baseline, in both groups there was a significant improvement in the global heart T2* value (DFP-DFO: 4.8±3.9 ms P=0.004 and DFX: 3.5±4.7 P=0.001) and a significant reduction in the number of pathological segments (DFP-DFO: −3.2±3.8 P=0.026 and DFX: −2.4±3.8 P=0.003). Only in sequential group there was a significant increment in the left and right ventricular ejection fractions (4.3±5.1% P=0.035 and 6.7±6.6% P=0.017, respectively). The improvement in the global heart T2* was not significantly different between groups. The improvement in the left as well in the right ventricular ejection fractions was significantly different between groups (P=0.009 and P=0.015, respectively) (Figure 1).
Inter-treatment prospective comparisons in patients with basal global heart T2* <20 ms.
Inter-treatment prospective comparisons in patients with basal global heart T2* <20 ms.
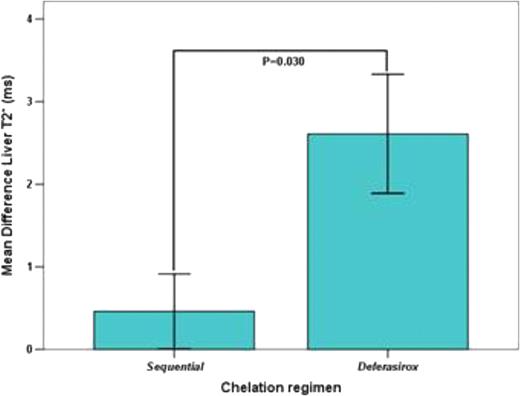
Among the patients with hepatic iron at baseline (T2*<9.2 ms), only in the DFX group there was a significant improvement in the liver T2* value (2.6±5.3 ms P=0.001). The changes in liver T2* were significantly higher in DFX group than in DFP-DFO (0.5±2.0 ms) group (P=0.030) (Figure 2).
Inter-treatment prospective comparisons in patients with basal liver T2* < 9.2 ms.
Inter-treatment prospective comparisons in patients with basal liver T2* < 9.2 ms.
In TM patients prospectively no significant differences on cardiac iron were found between sequential DFP–DFO treatment versus DFX in monoterapy, although the DFP-DFO treatment was significantly more effective in improving biventricular global systolic function. Conversely, DFX was significantly more effective in reducing hepatic siderosis.
Pepe:Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Apotex: Speakers Bureau; Chiesi: Speakers Bureau. Off Label Use: Association of two chelators commercially available in order to obtain a higher efficacy. Borgna-Pignatti:Apotex: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal