Abstract
Allogeneic stem cell transplant (SCT) remains the only curative option for patients with β thalassemia major (TM). However, the clinical outcome following SCT in patients with TM who belong to the Class III and the Class III high risk (HR) group remains poor. (Class III HR = age≥7 years and liver size≥5 cms: defined by us previously; BBMT 2007;13:889).
From October, 1991 to June, 2011, 332 HLA matched related transplants for TM were done at our center. In an attempt to improve the clinical outcomes we used a Fludarabine (Flu) with intensity reduced Bu/Cy conditioning regimen, for a short period in 2006 and from August, 2009 a treosulphan based conditioning regimen (thiotepa: 8 mg/kg on day-6, treosulphan: 14gm/m2 for 3 days from day −5 to −3 and fludarabine 40mg/m2 for 4 days from day -5 to -2). We undertook a retrospective analysis to compare the impact of these alterations on the clinical outcome, especially in the high risk groups.
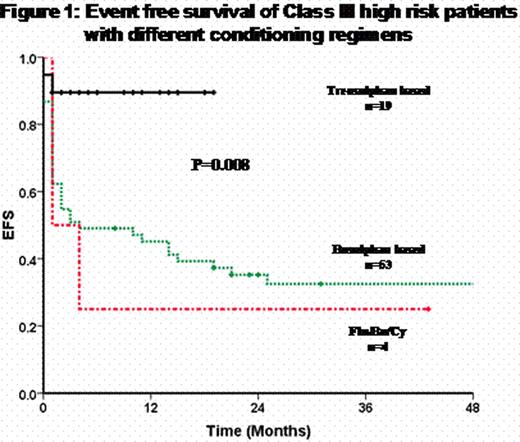
A total of 178 (53.6%) Class III underwent SCT and 76 (42% of Class III) of these were Class III HR. Of the Class III patients, 135 received a conventional oral busulphan based conditioning regimen, 13 the Flu/Bu/Cy regimen and 30 the treosulphan based regimen (baseline characteristics of three groups summarized in Table 1). The treosulphan based regimen was associated with a significant reduction on the incidence of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS), TRM and rejections (table 1). The 2 year Kaplan-Meier estimate of EFS for these three groups was 59.6 ± 4.3, 23.1 ± 11.7 and 89.1 ± 6.0) respectively (P=0.000). Among those conditioned with a treosulphan based regimen DAH occurred in 4 and two of them (who also had features of SOS) succumbed to subsequent complications. With the treosulphan based regimen, initially bone marrow was the stem cell source (n=12) and this was associated with a delay in engraftment (median time to ANC>1000/mm3 was 19 days: range: 15–21), greater morbidity and a higher incidence of mixed chimerism on day 28 post transplant (50%) compared to PBSC (n=18, median time to ANC>1000/mm3= 15 days; range: 12–28, day 28 mixed chimerism in 12%). Use of PBSC was not associated with a significant increased risk of acute or chronic GVHD. It was noted that these favorable observations were retained in the Class III HR subset and the 2 year Kaplan-Meier estimate of EFS in this subset, with a treosulphan based conditioning regimen (n=19), was 89.5 ± 7.0% (Figure 1).
Baseline characteristics and clinical outcomes of Class III patients conditioned with different conditioning regimens.
| . | Busulphan based N (%)/ Mean ± SD/ Median(Range) . | Fludarabine based N (%)/ Mean ± SD/ Median(Range) . | Treosulphan based N (%)/ Mean ± SD/ Median(Range) . | P-value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 135 | 13 | 30 | |
| Age | 9 (2–24) | 11 (4–14) | 11 (4–21) | 0.102 |
| Sex: M | 85 (63) | 8 (61.5) | 19 (63.3) | 0.994 |
| Class III HR* | 53 (39.3) | 4 (30.8) | 19 (63.3) | 0.036 |
| Live size | 4 (2–11) | 4 (3–7) | 5 (2–10) | 0.066 |
| F>M# | 49 (36.3) | 5 (38.5) | 7 (23.3) | 0.379 |
| Splenectomy | 30 (22.2) | 1 (7.7) | 7 (23.3) | 0.455 |
| HbsAg | 5 (3.7) | 0 | 0 | 0.441 |
| HCV | 28 (20.7) | 1 (7.7) | 4 (13.3) | 0.371 |
| Stem cell source$ | — | — | — | 0.000 |
| BM | 125 (92.6) | 13 (100) | 12 (40) | |
| GBM | 9 (6.7) | — | — | |
| PBSC | 1 (0.7) | — | 18 (60) | |
| CD34 dose | 6.4 (2.64–15.8) | 7.1 (2.80–12.7) | 11.4 (4.1–24.4) | 0.001 |
| ANC>0.5 × 109/Lt (days) | 16.88 ± 4.14 | 19.12 ± 2.75 | 16.03 ± 2.91 | 0.047 |
| Platelet>20 × 109/Lt (days) | 30 (10–137) | 32 (22–49) | 16.5 (9–44) | 0.000 |
| SOS@ | 89 (65.9) | 4 (30.8) | 4 (13.8) | 0.000 |
| Treatment related mortality | 40 (31.7) | 5 (41.7) | 2 (6.7) | 0.012 |
| Rejections | — | — | — | 0.034 |
| Primary graft failure | 4 (2.9) | 6 (46.2) | 1 (3.3) | |
| Secondary graft rejection | 12 (8.9) | 12 (15.4) | 0 (0) | |
| Ac GVHD | 55 (45.8) | 2 (20.0) | 11 (37.9) | 0.240 |
| Ch GVHD | 17 (18.1) | 0 | 3 (13) | 0.412 |
| 2 yr KM estimate of EFS | 59.6 ± 4.3 | 23.1 ± 11.7 | 89.1 ± 6.0 | 0.000 |
| 2 yr KM estimate of OS | 65.8 ± 4.2 | 53.8 ± 13.8 | 93.3 ± 4.6 | 0.028 |
| . | Busulphan based N (%)/ Mean ± SD/ Median(Range) . | Fludarabine based N (%)/ Mean ± SD/ Median(Range) . | Treosulphan based N (%)/ Mean ± SD/ Median(Range) . | P-value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 135 | 13 | 30 | |
| Age | 9 (2–24) | 11 (4–14) | 11 (4–21) | 0.102 |
| Sex: M | 85 (63) | 8 (61.5) | 19 (63.3) | 0.994 |
| Class III HR* | 53 (39.3) | 4 (30.8) | 19 (63.3) | 0.036 |
| Live size | 4 (2–11) | 4 (3–7) | 5 (2–10) | 0.066 |
| F>M# | 49 (36.3) | 5 (38.5) | 7 (23.3) | 0.379 |
| Splenectomy | 30 (22.2) | 1 (7.7) | 7 (23.3) | 0.455 |
| HbsAg | 5 (3.7) | 0 | 0 | 0.441 |
| HCV | 28 (20.7) | 1 (7.7) | 4 (13.3) | 0.371 |
| Stem cell source$ | — | — | — | 0.000 |
| BM | 125 (92.6) | 13 (100) | 12 (40) | |
| GBM | 9 (6.7) | — | — | |
| PBSC | 1 (0.7) | — | 18 (60) | |
| CD34 dose | 6.4 (2.64–15.8) | 7.1 (2.80–12.7) | 11.4 (4.1–24.4) | 0.001 |
| ANC>0.5 × 109/Lt (days) | 16.88 ± 4.14 | 19.12 ± 2.75 | 16.03 ± 2.91 | 0.047 |
| Platelet>20 × 109/Lt (days) | 30 (10–137) | 32 (22–49) | 16.5 (9–44) | 0.000 |
| SOS@ | 89 (65.9) | 4 (30.8) | 4 (13.8) | 0.000 |
| Treatment related mortality | 40 (31.7) | 5 (41.7) | 2 (6.7) | 0.012 |
| Rejections | — | — | — | 0.034 |
| Primary graft failure | 4 (2.9) | 6 (46.2) | 1 (3.3) | |
| Secondary graft rejection | 12 (8.9) | 12 (15.4) | 0 (0) | |
| Ac GVHD | 55 (45.8) | 2 (20.0) | 11 (37.9) | 0.240 |
| Ch GVHD | 17 (18.1) | 0 | 3 (13) | 0.412 |
| 2 yr KM estimate of EFS | 59.6 ± 4.3 | 23.1 ± 11.7 | 89.1 ± 6.0 | 0.000 |
| 2 yr KM estimate of OS | 65.8 ± 4.2 | 53.8 ± 13.8 | 93.3 ± 4.6 | 0.028 |
HR high risk
F>M female donor to male recipient
Stem cell source. BM=bone marrow, GBM=G-CSF primed BM, PBSC=peripheral blood stem cells
SOS sinusoidal obstruction syndrome
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal