Abstract
Abstract 5164
Using T2* MR a randomised placebo controlled study from Sardinia demonstrated combination therapy with deferiprone and desferrioxamine (DFP+DFO) significantly more effective than DFO in improving myocardial iron. One non-randomised study from Sardinia and one observational study from Greece seem to confirm for DFP+DFO therapy the most rapid clearance of cardiac iron. No data are available in literature about prospective comparisons on cardiac iron and function and liver iron in TM patients treated with DFP+DFO versus DFP and DFO in monotherapy. The aim of this multi-centre study was to assess prospectively in a large clinical setting the efficacy of the DFP+DFO versus DFP and DFO in TM patients by quantitative MR.
Among the first 739 TM patients enrolled in the MIOT (Myocardial Iron Overload in Thalassemia) network, 253 patients performed a MR follow up study at 18±3 months according to the protocol. We evaluated prospectively the 43 patients treated with DFP+DFO versus the 30 patients treated with DFP and the 66 patients treated with DFO between the 2 MR scans. Myocardial and liver iron concentrations were measured by T2* multislice multiecho technique. Biventricular function parameters were quantitatively evaluated by cine images.
The doses of the combination treatment were DFP 66±23 mg/kg/d for 6±1 d/w and DFO 41±7 mg/kg/d for 4±1 d/w, the dose of DFP was 73±16 mg/kg/d, DFO was 41±7 mg/kg/d for 5.5 d/w. Excellent/good levels of compliance were similar in the 3 groups (DFP+DFO 91% versus DFP 97% versus DFO 92%; P =0.76).
Among the patients with no significant myocardial iron overload at baseline (global heart T2*≥20 ms), there were no significant differences between groups to maintain the patients without myocardial iron overload (DFP+DFO 90% versus DFP 100% versus DFO 100%; P = 0.053).
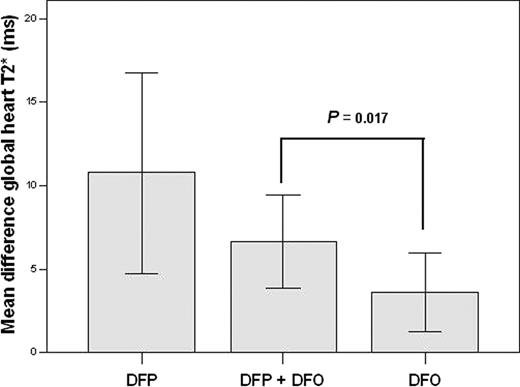
Among the patients with myocardial iron overload at baseline (global heart T2*<20 ms), in all groups there was a significant improvement in the global heart T2* value (DFP+DFO P=0.0001, DFP P=0.001 and DFO P=0.003), in the number of segment with a normal T2* value (DFP+DFO P=0.0001, DFP P=0.031, DFO P=0.0001) and in the right global systolic function (DFP+DFO P =0.002, DFP P=0.031, DFO P=0.045). The improvement in the global heart T2* was significantly different among groups (mean difference global heart T2* DFP+DFO 6.6±6.5 ms, DFP 10.7±7.2, DFO 3.6±5.4; P=0.009). The improvement in the global heart T2* was significantly higher in the DFP+DFO versus the DFO group (P=0.017), but it was not significantly different in the DFP+DFO versus the DFP group (P = 0.36) (see the figure). The changes in the global systolic bi-ventricular function were not significantly different among groups.
In patients with liver iron overload at baseline (liver T2*<5.1 ms), the change in the liver T2* was not significantly different among groups (mean difference liver T2* DFP+DFO 2.9±4.7 ms, DFP 2.3±5.8, DFO 2.9±4.9; P=0.91).
Prospectively in a large clinical setting over 15 months in TM patients combined therapy DFP+DFO confirmed superior reduction in myocardial iron in comparison to DFO, but no significant differences were found versus DFP monotherapy.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal