Abstract
Abstract 4983
Full length Hepatocyte growth Factor (HGF) (consisting of four “kringle”-domains) is known to be produced by multiple myeloma plasma cells (MM PC) in vivo and HGF is among the 70 most up regulated genes in MM. Elevated serum levels of HGF are known to be an adverse prognostic factor and recently, MM PC expression of the HGF receptor cMET has been shown to be an adverse prognostic factor. Functionally, HGF inhibits osteoblastogenesis in vitro and promotes migration of MM PC. So far, studies on HGF and its impact in MM have focused on measuring full-length or all isoforms of HGF expression. However, naturally occurring shorter isoforms of HGF (known as NK1 and NK2) are known to work as partial inhibitors of full-length HGF (Otsuka et al, Mol and Cell Biol, 2000). We examined the HGF isoforms and cMET expression at the mRNA level in isolated MM PC of >150 newly diagnosed patients with MM, 18 MGUS patients and 8 healthy volunteers (HV) and associated it to overall survival (OS) and degree of osteolytic bone disease (OBD).
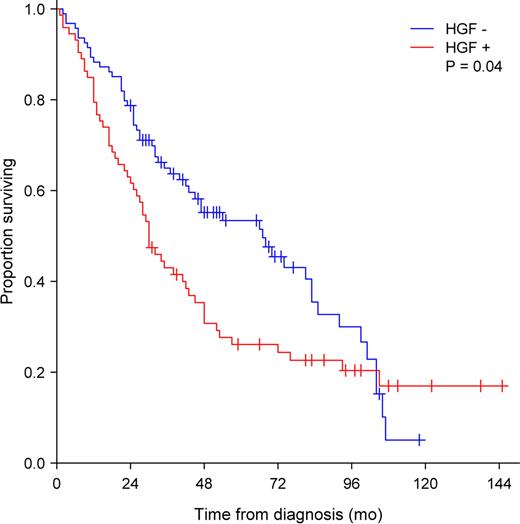
Aberrant MM PCs (CD38++/CD19-/CD45-/i/CD56-/+/++) were sorted directly into PCR tubes by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) using a FACS Aria (BDIS). In all cases a PC-purity above 98% was obtained. A cDNA archive was generated by global reverse transcription. By using a polyadenylating step 5x-oligo(dT)-transcript-poly(A)-3xcDNA were generated and finally amplified by PCR using a sequence independent X-(dT)24 primer. The conditions of the reverse transcriptase reaction is designed to limit the size of the first strand cDNA to 300–700 bases, which leads to a more uniform and unbiased amplification. Isoform specific primers were designed using the Primer Express program and experimentally tested. The HGF version covered full-length HGF (transcript variant 1 and 3), HGF2 covered the 2 kringle domain versions (transcript variant 2 and 4) and HGF5 covered the 1 kringle domain version (transcript variant 5). cMET only exists in one isoform. Quantitative PCR was performed using β-actin as internal reference gene, using the δCt method. Determination of positivity or negativity was made from a cut-off-value at 10E-05. OBD was evaluated by standard radiographic methods. The MM patients were treated with either high-dose melphalan with ASCT or melphalan-prednisone according to age recommendations. Results: At least one of the HGF isoforms were found to be expressed in PCxs from 43% of MM patients compared to 32% of MGUS patients, and 0% of HV. Full length HGF was expressed in 17 %, HGF2 in 29%, and HGF5 in 26% of the MM patients. Expression of any HGF variant was associated to an adverse OS (p=0.04) (Fig. 1). The quantitative expression of the transcript variant 5 associated negatively to OS (p=0.02), while expression of the other specific isoforms showed no association to OS. Thus, somehow surprisingly, MM PC expression of the shorter isoform of HGF (HGF5) was more predictive of poor prognosis.
A tendency towards elevated expression of full-length HGF in patients with no OBD compared to limited or advanced was observed but did not reach statistically significance (p=0.13). Pre-liminary analysis of cMET expression data showed no correlation between MM PC cMet expression and degree of OBD. Further data on cMet will be presented at the meeting.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal