Abstract
Abstract 4166
EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) of the elderly is an entity recently described and included in the WHO classification of lymphomas. It usually affects patients older than 50 years with poor responses to chemotherapy and short survival. However, the majority of the cases are from Asian origin. In fact, in Western countries the incidence of EBV in patients with DLBCL is reported as <5%. The primary objective of this study is to establish the prevalence of EBV in patients with DLBCL and identify prognostic factors in these patients.
We investigated the EBV status by detection of EBV-encoded RNA (EBER) using a chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH) technique in newly diagnosed patients with primarily nodal DLBCL, identified between January 2002 and December 2009. Clinical data were reviewed retrospectively and biopsies were analyzed for the presence of EBER by CISH and the immunohistochemical expression of BCL6, CD10 and MUM-1/IRF4 using standard procedures. Chi-square was used to compare the characteristics between EBER-positive and EBER-negative cases and to evaluate the association between complete response (CR) to chemotherapy and other clinical variables. Univariate survival estimates in patients who received chemotherapy were obtained using the Kaplan-Meier method. The multivariate survival analysis was performed using the Cox proportional-hazard regression test.
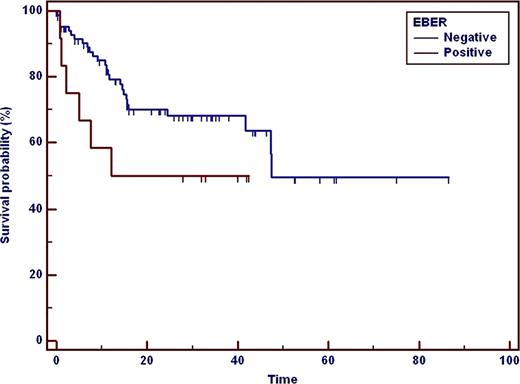
A total of 134 consecutive patients were eligible and were included in the comparative clinical analysis. In this cohort, the median age was 71 years (range 23–84) with a male-to-female ratio of 1.1 (71 male and 65 female cases) and a median overall survival (OS) of 47 months. 75% of the cases were 60 years or older, 62% had advanced clinical stage (III or IV), 63% has elevated LDH levels, 13% had involvement of 2 or more extranodal sites, 48% had an ECOG performance status of 2 or higher and 71% had a non-germinal center (NGC) immunohistochemical profile. Nineteen patients were positive for EBER but only 17 patients were included in the analysis because 2 patients were older than 50 years. When comparing EBER-positive and EBER-negative cases, there was an association between EBER expression and a worse outcome (p=0.003). EBER expression was not associated with gender, age, performance status, LDH levels, clinical stage, number of extranodal sites, B symptoms, immunohistochemical profile, overall response rate (ORR), CR rate, exposure to chemotherapy or IPI score. The only factors associated with CR were IPI score (p=0.047) and B symptoms (p=0.0004). Ninety nine patients received chemotherapy and were included in our survival analysis. In the univariate analysis, age over 60, performance status, LDH levels, number of extranodal sites, clinical stage, immunohistochemical profile and EBER expression were associated with OS. EBER-positive patients had a median OS of 12 months vs. 47 months in EBER-negative patients (p=0.045; Figure). In the multivariate analysis, performance status, LDH levels and EBER expression were independent factors for OS (p=0.02, 0.01 and 0.006, respectively). When evaluating EBER expression against the IPI score, both were independent prognostic factors for OS (p=0.002 and 0.03, respectively).
The prevalence of EBV-positive DLBCL of the elderly in Peru is the highest reported in the world (13%). DLBCL patients expressing EBER had a worse outcome in comparison to EBER-negative DLBCL patients. In the multivariate analysis, EBER expression in the tumoral cells was an independent prognostic factor for OS along with the IPI score.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal