Abstract
Abstract 3965
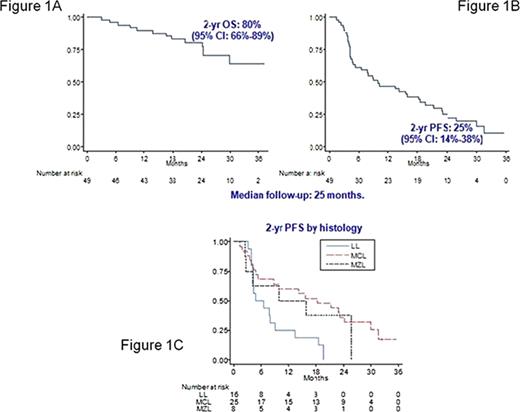
Introduction. Gene-profiling studies demonstrated a constitutive activation of the NFκB signalling pathway in Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL) and Marginal Zone Lymphoma (MZL). Bortezomib, a potent inhibitor of the 26S proteasome, is a good candidate to block this pathway and was tested in relapsed or refractory MCL with encouraging results (objective response up to 45%, with a median PFS of 5–7 months). In vitro, the combination of Bortezomib and Rituximab has been shown synergistic apoptosis and enhanced NFkB depletion in MCL and MZL cells. Aim. On these bases, the IIL conducted a phase II multicenter study to evaluate safety and efficacy of Rituximab and Bortezomib combination in relapsed/refractory indolent non-follicular lymphoma (Linfocytic Lymphoma, LL, or MZL) and MCL not eligible for high-dose chemotherapy. Patients and methods. Inclusion criteria were: age 18–75 years, histological proven relapsed or refractory LL, MZL and MCL after 1–4 lines of therapies. Treatment plan was: one course of four weekly intravenous bolus of 1.6 mg/sqm Bortezomib in combination with four infusion of 375 mg/sqm Rituximab followed by two courses of four weekly bolus of 1.6 mg/sqm Bortezomib. Patients with complete (CR), partial remission (PR) and stable disease at the intermediate evaluation were planned to be given three further courses with the same schedule. Results. From September 2006 to March 2008, 55 patients entered into the study. Central histology revision was performed. Forty-nine patients fulfilled inclusion criteria and were evaluable. Clinical characteristics were: median age 68 (50-74) years; 16 LL, eight MZL, 25 MCL; 42 stage III/IV; 33 bone marrow involvement; 20 at intermediate-high/high International Prognostic Index (IPI) risk. Thirty-eigh patients performed more than two prior lines of chemotherapy; 34 were Rituximab-pretreated; 21 refractory and 28 relapsed disease. Overall Response Rate (ORR) was 53% (CR 26.5%, PR 26.5%); no response 43% and 4% off therapy for other causes. ORR by histology was: 37% in LL, 50% in MZL and 64% in MCL. ORR was not adversely affected by Rituximab pretreatment: Rituximab-pretreated 62% and Rituximab-naïve 33%. ORR was higher in relapsed patients compared with refractory ones: 64% and 38% (p .06). (Table 1). With a median follow-up of 25 months, 2-year Overall Survival (OS) was 80% (95%CI: 66–89) and 2-year PFS was 25% (95%CI: 14–38) (Figure 1A, 1B). Two-year PFS by histology was shown in Figure 1C. A total of 233 courses were delivered with a median of 4.7 courses/patient. Thirty patients completed the treatment plan; 19 did not due to progression disease in 13, adverse events in five (concomitant gastric neoplasia, neurotoxicity grade II, sepsis, pleural effusion and toxic death due to interstitial pneumonia). Grade 3–4 CTC haematological toxicity was rare: neutropenia in 5% of the courses and thrombocytopenia in <2%. Grade 3–4 CTC cumulative non-hematological toxicity was observed in 4.7% of all courses. The most frequent non-hematological toxicities were: neurotoxicity grade III in four patients, with complete recover or return to grade I in all of them. Infections were observed in eight patient with ten events: viral reactivation in four, pneumonia in three, sepsis in one and micosis in two. Conclusions. The combination of Rituximab and Bortezomib in weekly schedule was effective and safe in treatment of relapsed/refractory indolent and MCL. PFS was promising also in Rituximab-pretreated patients and mainly in MZL and MCL.
ORR (%)
| MCL/MZL/LL . | 64/50/37 . |
|---|---|
| Rituximab-pretreated/Rituximab-naive | 62/33 |
| N of prior therapies <2/≥2 | 75/46 |
| Relapsed/Refractory | 64/38 |
| MCL/MZL/LL . | 64/50/37 . |
|---|---|
| Rituximab-pretreated/Rituximab-naive | 62/33 |
| N of prior therapies <2/≥2 | 75/46 |
| Relapsed/Refractory | 64/38 |
Off Label Use: The use of Bortezomib is off-label in Relapsed/Refractory Indolent Non-Follicular and Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Vitolo:Roche-Italy: Advisory committee; Celgene-Italy: Advisory committee; Janssen-Cilag: Lecture Fee.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal