Abstract
Abstract 3537
Donor-recipient HLA mismatches are associated with increased morbidity and mortality after UD hematopoietic stem cell transplants (HSCT). We hypothesized that HLA-DP mismatches would worsen outcomes of HSCT using donors mismatched at HLA-A,-B,-C,-DRB1 or -DQB1 and evaluated 391 consecutive patients (pts) with myeloid malignancies treated at our institution with 0,1,2,3 mismatches out of 12 alleles typed by high resolution at HLA-A,-B,-C,-DR,-DQ,-DP loci. Eighty-one pts were 12/12, 180 pts were 11/12, 113 pts were 10/12, and 15 pts were 9/12 HLA match with the recipients. Characteristics of the 4 groups (12/12, 11/12, 10/12, 9/12) were similar except source of stem cells; 87% of pts with 9/12 donors received bone marrow versus 60–62% for the other 3 groups.
Two-year overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were 40%, 44%, 45%, 53% and 33%, 40%, 44%, 49%, respectively (p=NS). However, OS was significantly worse with increasing number of mismatches for patients with AML/MDS with poor-risk cytogenetics (p=0.005, HR 1.6, 95% CI 2.1–4.2). Except for the 9/12 group, pts had a significantly higher non-relapse mortality (NRM) (11%, 24%, 36%) and lower risk of progression (32%, 25%, 20%). In the 9/12 group, NRM was 27% and progression rate was 40%. Grade II-IV, III-IV aGVHD as well as cGVHD were also progressively worse with increasing number of mismatches. Gr II-IV and III-IV aGVHD rates were 35%, 37%, 41%, 69%, and 8%, 8%, 15%, 16%, respectively. Cumulative incidence of cGVHD was 35%, 39%, 44% and 61%, respectively. Compared with 11–12/12 donors, pts who received a 9–10/12 donor had significantly higher rates of gr III-IV aGVHD and cGVHD (p=0.03, HR 2.1, CI 1.1–3.7 and p=0.02, HR 1.5, CI 1.1–2.1, respectively).
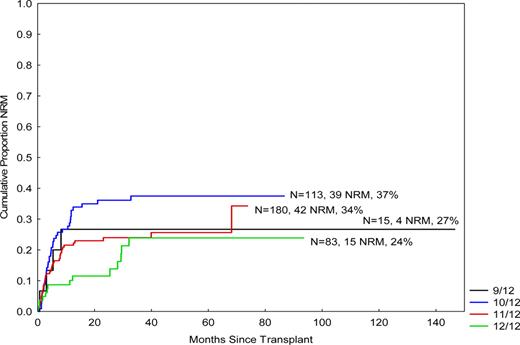
Univariate analysis revealed that there is less NRM with a 12/12 donor (vs. other) (p=0.008, HR 1.9, 95% CI 1.2–2.9), while in multivariate analysis, compared with a 12/12 donor, the use of a donor with mismatch was significantly associated with higher NRM [HR and 95%CI were 2.1 and 1.04–4.4 for 11/12 donor (p=0.04); 3.1 and 1.5–3.3 for 10/12 donor (p=0.003); 2.8 and 0.9–9.3 for a 9/12 donor (p=0.08), respectively] (Figure). In multivariate analysis, factors significantly associated with OS were disease status at transplant (active disease vs. not) (p<0.001), cytogenetics for AML/MDS pts (poor-risk vs. other) (p=0.006, HR) and the use of fludarabine and busulfan conditioning (Bu 130mg/m2 × 4 days and Flu vs. other) (p=0.04, HR 0.7, CI 0.5–0.98), while factors significantly associated with NRM were, in addition to degree of mismatch, disease status at transplant (p=0.008, HR 1.9, CI 1.2–3.1) and use of BuFlu conditioning (p=0.004, HR 0.5, CI 0.4–0.8).
In conclusion, these results suggest that, using 12/12 high-resolution HLA typing, a progressively higher NRM is encountered for unrelated donor pts with higher number of mismatches, at least in part related to higher rates of GVHD. Matching at DP loci appears to be protective of NRM and is associated with improved survival for patients with AML/MDS with poor-risk cytogenetics.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal