Abstract
Abstract 3353
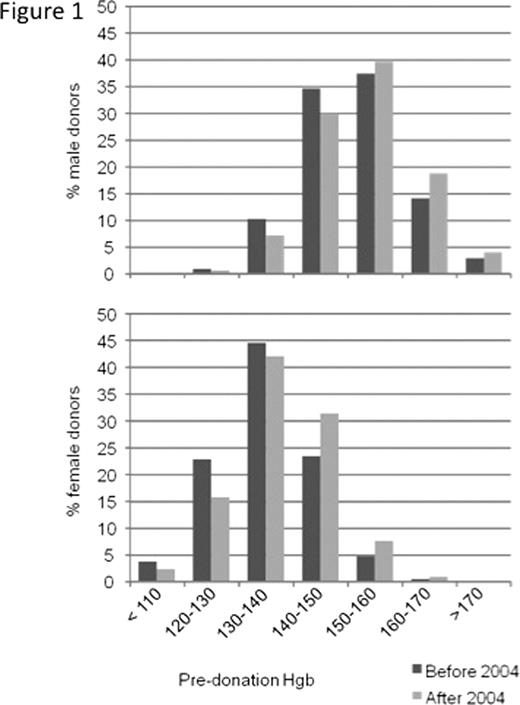
Iron store depletion is a common side effect of whole-blood donation. Iron loss may lead to iron deficiency symptoms such as fatigue, decreased physical and job performance then gradually result in iron deficiency anemia. As of 2004, routine serum ferritin testing was implemented at our Center. We analyzed the impact of this measure on our donor population with regard to hemoglobin level, anemia occurrence and donor deferral due to low hemoglobin. A total of 160'612 intended donations of 23'557 healthy blood donors at a single institution (Blutspendezentrum beider Basel, Basel, Switzerland) between 1996 and 2009 were analyzed. At each visit, complete blood counts were taken from fingerprick samples and donors were deferred if the capillary hemoglobin concentration proved <133 g/L (m) or <123 g/L (f). From 2004 on, serum ferritin was measured systematically. Upon detection of ferritin levels indicative of iron depletion or iron deficiency anemia, donors were contacted by a blood bank physician and received medical counseling. The further procedure of iron supplementation, donation interval extension or GP referral in the case of abnormal history remained at the physician and donor's discretion.Our donor population consisted of 10'893 males and 12'664 females, 8165 being women of childbearing age (age 18–45). Mean hemoglobin concentration of male donors rose from 151.7 g/L (before 2004) to 153.6 g/L after 2004 (difference 1.9 g/L, 95% CI 1.7 – 1.9 g/L). In women of all ages, the mean hemoglobin concentration increased from 135.7 to 138.3 g/L (difference 2.6 g/L, 95% CI 2.4 – 2.7 g/L) (Figure 1). The hemoglobin concentration of women of childbearing age was 134.2 g/L before 2004 and 137.0 g/L thereafter (difference 2.8 g/L, 95% CI 2.6 – 3.0 g/L). To rule out an alternative cause for the increase in hemoglobin, we assessed the evolution of hemoglobin levels in the periods of 1996–2003 and 2004–2009. In the former period, hemoglobin levels decreased at a mean rate of 0.22 g/L (95% CI -0.19 - -0.26 g/L) per year in male donors, whereas no significant change was seen in female donors (mean change 0.04 g/L, 95% CI -0.01 – 0.09 g/L). In the second period (2004 – 2009), mean hemoglobin levels increased in both male (mean increase per year 0.20 g/L, 95% CI 0.14 – 0.25 g/L) and female donors (mean increase per year 0.16 g/L, 95% CI 0.09 – 0.23 g/L). Before the introduction of routine ferritin measuring, 1.6% (95% CI 1.5 – 1.7%) of donors showed anemia according to WHO definitions (m: Hb<130; f: Hb<120). Anemia occurred in 1.1% of our donors after 2004 (95% CI 1.0 – 1.2%, difference before/after 2004 0.5%, 95% CI -0.6 – -0.3%). Frequency of anemia declined in both male donors (before 2004 0.7%, after 2004 0.5%) and in female donors (before 2004 3.6%, after 2004 2.2%). In the group of women of childbearing age, 4.9% (95% CI 4.6 – 5.3%) were anemic before and 3.1% (95% CI 2.7– 3.4%) after 2004 (difference before/after 2004 -1.8%, 95% CI -1.4 – -2.4%). In all visits to our center before 2004, 2.8% of donors (95% CI 2.7 – 2.9%) were not accepted for phlebotomy due to a hemoglobin count below the mandatory threshold. After 2004, the percentage of rejected donors due to a low hemoglobin count decreased to 1.9% (95% CI 1.8 – 2.0%, difference before/after 2004 -0.9%, 95% CI -0.7 – -1.0%). In particular in the group of women in childbearing age a clear reduction of the rejection rates was noted (before 2004: 7.6% CI 7.2 – 8.1%, thereafter: 4.8% CI 4.4 – 5.2%, difference before/after 2004 -2.8%, 95% CI -2.2 – -3.4%). In conclusion, the introduction of systematic serum ferritin measurements allowed an optimized management of donors with iron deficiency, with efficacious prevention of iron deficiency anemia. This resulted in an increase of mean hemoglobin levels in blood donors particularly in women of childbearing age, the population at highest risk for iron deficiency anemia. Both the incidence of pre-donation anemia and the frequency of donors rejected due to low hemoglobin decreased significantly.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This icon denotes an abstract that is clinically relevant.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal