Abstract
Abstract 324
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) may be curable with current immuno-chemotherapy, however nearly 30% of patients fail to benefit from this therapeutic approach. Gene expression profiling studies identified lymphocyte as well as stroma-based mRNA signatures that are predictive of response to R-CHOP; however the need for optimally cryopreserved samples has limited their clinical applicability. MicroRNAs (miRNA) are highly preserved non-coding RNAs that act post-transcriptionally to regulate gene expression by binding to the 3′UTR of mRNAs. To date multiple studies have reported selective miRNAs expression at different lymphocyte differentiation stages, distinct expression in mRNA-defined DLBCL subgroups and have correlated the expression of “selected” miRNAs with disease outcomes. Herein, we have conducted a comprehensive profiling of miRNA expression in R-CHOP treated DLBCL patients and established a miRNA-based risk score that is predictive of response to therapy.
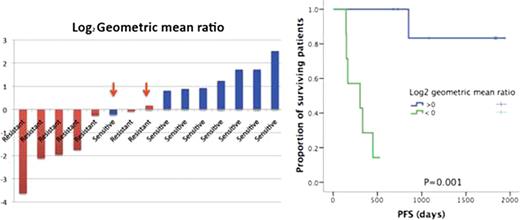
We have postulated that a miRNA signature in DLBCL is predictive of survival post R-CHOP chemotherapy. To test this hypothesis, we analyzed the miRNA and mRNA signatures of R-CHOP sensitive “S” and resistant “R” DLBCLs (n=20). miRNAs were hybridized to the miRNA Affymetrix gene-chip (847 hsa-miRNA probes) and raw miRNA expression values were log2 transformed and normalized (miRNA-QC tool, Affymetrix). Comparison of normalized miRNAs expression in “S” versus “R” patients (Anova testing) identified 59 differentially expressed miRNAs (Fold change < -1.5 or > 1.5 with a p value and FDR <0.05). In order to establish a risk score based on the expression of these 59 miRNAs, column-dendrogram branches were then sorted left to right based on each patient's difference between the average log2-scale expression of the 37 up-regulated and the 12 down-regulated miRNAs: this difference is interpreted as an up-/down-regulated mean ratio (ie, geometric mean) on the log2 scale [Log2 Geometric mean ratio [GMR] up-/down-regulated miRNA = Log2 [(2^ΣupregulatedümiRNA/ni)/(2^ΣdownregulatedümiRNA/nii)] where ni and nii represent the number of up-regulated and down-regulated miRNAs. This univariate summary (ie, GMR) of the 59-miRNA expression profiles for each patient enabled accurate prediction of all S versus R patients. Patients with log2 GMR > 0 had a 6-years PFS rate of 100%, while all patients with log2 GMR < 0 relapsed (HR=0.293 [95% CI 0.132–0.647]). Cox regression was then used to model relapse free survival times from treatment as a function of miRNA expression. Separate regression models were also built looking at fit measures, proportionality assumption, and discrimination ability (Harrell C statistics) and only miRNA with a discrimination ability (Harrell C) of > 85% (n=12 miRNA) were used to calculate the log2 GMR of up-/down-regulated miRNAs. A simplified model based on 12 miRNAs (Sensitive vs Resistant: upregulated: hsa-let-7i; hsa-miR-130a; hsa-miR-199a-3p; hsa-199b-3p; hsa-miR-223; hsa-miR22; hsa-miR-24; hsa-miR-26b; hsa-miR-27a; hsa-miR-331-5p; downregulated: hsa-miR-1288) accurately predicted sensitivity or resistance to R-CHOP. With this 12 miRNAs model, only 1 patient in each group (S and R) was misclassified (Fig 1). In addition we have validated the differential expression of these miRNA by short-stem loop RT-PCR and found a strong correlation between the gene-chip and qRT-PCR results (correlation coefficient 0.717). mRNA profiling (U133A Plus2 array chip) was also performed on the whole lymph node sections; 176 genes were identified as differentially expressed between S and R patients with many of these genes belonging to the “stroma-1 and -2” DLBCL signature. Using the TargetScan miRNA target mRNA prediction tool, combinatory analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression profiles of DLBCL patients identified positive and negative correlations (P <0.05) between differentially expressed miRNA and mRNAs. Lastly in a multivariate Cox regression analysis that included the IPI and the 12 miRNA based GMR risk score, both variables were independent predictors of survival post R-CHOP therapy.
We believe that this log2 GMR score based on the 12 identified miRNA provides a robust method of predicting sensitivity to R-CHOP in DLBCL patients and it is currently being tested in a larger independent validation cohort.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This icon denotes an abstract that is clinically relevant.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal