Abstract
Abstract 3052
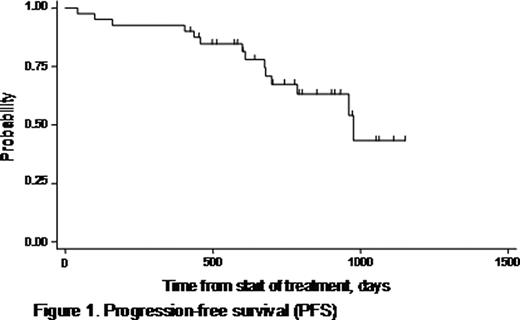
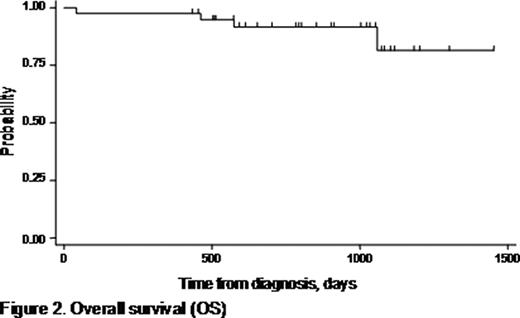
The combination of bortezomib, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone (PAD) has shown efficacy in both relapsed/refractory and untreated, symptomatic multiple myeloma (MM). The activity of this regimen is largely attributed to the recognized synergy between bortezomib and doxorubicin. Bortezomib is capable of reversing resistance to chemotherapy in MM with adverse prognostic features (high-risk myeloma), which has an unfavorable outcome with conventional chemotherapy followed by high-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). In addition, disease status prior to ASCT has prognostic significance for survival, underscoring the need for highly efficient remission induction strategies. In a prospectively designed phase II trial, we focused on the efficacy and safety of the PAD combination as front-line treatment for high-risk myeloma. The study recruited patients aged ≤70 years with newly diagnosed, symptomatic MM with high-risk features (defined by at least one of the following criteria: ISS stage II/III according to serum albumin and beta2-microglobulin, and/or detection of 13q deletion by FISH or conventional karyotyping). Between 2005 and 2008, 40 patients were enrolled in the protocol. The median age of patients was 59 years (range: 41–70 years), and 27 (67.5%) were male. Each 21-day cycle of PAD included bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 on days 1, 4, 8, and 11 plus doxorubicin 9 mg/m2 on days 1–4, and dexamethasone 40 mg on days 1–4 and 8–11. According to protocol, patients received 4 induction cycles of PAD before proceeding to stem cell harvest and ASCT. Acyclovir and ciprofloxacin prophylaxis were routinely used. Patients were evaluated for toxicity at each cycle and for response after the end of the fourth cycle. The primary study endpoint was the response rate at the end of induction (assessed by the International Myeloma Working Group uniform response criteria, 2006). Secondary endpoints were toxicity, progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), ability to mobilize stem cells, and response after ASCT. ISS stage was I in 2 patients (5%), II in 18 (45%), and III in 20 (50%). Nine out of 40 patients (22.5%) presented with renal failure (creatinine >2mg/dl) due to myeloma at diagnosis. Deletion 13q was detected in 19 patients. Bone disease was present in 30 patients (75%) at diagnosis, and 19 (47.5%) had ≥3 lytic lesions on plain skeleton radiograms. Median patient follow-up time was 28.3 months (range, 1.4–49.3). All patients completed the 4 cycles of PAD, with the exception of one who died during the 2nd cycle. The overall response rate assessed after the 4th cycle of PAD was 95%. Complete remission (CR) was achieved in 12/39 (31%), very good partial remission (VGPR) in 15/39 (38.5%), and PR in 10/39 (25.5%). Thirty-one patients were considered eligible for ASCT, and an adequate stem cell harvest was achieved in all. Following ASCT, CR rate reached 52% (16/31) with a CR+VGPR rate of 84% (26/31). PFS was 67% at 2.1 years, and calculated OS was 81.4% at 4 years (Figures 1 and 2). Factors associated with shorter OS were beta2-microglobulin ≥5.5 mg/L (p=0.03), and ISS stage III (p=0.03). By assessment of the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), a significant improvement in renal function was demonstrated after induction with PAD (median GFR pre- and post-induction: 59.7 versus 82.1 ml/min, respectively; p<0.001). Improvement in kidney function was observed irrespective of the type of response. There was only one treatment-related death secondary to infection. Toxicities were manageable in general, and included grade 3–4 neutropenia in 8/40 patients (20%), grade 3–4 thrombocytopenia in 4/40 (10%), and grade 3 peripheral neuropathy in 4/40 (10%). No grade 4 peripheral neuropathy was encountered. We conclude that the PAD regimen is very effective, and produces high-quality responses in a substantial proportion of patients with newly diagnosed, high-risk MM (CR+VGPR: 69.5%). PAD is well tolerated and does not compromise stem cell mobilization and harvest. Upfront treatment with 4 cycles of PAD followed by ASCT resulted in notable PFS and OS rates in this patient group with adverse-prognosis MM. PAD was shown to be particularly beneficial in patients with renal impairment at diagnosis due to myeloma.
Baltathakis:Janssen-Cilag: Research Funding. Terpos:Janssen-Cilag: Honoraria. Delimpasi:Janssen-Cilag: Research Funding. Dimopoulos:Janssen-Cilag: Honoraria. Harhalakis:Janssen-Cilag: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal