Abstract
Abstract 231
DNA methylation induces gene silencing in a nonrandom fashion in many types of malignancies. In AML there is no consensus regarding the clinical implications of DNA methylation on a global level. Normal karyotype AML (NK AML) can be prognostically stratified by molecular mutations in genes such as FLT3 and NPM1. We have previously reported that increased gene promoter methylation levels may have positive prognostic implications in AML. Now we have focused and expanded our analysis in a homogenous group of NK AML in an effort to illuminate these issues.
We analyzed genome wide DNA methylation signatures from the diagnostic bone marrow samples of 58 de novo NK AML with the IlluminaHuman27 Methylation array, covering 27000 CpG sites, mainly located in the promoter regions of 15000 individual genes. Global methylation was defined as the average methylation values of all measured CpG sites in the specific sample. All patients were between 18 and 67 years of age and received standard induction chemotherapy. All were eligible for intensive consolidation therapy including allogeneic transplantation. FACS sorted normal bone marrow separated into four stages of myeloid differentiation were analyzed as normal controls. Methylation data were correlated to clinical outcomes and molecular mutational status of NPM1 and FLT3. Functional annotation analyses were performed on differentially methylated genes to find epigenetically perturbed pathways. Further molecular analysis of CEBPA, IDH1 and IDH2 is currently performed.
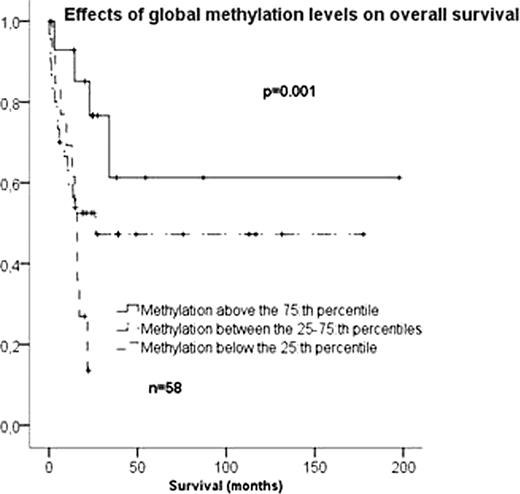
Global methylation levels varied substantially between AML samples but remained mainly unchanged during normal myeloid differentiation. Methylation levels were significantly higher in AML cases than in the normal myeloid progenitors (p<0.001). There were no correlations between methylation levels, age, white blood cell (WBC) count or bone marrow blast percentage at diagnosis. Increased global methylation correlated significantly to increased in vivo chemosensitivity and to patient survival. CR rates after one course of induction chemotherapy were 64% in the quartile of patients with the highest level of global DNA methylation compared to 32% in others (HR 3.9, p=0.04). Median overall survival of patients of the most methylated quartile was not reached and significantly longer than the 16 months median survival of the least methylated quartile (p=0.001) (see figure below). In a Cox Regression model stratified for FLT3-mutational status, methylation level was an independent prognostic factor for survival (p=0.01) together with WBC count (p=0.01).
A functional annotation analysis revealed that NPM1 wild type samples had an enrichment of Homeobox (HOX) gene methylation as compared to NPM1 mutated cases (p=1.7×10−11), providing a mechanism for the previously described difference in HOX gene expression in NPM1 wt vs. NPM1 mutated AML. The average methylation levels of all HOX genes were higher in wild type NPM1 cases compared to NPM1 mutated cases (p=0.02). Additional gene expression array data in our cohort of patients also showed methylation levels of individual HOX genes to be correlated inversely with expression. HOX genes were also enriched in non-FLT3ITD cases compared to FLT3ITD-cases, however, not to a statistically significant degree.
In conclusion we show that global DNA methylation levels are predictive of response to chemotherapy and an independent prognostic factor for survival in normal karyotype AML. Furthermore, our results suggest that HOX gene methylation may be the mechanism underlying the previously known difference in HOX-gene expression between NPM1 mutated and unmutated AML cases.
Nahi:Jansen-Cilag: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal