Abstract
Abstract 1400
Hemostatic abnormalities are frequently encountered during initial presentation of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) as well as during induction treatment. Patients often present with decreased platelet counts and sometimes with abnormalities of the coagulation parameters with or without bleeding manifestations. In the absence of overt disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC), transfusion practices during treatment are essentially based on the platelet count. Fibrinogen is an important element of the clotting mechanisms, constituting a template for both thrombin binding and the fibrinolytic system. We sought to determine the prevalence of altered serum fibrinogen levels during induction treatment in AML and its clinical significance.
We prospectively measured serum fibrinogen on a daily basis in patients with newly diagnosed AML treated with induction anti-tumor chemotherapy at our institution from February 2007 to July 2010. Inclusion criteria included the diagnosis of AML and no overt DIC.
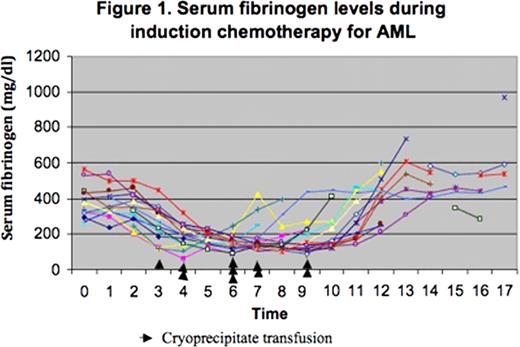
The study population included 17 patients (47% females) with mean age of 55.3 years (range 18 –80 years). At presentation, the mean platelet count was 62 × 109/L (range 3 – 252 × 109/L), the mean prothrombin time was 11.4 seconds (range 9.6–13.4 secs, normal range 10—13.7 secs), the mean international normalized ratio was 1.1 (range 0.9–1.3; normal range 0.9–1.1) and the mean activated partial thromboplastin time was 26.56 seconds (range 20.1–41 secs, normal range 22.3–34.0 secs). All patients had normal serum fibrinogen levels at presentation (mean 380.6 mg/dl; range 258–567 mg/dl; normal range 200–400 mg/dl). Thirteen patients were treated with idarubicin and cytarabine, 3 patients received a FLAG (fludarabine, cytarabine and G-CSF) regimen and one patient had amonafide and cytarabine. Serum fibrinogen levels were recorded on all patients on a daily basis (Figure 1). Nine (53%) developed hypofibrinogenemia on the fourth day of induction, 2 (12%) on day 5, 3 (17%) on day 6, 2 (12%) on day 7, and one (6%) on day 8 of the induction. Eight patients (47%) received prophylactic cryoprecipitate when the serum fibrinogen levels fell below 150 mg/dl. We did not observe a significant trend difference in serum fibrinogen levels between patients who received cryoprecipitate and those who did not. Serum fibrinogen levels were back to normal without transfusion support by day 6 for one patient (5.88 %), day 7 for 2 patients (11.76 %), day 8 for 3 patients (17.65 %), day 9 for one patient (5.88 %), day 10 for one patient (5.88 %), day 11 for 3 patients (17.65 %), day 12 for 6 patients (35.3 %).
Patients with acute myeloid leukemia receiving induction chemotherapy may frequently develop isolated hypofibrinogenemia without evidence of disseminated intravascular coagulation. This finding is usually self-limited and disappears shortly after the completion of antitumor chemotherapy, usually by day 12. The mechanism of this under-recognized phenomenon is unclear. Its common occurrence raises questions about the appropriateness of transfusion practices in AML based solely on the platelet count and argues in favor of the need of more global tests such as thromboelastography.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This icon denotes an abstract that is clinically relevant.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal