Abstract
Abstract 1349
High dose melphalan is the most common conditioning regimen for patients undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (ASCT) for multiple myeloma (MM). However, toxicity and efficacy of this treatment are variable, with the sources of variability poorly understood. We hypothesized that variation in melphalan pharmacokinetics would explain differences in outcomes after transplant.
We evaluated 41 patients with MM undergoing ASCT with high-dose melphalan conditioning. Patients received melphalan on day -2 at a dose of 200 mg/m2 (one patient with poor renal function received 180 mg/m2) and ASCT on day 0. Melphalan dose was calculated using ideal body weight (IBW), with adjusted IBW used for patients weighing >120% of IBW. We assessed toxicity on day +7 using the Oral Mucositis Assessment Scale (OMAS), a physician evaluated measurement of erythema and ulceration (on a scale of 0–5, with higher scores indicating more severe mucositis). Patients reported the severity of mouth soreness on a scale of 0–10 using the Mucositis Daily Questionnaire (MDQ) on days 0, +3, +7, +11, +19, and +28. Melphalan concentrations were measured using HPLC/tandem mass spectrometry in plasma samples obtained during infusion and 2, 4, 8, 15, and 30 minutes, and 1, 2, 3.5, 8, and 14 hours after its completion, as well as immediately prior to stem cell infusion. Melphalan area under the curve (AUC) was estimated by non-compartmental analysis.
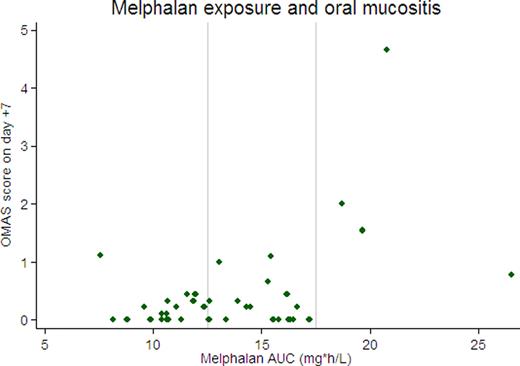
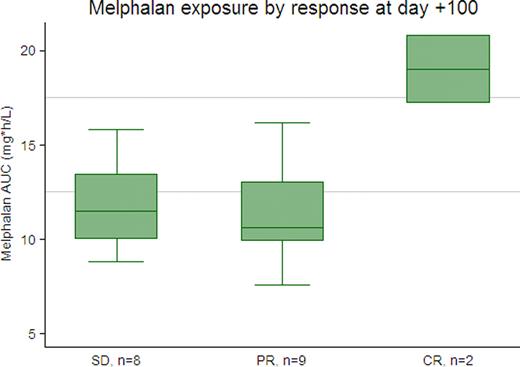
Patients' median age was 57 years (range 39–72); 59% were male. We observed significant variation in melphalan exposure, with a range of 7.6–26.6 mg*h/L (median 13.5). Severity of oral mucositis was directly related to AUC (with an increase of 0.1 on the OMAS score for every 1 unit increase in AUC, p=0.003). The most severe mucositis was seen in the 4 patients with an AUC ≥17.5 (75% had OMAS scores >1), while severe mucositis was rarely seen in the 18 patients with AUC ≤12.5 (only 1 of 18 had an OMAS score >1). The association between AUC and maximum reported mouth soreness was not statistically significant (an increase of 0.2 on the MDQ scale for every 1 unit increase in AUC, p=0.17), but there was a trend toward higher maximum reported mouth soreness in the 4 patients with AUC≥17.5 (mean 7.5 vs. 4 for other patients, p=0.07). Eight patients had detectable melphalan concentrations at the time of stem cell infusion (mean 3.8 ng/mL, range 1.8–7.1), though time to neutrophil and platelet recovery did not differ for these patients compared with those with undetectable melphalan levels. Of 19 patients with measurable disease at the time of transplant, 8 had stable disease (SD), 9 partial response (PR), and 2 complete response (CR) at day +100. The 2 patients with CR had higher melphalan exposure than patients without a CR (mean AUC 19 vs 11.6, p= 0.002), but there was no discernable difference in melphalan levels between patients with a PR or SD.
Using standard dosing calculations in a representative sample of patients with myeloma, melphalan drug exposure was highly varied. Drug exposure was correlated with severity of oral mucositis, and complete responses were seen only in patients with high drug exposure. Further analyses are planned into the effect of obesity and renal dysfunction on pharmacokinetics. Exploration of the appropriate target AUC and strategies for reducing variability in drug exposure have the potential to improve both efficacy and toxicity of this effective and commonly used therapy.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal