Abstract
Abstract 559
Different cellular components of the normal hematopoietic niche have been identified. However, the niche for malignant hematopoiesis remains to be elucidated. Recent work of other groups has suggested that hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) within the bone marrow anchor themselves in place by attaching to osteoblasts and/or vascular sinusoid endothelial cells. We have recently identified mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) as niche-maker cells and found a crucial role of the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in this process. Stromal Derived Factor-1 (SDF-1/CXCL12) regulates stem cell trafficking and the cell cycle via its receptor CXCR4.
Polyurethane scaffolds, coated in vitro with human bone marrow MSC, were implanted subcutaneously in non-irradiated NOD/SCID mice. CD34+ HSC or primary AML cells (from a leukapheresis product) were injected either in situ or retro-orbitally in the mice and analyzed for engraftment. The mice were treated twice per week with in situ injections of SDF-1, AMD3100 (a CXCR4 antagonist) or PBS (control). After 2 to 4 weeks, the scaffolds were processed and evaluated for cell survival in the mesenchymal niche by immunohistochemistry.
We created in vitro MSC-coated scaffolds that retained inoculated AML cells in the presence of SDF-1, while AML cells seeded on empty scaffolds were not retained. In vivo in NOD/SCID mice, the MSC-coated scaffolds, in the presence of SDF-1 enabled homing of both in situ injected normal CD34+ HSC and retroorbital- or in situ injected primary human AML cells. The scaffolds were vascularized and showed osteoclasts and adipocytes present, suggestive of an ectopic human bone marrow microenvironment in the murine host. Finally, the SDF-1-treated scaffolds showed proliferation of the MSC stromal layer with multiple adherent AML cells, while in the AMD3100-treated scaffolds the stromal lining was thin and disrupted at several points, leaving AML cells free floating in proximity. The PBS-treated control-scaffold showed a thin single cell MSC stromal layer without disruption, with few AML cells attached.
The preliminary data of this functional ectopic human microenvironment in NOD/SCID mice suggest that AMD3100 (a CXCR4 antagonist) can disrupt the stem cell niche by modulation of the mesenchymal stromal. Further studies are needed to define the role of mesenchymal stem cells in maintaining the hematopoietic/leukemic stem cell niche in vivo.
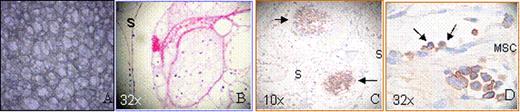
(A) Empty polyurethane scaffold. (B)Vascularization in SQ implanted MSC-coated scaffold (s) niche in NOD/SCID mice. (C) DAB Peroxidase (brown) human CD45 positive nests of AML cells (arrows) 1 week after direct in situ AML injection. (D) Human CD45 positive myeloid cells adhere to MSC in vivo (arrows).
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal