Abstract
Abstract 4945
Current goals in MM-treatment are to achieve prolonged remission- and treatment-free-intervals and to transform the disease into an indolent course. Effective anti-MM-substances are IMIDs, such as thalidomide and lenalidomide, the latter showing a different mode of action and favorable side-effect profile. Lenalidomide-induced side effects may, however, increase with renal impairment (RI) and dose adjustments are recommended, thus sensitive RI-monitoring is desirable. We assessed renal function (RF) via estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR by MDRD) and correlated this with lenalidomide-response, since we have shown that eGFR-monitoring is a sensitive method to detect RI in various hematological and solid tumor- (Kleber M. et al., Ann Oncol 2007) and explicitly valuable in MM-pts (Kleber M. et al., EJH 2009).
Thirty-two consecutive MM pts received lenalidomide in G1-4 treatment groups at our center between 6/2006-7/2009 (G1=lenalidomide 25mg/dex 40mg [n=12]; G2: lenalidomide 25mg/low-dose-dex-[n=10]; G3: lenalidomide 10mg [n=7]; G4: lenalidomide plus chemotherapy [n=3]). Serum creatinine and eGFR were determined before lenalidomide and after 1, 3 and 6 months. RI was assessed by NKDOQI- and MM-response according to EBMT-criteria.
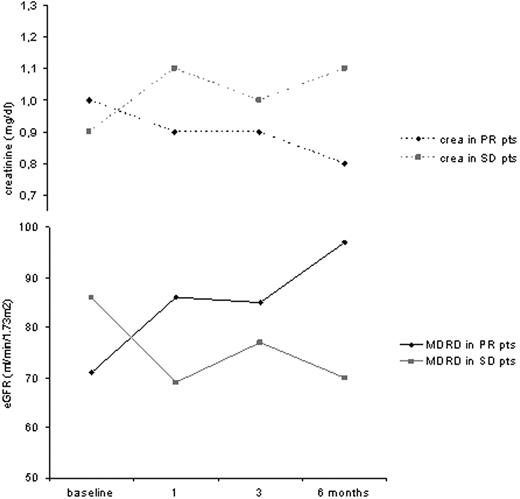
The median pt age was 67 years (range; 44-78), with most having stage II/III disease by Durie&Salmon (97%; ISS II/III: 75%). IgG-myeloma and normal cytogenetics were present in 84% and 56%, respectively. Pretreatment was considerable with ≥2 previous therapy lines in 71% and autologous or allogeneic stem cell transplantations performed in 62% and 12%, respectively. Median β2-MG- and hemoglobin-levels were 3.4mg/dl and 11.3mg/dl, respectively. Before lenalidomide-initiation, RF appeared normal with median creatinine levels of 1.0mg/dl (range; 0.6-2.7), nevertheless, mild RI was readily detectable via eGFR (81ml/min/1.73m2, range; 27-119). Of note, mild (eGFR<90) and moderate RI (eGFR<60) before lenalidomide-initiation was prominent in 65% and 31% of pts, respectively. In pts achieving a PR due to lenalidomide treatment, median creatinine-values before and during treatment (1, 3 and 6 months) decreased from 1.0mg/dl to 0.9, 0.9 and 0.8mg/dl, which was even more prominently detectable via eGFR with 71 at baseline, increasing to 86, 85 and 97ml/min/1.73m2, respectively. Pts with SD showed creatinine-values before and during treatment (1, 3 and 6 months) of 0.9 at baseline, increasing to 1.1, 1.0 and 1.1mg/dl, whereas eGFR changed from 86 to 69, 77 and 70ml/min/1.73m2, respectively (Fig. 1). With PD, the creatinine increased from 0.9 to 1.3mg/dl, and eGFR values substantially deteriorated from 87 to 61ml/min/1.73m2; this demonstrating that with lenalidomide response, RI recovered and response was readily detected via eGFR-assessment. The median lenalidomide treatment duration lasted 36 weeks (range; 4-96), inducing an ORR (CR/PR) in 31% (n=10), clinical benefit rate (CBR=CR+PR+MR) in 37% (n=12) and stunning disease stabilisation rate (CBR+SD) in 97% (n=31 pts), this comparing favorably with previous reports, albeit our pt cohort was older, more pretreated and bearing substantial comorbidities than in both trials leading to lenalidomide/dex-FDA-approval. Lenalidomide was well tolerated with WHO-CTC-grade (G) ≥2 side effects in 8 pts (25%): 3 showed neutropenia (G2+3), 2 pts skin rash/exanthema (G2), and disorientation (G2), GvHD-exacerbation (G3) and atrial fibrilation (G3) in each one pt.
We highlight the importance to detect RI by means of eGFR-assessment, which allows to identify mild and moderate RI more prominently and reliably than via creatinine determination. Our results underline that lenalidomide in elderly MM pts is feasible and well tolerated. Renal improvement by eGFR analysis was associated with lenalidomide-response which is currently being assessed in even more detail.
Kleber:Celgene: Research Funding. Haas:Celgene: Research Funding. Engelhardt:Celgene: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal