Abstract
Abstract 4255
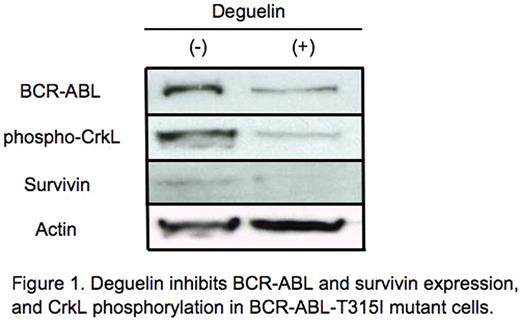
Development of kinase domain mutation is a major drug-resistance mechanism for tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) in cancer therapy. A particularly challenging example is found in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) where TKI STI571 is ineffective against the BCR-ABL mutant, E255K or T315I. Therefore, new agents that effectively kill these cells with kinase domain mutation are absolutely necessary. Deguelin is a rotenoid from African plant Mundulea sericea, which has been recently shown to suppress the lung tumorigenesis via inhibiting the activation of PI3kinase-Akt signaling. More recently, deguelin has been shown to bind to ATP-binding pocket of heat shock protein (Hsp) 90 and inhibit functions of Hsp90 client proteins. However, the effects of deguelin on BCR-ABL mutant transformed cells are poorly understood. We investigated the effects of deguelin on the cell growth and cell death of BaF/3 pre-B-cells transformed with BCR-ABL-wild type (WT), BCR-ABL-E255K and BCR-ABL-T315I (kindly provided by Dr. Kimura, Saga University, Saga, Japan), by trypan-blue exclusion and Annexin V stain. Deguelin inhibited the proliferation of these transformed cells in a time-and a dose-dependent manner (IC50=1.0mM). In addition, flow cytometric analysis revealed a higher frequency of Annexin V(+) cells in deguelin-treated cells (mean ± SD : WT 80.1±15.3%, E255K 82.3±3.5%, T315I 94.0±0.4%, P< 0.05, respectively), compared to that in untreated cells (WT 11.5±1.6%, E255K 11.9±2.0%, T315I 15.3±4.8%, respectively). These results indicate that deguelin induces the cell-growth arrest and cell death in these cells. To better understand the mechanism of these effects, we examined the intracellular signaling and the expression of apoptosis associated proteins by immunoblot analysis. We found that deguelin suppressed BCR-ABL protein expression and prevented CrkL phosphorylation in these cells. In addition, the inhibitor of apoptosis protein, survivin expression was decreased at 24 hours after deguelin treatment. These results suggested that deguelin suppresses BCR-ABL and survivin expression, and inhibits CrkL phosphorylation in BCR-ABL mutant and WT cells. Since deguelin has been shown to inhibit the function of Hsp90 client proteins, deguelin may destabilize BCR-ABL and survivin by inhibiting Hsp90 function. Taken together, deguelin appears to induce cell growth arrest and apoptosis of BCR-ABL mutant and WT transformed cells via the suppression of BCR-ABL and survivin expression. Thus, deguelin merits further investigation as a potential therapeutic agent for CML with T315I ABL mutation.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal