Abstract
Abstract 2778
Poster Board II-754
Interstitial deletions involving the long arm of chromosome 5, one of the good prognostic factors, are the most common chromosomal abnormality either as a sole or in combination with other abnormalities in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). However, the prognostic impact of del(5q) accompanied by additional chromosome abnormalities remains controversial. We investigated the hematologic, cytogenetic and prognostic features of del(5q) in MDS. Also, we mapped the deleted region on 5q by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), whether the difference of deleted region between 5q- syndrome and MDS with del(5q) accompanied by additional abnormalities makes the clinical and prognostic differences.
137 adult patients, newly diagnosed as de novo MDS in Seoul National University Hospital from April 2000 through March 2009, were enrolled. We reclassified MDS subtypes according to WHO classification 2008. To compare the hematologic, cytogenetic and prognostic features according to presence of del(5q), we categorized the patients with del(5q) into 3 groups: patients with additional chromosomal abnormalities with del(5q) as 'MDS with del(5q)'; patients with other chromosomal abnormalities other than del(5q) as 'MDS with other chromosomal abnormalities (CA)'; and patients with isolated del(5q) as '5q- syndrome'. Also, the mapping with FISH for EGR1, CSF1R, and PDGFRβ on 5q, was performed in conjunction with G-banding to all patients and additional 16 patients with alleged del(5q) by G-banding from Korean MDS working party.
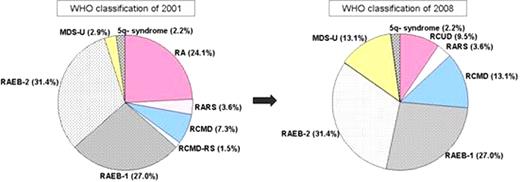
According to the new WHO classification of 2008, the 33 refractory anemia patients according to the previous WHO classification of 2001 were reclassified into refractory cytopenias with unilineage dysplasia (13 patients), refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia (six patients) and MDS - unclassified (14 patients) (Fig 1). The median age of Korean MDS was 59 years, and the frequencies of 5q- syndrome and 5q deletion was 2.2% (3/137 patients) and 15.3%, respectively. Among 137 patients, 17 patients were grouped into 'MDS with del(5q)', and 53 patients into 'MDS with other CA'. The 'MDS with del(5q)' were significantly older and showed higher % of blasts in PB and BM than 'MDS with other CA'. And, they were categorized into higher risk group according to the International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) (Table 1). As a results of mapping for EGR1, PDGFRβ and CSF1R, deletion of all 3 regions was 93.3% in patients of 'MDS with del(5q)' and 66.7% in patients of '5q- syndrome', showing no difference in deleted genes between the two groups. Half (53%) of patients of 'MDS with del(5q)' accompanied complex abnormalities including chromosome 7 abnormalities. The del(5q) was detected only by FISH, showing discrepant results between G-banding and FISH analysis. Especially, marker chromosomes by G-banding in some patients were proved to be chromosome 5 with del(5q) by FISH.
Change of the frequency in MDS subtypes according to change of the WHO classification from 2001 to 2008.
Change of the frequency in MDS subtypes according to change of the WHO classification from 2001 to 2008.
The hematologic, cytogenetic and prognostic features between 'MDS with del(5q)' and 'MDS with other CA'
| °° . | MDS with del(5q) . | MDS with other CA . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cases | 17 | 53 | |
| Age (yrs), mean | 62 | 51 | 0.013 |
| Male:Female | 8:9 | 35:18 | NS |
| (47.1%):(52.9%) | (66.0%):(34.0%) | ||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL), mean | 7.4 | 8.6 | NS |
| ANC (/μL), mean | 2168 | 1016 | NS |
| Platelet (k/μL), mean | 84 | 113 | NS |
| Blasts (%), mean | |||
| PB | 3.7 | 1.2 | 0.048 |
| BM | 11.2 | 5.9 | 0.001 |
| Cytogenetic group (IPSS) | <0.001 | ||
| Good | 0 ( 0.0%) | 3 ( 5.7%) | |
| Intermediate | 3 (17.6%) | 38 (71.7%) | |
| Poor | 14 (82.4%) | 12 (22.6%) | |
| Risk Group (IPSS) | <0.001 | ||
| Low | - | - | |
| Intermediate-1 | 1 ( 5.9%) | 29 (54.7%) | |
| Intermediate-2 | 5 (29.4%) | 14 (26.4%) | |
| High | 11 (64.7%) | 10 (18.9%) | |
| °° | °° | °° | °° |
| °° . | MDS with del(5q) . | MDS with other CA . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cases | 17 | 53 | |
| Age (yrs), mean | 62 | 51 | 0.013 |
| Male:Female | 8:9 | 35:18 | NS |
| (47.1%):(52.9%) | (66.0%):(34.0%) | ||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL), mean | 7.4 | 8.6 | NS |
| ANC (/μL), mean | 2168 | 1016 | NS |
| Platelet (k/μL), mean | 84 | 113 | NS |
| Blasts (%), mean | |||
| PB | 3.7 | 1.2 | 0.048 |
| BM | 11.2 | 5.9 | 0.001 |
| Cytogenetic group (IPSS) | <0.001 | ||
| Good | 0 ( 0.0%) | 3 ( 5.7%) | |
| Intermediate | 3 (17.6%) | 38 (71.7%) | |
| Poor | 14 (82.4%) | 12 (22.6%) | |
| Risk Group (IPSS) | <0.001 | ||
| Low | - | - | |
| Intermediate-1 | 1 ( 5.9%) | 29 (54.7%) | |
| Intermediate-2 | 5 (29.4%) | 14 (26.4%) | |
| High | 11 (64.7%) | 10 (18.9%) | |
| °° | °° | °° | °° |
Abbreviations: ANC, absolute neutrophil count; IPSS, International Prognostic Scoring System; NS, not significant
The biologic and prognostic features of MDS in Korea seem to be markedly different from those of Caucasian; younger age and low frequency of 5q- syndrome. The incidence of complex cytogenetic abnormalities including del(5q) was higher than that of Caucasian, while that of isolated del(5q) was quite low in Korea, which can explain that higher proportion of MDS with del(5q) belongs to higher risk IPSS group. And, we suggest FISH for del(5q) at initial diagnosis and during follow-up after treatment of MDS with alleged del(5q), since the presence of del(5q) in MDS is important for choosing the lenalidomide treatment.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal