Abstract
Abstract 206
Lenalidomide is an immunomodulatory agent that has clinical activity in CLL. In patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory CLL treatment with single agent lenalidomide induces an overall response rate of 32–47% when used as monotherapy (Chanan-Khan A.A. et al. 2006; Ferrajoli A. et al. 2008). Rituximab has modest activity as monotherapy, but significally synergizes with chemotherapy agents when administered to pts with CLL. The addition of rituximab to lenalidomide resulted in clinical responses in a small number of pts with CLL that had progressed while on lenalidomide monotherapy (Chanan-Khan A.A. et al. 2006). Because lenalidomide stimulates NK cell proliferation (Wu et al. 2008) we hypothesized that lenalidomide will enhance the activity of rituximab.
We, therefore, designed a phase II study to evaluate the combination of lenalidomide and rituximab in pts with relapsed CLL.
Pts with CLL and active disease were eligible if they had received prior treatment with purine analog-based therapy. Standard inclusion criteria were required in terms of organ function and performance status, and pts with any ANC or platelet count were eligible.
All pts received rituximab (375 mg/m2) intravenously on days 1, 8, 15 and 22 of cycle 1, and then once every 4 weeks during cycles 3–12. Lenalidomide was given orally at the dose of 10 mg/day starting on day 9 of cycle 1 and continued daily for 12 cycles. Each cycle consisted of 28 days of treatment. During the first two weeks of therapy, allopurinol at the dose of 300 mg daily was prescribed as prophylaxis for tumor lysis.
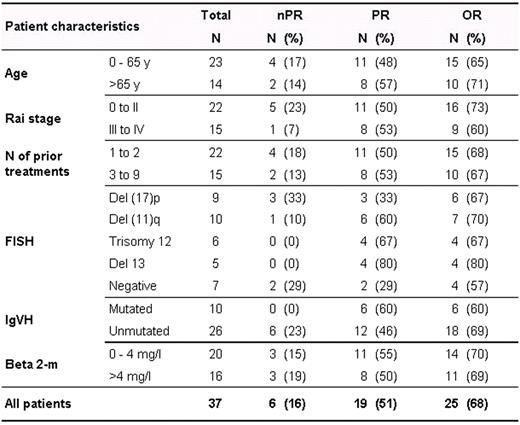
Sixty pts were accrued between October 2008 and July 2009. Thirty-seven pts have received treatment for at least 6 cycles and are evaluable for response and toxicity. The median age is 59 yrs (range 44–83), 15 pts (41%) have Rai stage III-IV disease and the median beta-2M level was 3.6 mg/dL (1.5–9). The median number of prior treatments was 2 (1–9), 9 pts (24%) were refractory to fludarabine and all pts had received prior rituximab. Twenty-six pts (70%) had unmutated IgVH, 9 pts (24%) had chromosome 17p deletion and 10 pts (37%) had 11q deletion by FISH analysis.
After 6 cycles of treatment, 25 pts achieved a response [6 nodular PR (16%), 19 PR (51%)] for an OR of 68% (according to 1996 NCI-WG criteria). Six pts (16%) attained stable disease or clinical improvement and are continuing on treatment, and 6 pts (16%) failed to respond, including one death that occurred on day 34 owing to infectious complications. Responses according to pts characteristics are summarized in the table:
Most common grade 3–4 treatment related adverse events observed were: neutropenia (16 pts, 43%), fatigue (6 pts,16%) and thrombocytopenia (4 pts, 11%). One pt (3%) developed grade 3 tumor lysis syndrome and 1 pt (3%) had grade 3 joint pain. Infectious complications occurred in 9 pts (24%): neutropenic fever (6 pts), pneumonia (2 pts) and urosepsis (1 pt). Lenalidomide-associated tumor flare reaction was limited to grade 1 (8 pts, 22%) and grade 2 (1 pt, 3%).
We examined the effect of therapy with lenalidomide and rituximab on the distribution of circulating B, T, and NK cell subsets. When compared to the baseline, there were significant decreases in the percentage of CD19+CD20+ B cells along with significant increases in the percentages of CD4+ T, CD8+ T, CD4+CD25hiCD127− regulatory T, and CD3−CD16+CD56+ NK cells after 3 cycles of therapy (paired sample t test).
In conclusion, our results suggest that the combination of lenalidomide and rituximab is superior to single agent lenalidomide, despite all our pts having received prior rituximab. Additionally, there was no increase in toxicity and lenalidomide-associate tumor flare reaction was less frequent and less severe with this combination compared to single agent lenalidomide.
Ferrajoli:Celgene: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding. Off Label Use: The use of Lenalidomide for the treatment of CLL is considered investigational.. O'Brien:Celgene: Consultancy; Genentech: Research Funding. Wierda:Genentech: Honoraria; Celgene: Speakers Bureau. Keating:Celgene: Data Monitoring Committee, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal