Abstract
Abstract 1952
Poster Board I-975
Vitamin D is a naturally occurring steroid hormone. In addition to its well-established role in maintaining serum calcium homeostasis, vitamin D has effects on cellular differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis. Vitamin D3 is naturally produced in skin in response ultraviolet-B (UVB) radiation from the sun. Several recent studies, however, have shown that a high proportion of community-dwelling subjects in both tropical and temperate climates are deficient in vitamin D, and that subjects in northern latitudes often require dietary supplementation to maintain vitamin D sufficiency. Further, several reports now suggest that vitamin D sufficiency is protective against the development of several cancers, including non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). However, it is not known whether vitamin D impacts prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common NHL subtype.
We evaluated serum vitamin D concentrations in two cohorts of DLBCL patients. The first cohort consisted of 374 patients newly diagnosed from September 2002-February 2008 who were prospectively enrolled in the University of Iowa/Mayo Clinic Lymphoma SPORE Molecular Epidemiology Resource, an observational study in which neither therapeutic nor diagnostic management is prescribed. All serum was obtained within 120 days of diagnosis, and was prior to treatment in 221 (59%). In the second study, 62 patients newly diagnosed from February 2006-August 2007 were enrolled on NCCTG clinical trial N0489, and all serum was obtained before the first course of therapy. Central pathology review was performed on all patients to confirm the diagnosis of DLBCL. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin (25-OH-VitD) levels were measured by the gold standard method for vitamin D determination: liquid chromatography tandem mass spectroscopy (LC-MS/MS). Vitamin D deficiency was defined as total serum 25-OH-VitD < 25 ng/mL (62.5 nmol/L). SPORE patients were followed per a standard protocol for event-free (progression, retreatment, or death due to any cause) and overall survival (EFS and OS, respectively); N0489 patients were followed in a similar way per the clinical trial protocol. We used Cox regression to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
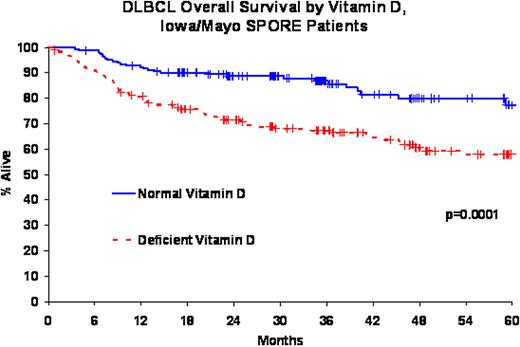
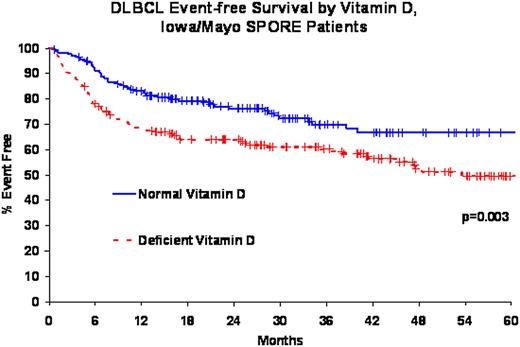
SPORE patients were primarily treated with immunochemotherapy (83%); all N0489 patients were treated with epratuzumab + R-CHOP21. The median age at diagnosis was 62 years (range, 19-93) for SPORE patients and 61 years (range, 21-82) for N0489 patients. Median follow-up for SPORE patients was 36 months (range, 1-77) with 95 deaths and 131 events; median follow-up for N0489 patients was 24 months (range, 7-39) with 13 deaths and 18 events. Vitamin D deficiency was identified in 188 SPORE patients (50%) and 15 N0489 patients (24%). There were no differences in the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency by age, IPI, or whether serum was obtained prior to starting treatment (all p > 0.28). Vitamin D deficiency was associated with inferior overall (HR=2.33, 95% CI 1.53-3.57, logrank p = 0.0001) and event-free survival (HR=1.71, 95% CI 1.20-2.44, logrank p = 0.003) in the SPORE cohort. These associations remained significant after adjusting for IPI and treatment: OS HR=1.97, 95% CI 1.27-3.07; EFS HR=1.47, 95% CI 1.02-2.21. These results were similar for the subset of SPORE patients who were treated with R-CHOP. The HRs for vitamin D deficiency and event-free survival were consistent in the N0489 patients (HR=1.63, 95% CI 0.61-4.35, IPI adjusted HR=1.43, 95% CI 0.53-3.85), although these results lacked precision due to a smaller sample size. We were unable to evaluate OS in N0489 due to the small number of deaths.
Approximately 50% of all DLBCL patients in this northern US latitude population are vitamin D deficient at the time of diagnosis and treatment. Vitamin D deficient patients have an inferior event-free and overall survival compared to patients with vitamin D levels within the normal range. Vitamin D supplementation during treatment of DLBCL patients with vitamin D deficiency should be evaluated in a clinical trial setting.
| Cohort . | Serum 25-OH-VitD levels (ng/mL) . | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| <10 (severe deficiency) . | 10 – 24 (mild to moderate deficiency) . | 25 – 80 (optimal levels) . | |
| SPORE | 29 (8%) | 159 (43%) | 186 (50%) |
| N0489 | 2 (3%) | 13 (21%) | 47 (76%) |
| All DLBCL | 31 (7%) | 172 (39%) | 233 (53%) |
| Cohort . | Serum 25-OH-VitD levels (ng/mL) . | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| <10 (severe deficiency) . | 10 – 24 (mild to moderate deficiency) . | 25 – 80 (optimal levels) . | |
| SPORE | 29 (8%) | 159 (43%) | 186 (50%) |
| N0489 | 2 (3%) | 13 (21%) | 47 (76%) |
| All DLBCL | 31 (7%) | 172 (39%) | 233 (53%) |
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal