Abstract
Abstract 1878
Poster Board I-900
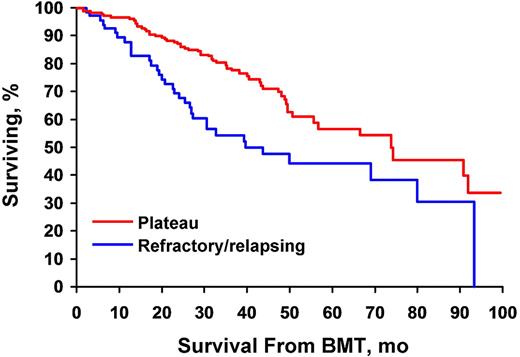
Autologous stem cell transplant as a platform for multiple myeloma treatment is the standard of care for patients who can safely withstand the procedure. Before novel agents were introduced, one-third to one-half of patients did not achieve partial response at transplant. Previously published medical literature has showed that in this past era, absence of initial response to induction therapy had no impact on progression-free survival and overall survival after high-dose therapy. Lack of response to initial induction did not preclude a good response after stem cell transplant. With the introduction of novel agents—immunomodulatory drugs and proteasome inhibitors—response rates with initial therapy are now between 70% and 100%. This retrospective study analyzes progression-free survival and overall survival in patients who do not have a partial response after induction therapy with a regimen that contains a novel agent. Unlike patients in reports published previously—before novel agents—patients who do not achieve partial remission have a significantly shorter overall survival from transplant (74.0 vs 43.5 months) and a shorter progression-free survival (22.6 vs 13.1 months; P<.001). Absence of a response to induction therapy with a novel agent predicts a poorer outcome after high-dose therapy.{abstabft}.b CR+VGPR for plateau, P<.001 compared with other 3 categories.
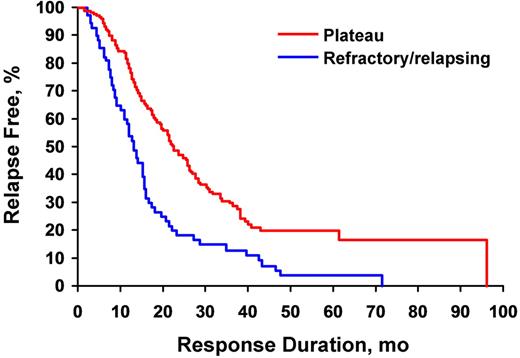
Failure to respond to novel-agent induction leads to shorter posttransplant progression-free survival (PFS).
Multivariable Analysis of Posttransplant Progression-Free Survival
| Variable . | P Value . |
|---|---|
| Plateau vs relapsed-refractory | .003 |
| Albumin | .86 |
| Sex | .94 |
| b2-Microglobulin | .89 |
| Bone marrow plasma cells | .18 |
| Age | .75 |
| Abnormal cytogenetics | .002 |
| CTX mobilization | .51 |
| Labeling index | .002 |
| Variable . | P Value . |
|---|---|
| Plateau vs relapsed-refractory | .003 |
| Albumin | .86 |
| Sex | .94 |
| b2-Microglobulin | .89 |
| Bone marrow plasma cells | .18 |
| Age | .75 |
| Abnormal cytogenetics | .002 |
| CTX mobilization | .51 |
| Labeling index | .002 |
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal