It is said that there are more than 400 blood group antigens on the red blood cell and of these, about 40 have known clinical significance. Significance in this context refers to transfusion-related concerns, typically meaning the ability of an antibody, when in proximity to the cognate antigen, to cause hemolysis—intravascularly, extravascularly or in utero (as in transfusion reactions or hemolytic disease of the newborn). More recently using precise molecular methods, investigators have been able to ascertain and assign biologic functionality and thus clinical significance to a number of blood group antigens, now including Pk.
Pk or Gb3 is a member of the GLOB collection which includes P, Pk, and LKE. Pk is related to the P blood group system discovered by Landsteiner and Levine in 1927 and has its name “as it was the first letter following M, N and O, which had already been used.”1 p76 Biochemically, Pk is Galα(1-4)GalB(1-4)Glc-CER (synthesized from lactosylceramide [or GalB(1-4)Glc-CER] by the sequential addition of galactose via α(1-4) galactosyltransferase encoded in the Pk gene), which when acted upon by the enzyme encoded by the presence of the P gene becomes P.1 Alternatively, lactoslyceramide can be modified to P1 via less understood reactions. In addition to the presence of Pk on erythrocytes, this antigen is also found on epithelial cells, monocytes, and B cells where it takes on the designation of CD77. Importantly, while P1 is found in approximately 80% of whites, Pk is found in only about 1 in a million.
Previously, this group has shown: (1) an accumulation of Pk, in patients with Fabry disease due to reduced α-galactosidase conferred resistance to R5 HIV-1,2 and (2) a soluble analog of Pk inhibits HIV infection in vitro.3 The current report also builds on the report of Fantini et al, demonstrating that HIV-infected mononuclear cells have increased Pk expression.4
It is upon this background that Lund et al assessed the susceptibility to HIV-1 of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from blood donors high in Pk (the P1k phenotype) compared with those with essentially no Pk expression (the p phenotype), and in HeLa and Jurkat cells modified to alter levels of Pk expression.5
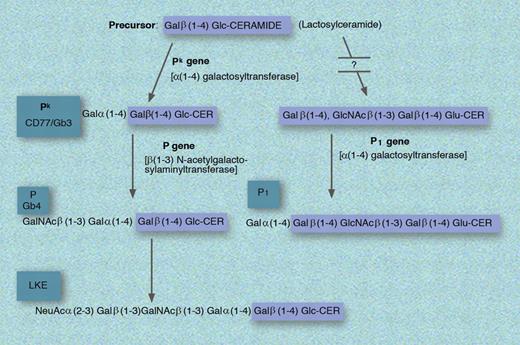
Biosynthesis of the P1, Pk, P, and LKE antigens. GLU indicates glucose; and CER, ceramide. Professional illustration by Marie Dauenheimer.
Biosynthesis of the P1, Pk, P, and LKE antigens. GLU indicates glucose; and CER, ceramide. Professional illustration by Marie Dauenheimer.
The results were significant. P1k cells were protected from R5 and X4 HIV-1 infection and had increased CD4, coreceptor, and Pk expression, while PBMCs with the p phenotype had heightened susceptibility to R5 and X4 HIV-1 infection. Further supporting a role for Pk was that Pk -liposome fusion in Jurkat cells decreased susceptibility to HIV and cells transduced with Pk -synthase (augmenting Pk expression) showed decreased HIV-1 infectability, while Pk depletion or Pk-synthase gene silencing promoted HIV infection.
Mechanistically, it may prove to be that the Pk effect is due to altered lipid raft formation and/or HIV receptor or coreceptor localization, function, or accessibility. Alternatively or perhaps additionally, Pk may be critical to viral internalization.
That Pk and indeed other blood groups have a more defined role in host-microbial infection is an important new finding. Other examples include Fya as the binding epitope for plasmodium6 and the P antigen as a receptor for the B19 parvovirus.7 With this discovery, Pk adds to our list of genetic polymorphisms that individually and/or in concert contribute to HIV resistance/susceptibility and potentially generates a site for possible future therapeutic use.8
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The author declares no competing financial interests. ■

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal