Cremophor (polyoxyethylated castor oil; BASF, Florham Park, NJ) is a nonionic surfactant that is used for solubilization of paclitaxel. Laboratory artifacts such as hyperlipidemia, rouleaux, red cell aggregation, thrombocytosis, and normocytic normochromic anemia can be associated with the use of Cremophor. Cremophor can be detected in plasma 24 hours after infusion, depending on the length of paclitaxel infusion.
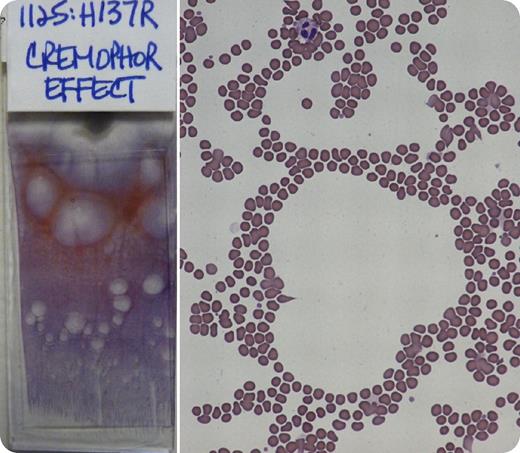
A patient received paclitaxel 1 day prior to blood testing. The automated hematology analyzer (CELL-DYN Sapphire; Abbott Diagnostics, Abbott Park, IL) rejected the complete blood count results because of “resistant RBCs.” Accurate results were subsequently obtained using the “resistant RBC” analysis mode. When a blood smear was made, large clear areas developed on the smear (see left image). Microscopic review showed circular gaps between the red cells (see right image) as well as rouleaux formation and red cell aggregates.
Laboratory artifacts associated with Cremophor use should be recognized to avoid unnecessary additional testing or incorrect diagnoses. Misleading surfactant effects can be anticipated when patients have received a hydrophobic drug that is solubilized in nonionic surfactants, such as Cremophor. Some of these hydrophobic drugs include anesthetics, sedatives, immunosuppressives, sensitizers, antineoplastics, and antifungals.
Cremophor (polyoxyethylated castor oil; BASF, Florham Park, NJ) is a nonionic surfactant that is used for solubilization of paclitaxel. Laboratory artifacts such as hyperlipidemia, rouleaux, red cell aggregation, thrombocytosis, and normocytic normochromic anemia can be associated with the use of Cremophor. Cremophor can be detected in plasma 24 hours after infusion, depending on the length of paclitaxel infusion.
A patient received paclitaxel 1 day prior to blood testing. The automated hematology analyzer (CELL-DYN Sapphire; Abbott Diagnostics, Abbott Park, IL) rejected the complete blood count results because of “resistant RBCs.” Accurate results were subsequently obtained using the “resistant RBC” analysis mode. When a blood smear was made, large clear areas developed on the smear (see left image). Microscopic review showed circular gaps between the red cells (see right image) as well as rouleaux formation and red cell aggregates.
Laboratory artifacts associated with Cremophor use should be recognized to avoid unnecessary additional testing or incorrect diagnoses. Misleading surfactant effects can be anticipated when patients have received a hydrophobic drug that is solubilized in nonionic surfactants, such as Cremophor. Some of these hydrophobic drugs include anesthetics, sedatives, immunosuppressives, sensitizers, antineoplastics, and antifungals.
Many Blood Work images are provided by the ASH IMAGE BANK, a reference and teaching tool that is continually updated with new atlas images and images of case studies. For more information or to contribute to the Image Bank, visit www.ashimagebank.org.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal