Abstract
Inadequate hepcidin synthesis leads to iron overload in HFE-related hemochromatosis. We explored the regulation of hepcidin by iron in 88 hemochromatosis patients (61 C282Y/C282Y, 27 C282Y/H63D) and 23 healthy controls by analyzing urinary hepcidin before and 24 hours after a 65-mg oral iron dose. Thirty-four patients were studied at diagnosis and had iron overload, and 54 patients were iron depleted. At diagnosis, hepcidin values in C282Y homozygotes were similar to controls, whereas values in C282Y/H63D heterozygotes were higher (P = .02). However, the hepcidin/ferritin ratio was decreased in both homozygotes (P < .001) and heterozygotes (P = .017), confirming the inadequate hepcidin production for the iron load with both genotypes. In iron-depleted patients of both genotypes studied at a time remote from phlebotomy, basal hepcidin was still lower than in controls (P < .001 for C282Y/C282Y and P = .002 for heterozygotes). After an iron challenge, mean urinary hepcidin excretion increased in controls (P = .001) but not patients, irrespective of genotype and iron status. Significant hepcidin increase ( ≥ 10 ng/mg creatinine) was observed in 74% of controls, 15% of homozygotes, and 32% of heterozygotes. The hepcidin response to oral iron is blunted in HFE-related hemochromatosis and not improved after iron depletion. The findings support the involvement of HFE in iron sensing and subsequent regulation of hepcidin.
Introduction
Hereditary hemochromatosis (HH) is an autosomal recessive disorder of systemic iron regulation in which dietary iron absorption is inappropriately high. In some patients this may lead to progressive iron loading and damage to the liver and other parenchymal organs. Most patients of Northern European ancestry are homozygous for the C282Y mutation of the HFE gene, and a minority are compound heterozygotes for the C282Y/H63D mutations. Other HFE or other gene mutations are rare1 . Newly available molecular tests have made it possible to accelerate the diagnosis to a preclinical stage and avoid the need for liver biopsy. In the preclinical stage, most patients display only alterations of iron parameters and/or of liver function tests.2 Although the C282Y/C282Y genotype is frequent, the clinical disease is relatively uncommon, and its natural history is not well defined. Disease expression may be influenced by age, sex, environmental, and genetic modifiers.3-5 No progression to clinical disease was reported in 2 prospective studies on a small number of C282Y homozygotes followed up for 17 and 25 years, respectively.6,7 These observations suggest that among subjects with at-risk genotypes, only a subgroup develop enough iron overload to induce clinical complications. Since it is not feasible to predict the outcome of patients based only on blood iron studies, it is common clinical practice that all HFE mutated individuals with altered iron parameters undergo iron depletion by phlebotomy.
Iron overload in all genetic types of hemochromatosis, except those due to ferroportin mutations, is explained by the insufficiency of the hepatic peptide hepcidin,8 the key regulator of systemic iron homeostasis. Hepcidin binds to the iron exporter ferroportin, causes its internalization and degradation, and thereby inhibits the flow of iron from duodenal enterocytes and macrophages into plasma.9 Decreased hepcidin production thus results in increased intestinal absorption of iron and systemic iron overload. Deficient/inadequate liver hepcidin mRNA levels have been documented in HFE patients10-12 and in animal models of HFE-related hemochromatosis.13,14
Hepcidin production is increased in response to elevated plasma and tissue iron. In preliminary experiments in normal adults, hepcidin excretion increased markedly 24 hours after the ingestion of a small dose (65 mg) of iron as ferrous sulfate, indicating a rapid hepatic response to iron, most likely in the form of transiently increased holotransferrin.15 We hypothesized that, irrespective of the variable basal level, hemochromatosis patients may have a decreased hepcidin response to oral iron. In this study, we measured iron parameters and urinary hepcidin excretion in response to acute oral iron challenge in HFE patients at diagnosis or after iron depletion and compared it to the response in healthy subjects.
Patients, materials, and methods
Patients and controls
All patients and controls were residents of Italy and were enrolled in one of the following centers: Università Vita-Salute Istituto Scientifico San Raffaele, Milano; Dipartimento Medicina Clinica e Prevenzione Università Milano-Bicocca, Azienda Ospedaliera San Gerardo, Monza; Dipartimento di Medicina Clinica e Sperimentale, Università di Verona, Policlinico G.B. Rossi.
The study protocol was approved by the ethical committees of all the institutions. Informed consent was obtained from all patients and controls in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
The protocol included adult hemochromatosis patients of both sexes who at diagnosis had transferrin saturation (TS) of at least 45% and/or serum ferritin (SF) more than 200 ng/mL in females and more than 300 ng/mL in males. HFE genotypes were either C282Y homozygotes or C282Y/H63D compound heterozygotes. Since hepcidin production is suppressed by erythropoiesis expansion16,17 and stimulated by inflammation,15,18 exclusion criteria were anemia, including beta-thalassemia trait, inflammatory conditions/infections, coincidental chronic B and C viral hepatitis, pregnancy, heavy alcohol intake, and other known iron-loading disorders. Controls were volunteer subjects with normal iron parameters.
None of the participants took any medication known to affect iron absorption (proton pump inhibitors or anti-H2 receptors) during the study.
Patients were divided into 2 groups: group A included patients studied at diagnosis, and group B were iron-depleted patients studied in steady state at a minimal time delay of 30 days from the last phlebotomy.
After medical evaluation and routine laboratory tests (CBC, transferrin saturation, serum ferritin), on day 1 patients collected first-morning urines (50 mL) and ingested 65 mg oral iron as ferrous sulfate (iron, 65 mg, CVS Pharmacy). On day 2, first-morning urines were collected and blood samples obtained to repeat measurements of serum iron, transferrin and serum ferritin.
Methods
Transferrin saturation and serum ferritin were measured by standard methods. For patient group B, the amount of iron removed by phlebotomy (in grams) was calculated as previously reported.19
Urinary hepcidin measurement
After collection, urines were preserved with 0.01% sodium azide and stored in a 50-mL polypropylene tube frozen at −20°C until shipping on dry ice to UCLA.
Urinary creatinine concentrations were measured by UCLA Clinical Laboratories. Urinary hepcidin was determined as described.20 Briefly, cationic peptides were extracted from urine using CM Macroprep (BioRad, Hercules, CA), eluted with 5% acetic acid, lyophilized, and resuspended in 0.01% acetic acid. Urinary hepcidin concentrations were determined by immuno-dot assay. Urine extracts equivalent to 0.1 to 0.5 mg of creatinine were dotted on Immobilon P membrane (Millipore, Bedford, MA) along with a range of synthetic hepcidin standards (0-80 ng). Hepcidin was detected on the blots using rabbit antihuman hepcidin antibody with goat antirabbit horseradish peroxidase as second antibody. Dot blots were developed by chemiluminescent detection method (SuperSignal West Pico Chemiluminescent Substrate; Pierce, Rockford, IL) and quantified with the Chemidoc cooled camera running Quantity One software (BioRad). Hepcidin concentration was expressed as ng hepcidin/mg creatinine.
Statistical analysis
All calculations were performed with SSPS 13.0 statistical package (SPSS, Chicago, IL). Logarithmic transformation was performed on all skewed variables. Hence, data are presented as geometric means with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Quantitative data were assessed using the Student t test. Correlations between quantitative variables were assessed using Pearson correlation test, and P value < .05 was considered significant.
Results
Patients and controls
From February 2005 to January 2007, 94 patients and 24 controls were enrolled in the study. Eighty-eight patients (69 males and 19 females) with either C282Y homozygous or C282Y/H63D compound heterozygous genotype were eligible for the analysis, as well as 23 controls with wild-type or H63D heterozygous HFE genotype. Their clinical and hematological parameters are presented in Table 1.
Characteristics of patients and controls at the test time, unless otherwise specified
| . | Controls, n = 23 . | Cases, n = 88 . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A, n = 34 . | Group B, n = 62* . | ||||
| C282Y/C282Y, n = 19 . | C282Y/H63D, n = 15 . | C282Y/C282Y, n = 46 . | C282Y/H63D, n = 16 . | ||
| Sex, M/F | 19/4 | 12/7 | 12/3 | 36/10 | 15/1 |
| Mean age, y (±SD) | 36 (±10)† | 45 (±14) | 46 (±15) | 50 (±13) | 51 (±13) |
| Hb, g/L | 147 (142-153) | 148 (143-152) | 149 (143-155) | 149 (146-152) | 150 (144-156) |
| Basal TS, % | 26.3 (23.7-29.1) | 84.1 (78.9-89.5) ‡ | 48.4 (41.4-56.6) | 38.6 (34.2-43.6) | 34.1 (27.9-41.6) |
| Basal SF, μg/L | 85.7 (60.9-120.6) | 734.4 (437.7-1232) | 567.9 (415-777) | 29.5 (24.8-35) | 54 (43.5-67.2) |
| Iron removed, g | — | — | — | 4.98 (3.9-6.1)‡ | 2.56 (2.1-3.2) |
| TS at diagnosis, % | — | — | — | 79.6 (75-84)‡ | 52.7 (45.7-60.7) |
| SF at diagnosis, μg/L | — | — | — | 897.4 (691.1-1165) | 667.3 (569.3-782.3) |
| . | Controls, n = 23 . | Cases, n = 88 . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A, n = 34 . | Group B, n = 62* . | ||||
| C282Y/C282Y, n = 19 . | C282Y/H63D, n = 15 . | C282Y/C282Y, n = 46 . | C282Y/H63D, n = 16 . | ||
| Sex, M/F | 19/4 | 12/7 | 12/3 | 36/10 | 15/1 |
| Mean age, y (±SD) | 36 (±10)† | 45 (±14) | 46 (±15) | 50 (±13) | 51 (±13) |
| Hb, g/L | 147 (142-153) | 148 (143-152) | 149 (143-155) | 149 (146-152) | 150 (144-156) |
| Basal TS, % | 26.3 (23.7-29.1) | 84.1 (78.9-89.5) ‡ | 48.4 (41.4-56.6) | 38.6 (34.2-43.6) | 34.1 (27.9-41.6) |
| Basal SF, μg/L | 85.7 (60.9-120.6) | 734.4 (437.7-1232) | 567.9 (415-777) | 29.5 (24.8-35) | 54 (43.5-67.2) |
| Iron removed, g | — | — | — | 4.98 (3.9-6.1)‡ | 2.56 (2.1-3.2) |
| TS at diagnosis, % | — | — | — | 79.6 (75-84)‡ | 52.7 (45.7-60.7) |
| SF at diagnosis, μg/L | — | — | — | 897.4 (691.1-1165) | 667.3 (569.3-782.3) |
Data are presented as GM (95% CI) unless specified otherwise.
TS indicates transferrin saturation; SF, serum ferritin; Hb, hemoglobin; and —, not available.
Group B includes 8 patients of group A studied after iron depletion.
P < .01 versus A and P < .001 versus B.
P < .001 versus compound heterozygotes.
Thirty-four patients (19 C282Y homozygotes and 15 C282Y/H63D compound heterozygotes) were newly diagnosed and enrolled in group A. Of these patients, 8 (4 homozygotes and 4 compound heterozygotes) were also enrolled in group B after iron depletion, together with 54 other patients (42 homozygotes and 12 compound heterozygotes). Thus, 62 tests were available for iron-depleted patients. The interval from the last phlebotomy varied from 30 to 365 days (mean, 77 days).
All patients at diagnosis had serum ferritin concentrations higher than 300 μg/L in men and 200 μg/L in women, and transferrin saturation above 45%, except for 8 compound heterozygous patients who had transferrin saturation below 45%. As expected, because of more severe iron loading, treated C282Y homozygotes had significantly more blood removed compared with treated compound heterozygotes (P < .001). All controls had normal serum iron indices and were younger than the hemochromatosis patients. No adverse events or side effects were observed after oral iron administration in patients or in controls.
Basal urinary hepcidin levels
The mean basal hepcidin levels for all patients was 18 ng/mg creatinine (C.I 13.87-23.38), a value significantly lower than in controls (36.44 ng/mg creatinine, 95% CI, 24.3-54.7), but a large variability was observed according to patients' genotype and iron status at the time of the test.
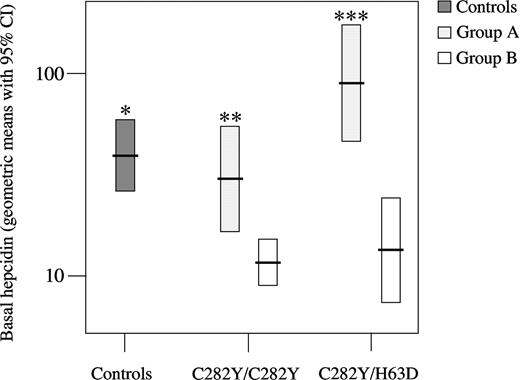
In group A, basal hepcidin levels of C282Y homozygotes were similar to normals, whereas those of compound heterozygotes were slightly higher (P = .02). Among patients, basal hepcidin levels of homozygotes were significantly lower than those of compound heterozygotes (P = .015) (Figure 1). To correct for iron overload, we calculated the baseline hepcidin/ferritin ratio in group A (Figure 2). Hepcidin/ferritin ratio was significantly decreased in both genotypes (P < .0001 for C282Y/C282Y and P = .017 for C282Y/H63D vs controls), confirming that hepcidin production is inappropriate to iron loading in both groups. However, the ratio was significantly lower in homozygotes as compared with compound heterozygotes (P = .006).
Hepcidin basal levels in controls and in patient groups A (at diagnosis) and B (iron-depleted) divided according to genotype. Geometric means with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) are shown. *P < .001 versus all patient group B; **P = .001 versus C282Y/C282Y group B, and P = .015 versus C282Y/H63D group A; ***P < .001 versus C282Y/H63D group B.
Hepcidin basal levels in controls and in patient groups A (at diagnosis) and B (iron-depleted) divided according to genotype. Geometric means with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) are shown. *P < .001 versus all patient group B; **P = .001 versus C282Y/C282Y group B, and P = .015 versus C282Y/H63D group A; ***P < .001 versus C282Y/H63D group B.
Hepcidin/ferritin ratio in controls and in patient group A divided according to genotypes. Geometric means with 95% CIs are shown. *P ≤ .01 versus cases; **P = .006 versus C282Y/H63D
Hepcidin/ferritin ratio in controls and in patient group A divided according to genotypes. Geometric means with 95% CIs are shown. *P ≤ .01 versus cases; **P = .006 versus C282Y/H63D
In group B, mean basal hepcidin levels in both genotypes were significantly lower than in controls (P < .0001 for C282Y/C282Y and P = .002 for C282Y/H63D, Figure 1). Basal hepcidin levels in group B were also lower than in group A considered as a whole (Figure 1), compatible with decreased hepcidin stimulation caused by iron depletion. The hepcidin decrease after iron depletion was significant in both genotypes and more evident in compound heterozygotes who had higher basal levels.
Basal hepcidin was inversely related with transferrin saturation only in patients at diagnosis (r = −0.45, P = .008), likely related to the higher transferrin saturation of C282Y homozygotes compared with compound heterozygotes. No correlation was observed between hepcidin levels and age (including in the control group) or serum ferritin. In iron-depleted patients, no correlation was found between hepcidin levels and time interval (days) from the last phlebotomy.
Hepcidin response to iron challenge
One day after oral iron challenge, mean hepcidin levels increased remarkably in controls (P = .001), but not in patients, irrespective of group and genotype (Table 2). When considering groups A and B separately, there was no significant increase of hepcidin at 24 hours compared with basal hepcidin, and no significant increase when the groups were further divided by genotypes.
Mean hepcidin values before and after iron challenge in different study groups
| . | Baseline hepcidin (ng/mg creatinine) . | 24-hour hepcidin (ng/mg creatinine) . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Controls (n=23) | 36.44 (24.3-54.7) | 86.9 (58.2-129.8) | .001 |
| Cases (n=96) | 18 (13.87-23.38) | 18.3 (14.33-23.4) | NS |
| C282Y/C282Y (n=65) | 13.95 (10.6-18.3) | 13.99 (10.8-18.1) | NS |
| C282Y/H63D (n=31) | 30.8 (17.7-53.6) | 32.2 (19.5-53.1) | NS |
| Group A C282Y/C282Y (n=19) | 27.8 (15.2-50.7) | 24.9 (14.5-42.7) | NS |
| Group A C282Y/H63D (n=15) | 83.4 (42.6-163.2) | 61.4 (31.5-119.6) | NS |
| Group B C282Y/C282Y (n=46) | 10.5 (8.1-13.6) | 11. (8.4-14.4) | NS |
| Group B C282Y/H63D (n=16) | 12.1 (6.6-22) | 17.6 (9.05-34.2) | NS |
| Group A (n=34) | 45.1 (28.3-71.9) | 37 (24.1-56.9) | NS |
| Group B (n=62) | 10.9 (8.6-13.8) | 12.4 (9.6-16.1) | NS |
| . | Baseline hepcidin (ng/mg creatinine) . | 24-hour hepcidin (ng/mg creatinine) . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Controls (n=23) | 36.44 (24.3-54.7) | 86.9 (58.2-129.8) | .001 |
| Cases (n=96) | 18 (13.87-23.38) | 18.3 (14.33-23.4) | NS |
| C282Y/C282Y (n=65) | 13.95 (10.6-18.3) | 13.99 (10.8-18.1) | NS |
| C282Y/H63D (n=31) | 30.8 (17.7-53.6) | 32.2 (19.5-53.1) | NS |
| Group A C282Y/C282Y (n=19) | 27.8 (15.2-50.7) | 24.9 (14.5-42.7) | NS |
| Group A C282Y/H63D (n=15) | 83.4 (42.6-163.2) | 61.4 (31.5-119.6) | NS |
| Group B C282Y/C282Y (n=46) | 10.5 (8.1-13.6) | 11. (8.4-14.4) | NS |
| Group B C282Y/H63D (n=16) | 12.1 (6.6-22) | 17.6 (9.05-34.2) | NS |
| Group A (n=34) | 45.1 (28.3-71.9) | 37 (24.1-56.9) | NS |
| Group B (n=62) | 10.9 (8.6-13.8) | 12.4 (9.6-16.1) | NS |
Data are geometric means with 95% CI by paired t test.
NS indicates nonsignificant.
Based on the first quartile (9 ng/mg creatinine) of basal hepcidin levels in controls, we defined iron challenge responders as those with hepcidin increase of at least 10 ng/mg creatinine and nonresponders as those with hepcidin increase less than 10 ng/mg creatinine. Using this definition, responders constituted 74% of controls, 15% of homozygotes, and 32% of compound heterozygotes in both groups without differences between groups A and B. All responders showed a percent increase greater than 10%, which is greater than the test variability reported for the urinary hepcidin assay.21
There was no correlation between basal and 24 hours transferrin saturation in patients of both groups. In controls, mean transferrin saturation 24 hours after iron challenge was lower than basal transferrin saturation, but the difference was statistically significant (P = .02) only in the group of responders.
Discussion
In normal iron homeostasis, an increase in plasma transferrin saturation raises hepcidin levels.22 Hepcidin then causes the internalization and degradation of the iron exporter ferroportin, which limits further intestinal iron absorption and release from macrophages.9 Pathological situations in which hepcidin synthesis is inadequate result in excessive cell surface expression of ferroportin and increased iron entry into the circulation from the gastrointestinal tract and macrophages. Physiologic regulation of hepcidin depends in part on the normal expression of HFE.13,14 This is the first comprehensive study of hepcidin peptide expression in HFE-hemochromatosis, including both of its main genotypes (C282Y/C282Y and C282Y/H63D). As a simple test to evaluate the homeostatic capacity of the iron-regulatory system in subjects with and without HFE-related hemochromatosis, we measured hepcidin and iron parameters in basal conditions and 24 hours after a single dose of oral iron. The test was well tolerated by patients and controls, and no adverse events were observed.
At diagnosis, basal hepcidin levels in homozygous patients were similar to controls and in compound heterozygotes were higher than in controls, indicating that the latter genotype retains some ability to increase hepcidin production in response to iron load. However, the low hepcidin/ferritin ratio in both genotypes suggests that hepcidin levels were inappropriately low for the iron load. Basal hepcidin in iron-depleted patients was uniformly low in both homozygotes and compound heterozygotes, indicating that the depletion of iron stores decreases the stimulus for hepcidin production even at a time remote from phlebotomy.
The responses to iron challenge were informative. Increased hepcidin production after acute iron challenge was observed in most healthy subjects, confirming previously reported results.9,22 In contrast, hepcidin response to oral iron was blunted in most patients with HFE mutations at diagnosis. This lack of response occurred in patients with either low or “normal” basal hepcidin levels. In addition, mean hepcidin response to iron did not increase after phlebotomy in either HFE genotype, indicating that not only homozygotes but also compound heterozygotes are defective in hepcidin production or that their hepcidin production is already maximal in basal state.
Interestingly, not all healthy subjects responded to the acute iron challenge by increasing hepcidin. This may be due to either the lack of iron absorption or the altered kinetics of hepcidin response. Recent studies in healthy subjects22 showed that the magnitude of hepcidin response was proportional to iron absorption as reflected by the increase in transferrin saturation 5 to 6 hours after iron challenge. We measured transferrin saturation at 24 hours after oral iron, which likely reflects the effect of hepcidin on plasma iron and not the absorption of the test dose. Accordingly, no changes in 24 hours compared with basal transferrin saturation were observed in patients, while a significant reduction was found in responder controls. Documenting an early increase in transferrin saturation after oral iron in HFE patients would increase confidence that the test dose is absorbed. Lin et al also showed that maximal urinary hepcidin response may occur earlier (hepcidin response 8-12 hours after oral iron). Thus, a more detailed time course of hepcidin response to iron challenge in HFE patients and healthy subjects would reveal whether HFE patients also have a kinetic defect in hepcidin response and would establish the optimal timing of the assay.
Translated into molecular pathophysiology, our results indicate that lack of HFE function in hepatocytes not only abrogates the acute iron sensing of transferrin saturation but also nearly abolishes chronic hepcidin increase in response to increased iron stores. This impairment appears to be more severe in homozygous HFE patients compared with the compound heterozygotes.
The lack of acute response in HFE patients implicates HFE as a regulator of hepcidin synthesis. It remains to be determined whether HFE is only involved in the iron-sensing pathway or also in setting baseline hepcidin levels.
As pointed out by the lack of response to oral iron in iron-depleted patients, the removal of excess iron fails to restore the physiological regulation of hepcidin production. Phlebotomy would be expected to elicit a transient increase in erythropoietic activity that could suppress hepcidin and interfere in the assessment of the effect of iron depletion. To avoid this complication, patients were studied at a time remote from the last phlebotomy, and their transferrin saturation and serum ferritin were well above the range of iron deficiency. The data from these patients argue that continued phlebotomy is needed as maintenance treatment, because persistently low hepcidin translates into chronically high intestinal iron absorption. The data from the 8 patients who were tested at diagnosis and then had the test repeated after iron depletion (ie, were members of both groups A and B) raise another potentially important clinical point. Mean basal hepcidin significantly decreased after iron depletion, with patients who reached the lowest transferrin saturation showing the greatest decrease of hepcidin levels. Based on our results in iron-depleted patients, an upward revision of the current target (serum ferritin < 50 μg/L)23 of phlebotomy treatment could be considered in order to increase hepcidin levels, decrease intestinal iron absorption, and allow less frequent maintenance phlebotomies. This hypothesis could be tested in a clinical setting.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
We thank Sara Pelucchi for valuable help in collecting urine samples, and Raffaella Mariani, Alessandra Salvioni, Alessia Riva, and Lucia Malabarba for recruiting patients. We are indebted to Silvano Rossini for advice and assistance.
This work was supported by Telethon Italy grants GGP06213 (D.G.) and GGP05024 (C.C.), Regione Veneto (D.G.), and National Institutes of Health grant RO1 DK 065029 (T.G.) P.T. is partially supported by a grant from the Associazione per lo Studio dell'Emocromatosi, Monza, Italy.
National Institutes of Health
Authorship
Contribution: A.P. and D.G. helped design the study, analyzed the data, and co-wrote the paper. E.N. performed the hepcidin assay, helped design the study, analyzed the data, and co-wrote the paper. P.T., C.B., and E.P. recruited patients and analyzed the data. Y.P. performed the hepcidin assay and analyzed the data. T.G. helped design the study, analyzed the data, and co-wrote the paper. C.C. designed the study and co-wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Prof Clara Camaschella, Università Vita-Salute San Raffaele, Via Olgettina, 60, 20132 Milano, Italy; e-mail:camaschella.clara@hsr.it.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal