Abstract
Goal: Compare results after allogeneic HSCT for AML in CR1 in pediatric population after myeloablative conditioning regimen either based on TBI or busulfan.
Patients and Methods: Retrospective analysis from French registry including all consecutive patients under 18 years of age (n=131) from Dec’1979 and Oct’2004 transplanted for AML in CR1 with either sibling (n=104) or matched unrelated donor and given either multi-fractionated TBI 12Gy and cyclophosphamide 120mg/kg (TBI-Cy) or Busulfan 16mg/kg and Cyclophosphamide 200mg/kg (BuCy200). Results were analysed according to EBMT statistical analysis guidelines i.e. OS and EFS were analyzed by KM method and Log-rank test for comparison where TRM and relapse incidence were analyzed by cumulative incidence method and Gray test for comparison. Multivariate analyses were performed using proportional hazard model for the distribution of competitive risks defined by Fine and Gray.
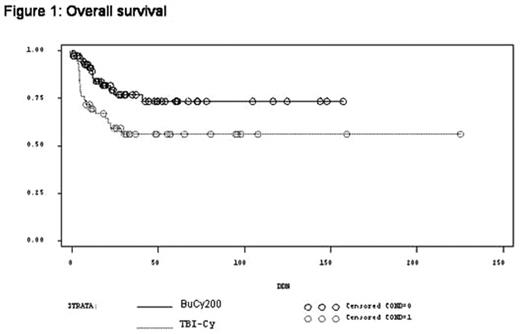
Results: 131 patients (female: 51.5%) were included. Median age at initial diagnosis was 11y (0.5 to 17.8). Median time from diagnosis to transplantation was 4.2 months. Eighty-three patients received BuCy200 and 48 patients were transplanted after TBI-Cy. Patient subgroups were comparable for age, gender, sex mismatch, source of graft (BMT vs PBSC), donor type (geno-identical vs 10/10 matched unrelated donor vs other), cytogenetical analysis and WBC at initial diagnosis, and for donor-recipient CMV status (−/+ vs others). Both 5 year-overall and event-free survival rates appeared significantly better in BuCy200 group than in TBI-Cy group with 73.3% vs 56.1% (p=0.02) and 67+/−7% vs 38+/−9% (p=0.002), respectively. TRM incidence at day 365 was dramatically better in BuCy200 group than in TBI-Cy group with 4,7% vs 26.1% of TRM rate (p=0.002), respectively. Even though there were no statistical significant differences for both acute and chronic GVHD cumulative incidences whatever given conditioning regimen, there was a trend for obtaining lesser GVHD in BuCy200 group: day 100 grade II-IV aGVHD cumulative incidence was 13% vs 37% and 2 year extensive cGVHD was 9 vs 19% for BuCy200 and TBI-Cy group, respectively. At 5 years, there was a trend for less relapse in BuCy200 group than in TBI-Cy 16+/−3% vs 32+/−6% (p=0.09), respectively.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the superiority of BuCy200 on TBI-Cy conditioning regimen for paediatric patients presenting with AML in CR1 and undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from either matched related or unrelated donor. These results, obtained from a larger cohort, confirm and update those published by our group in 1994.
Author notes
Disclosure:Paid Export Testimony Information: From Gilead France. Membership Information: Member of advisory board of Gilead France.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal