Abstract
The combination of anti-PF4 ELISA and serotonin release assay (SRA) has a reported sensitivity approximating 100% for diagnosing heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) - 7th ACCP Chest Supplement. Current therapeutic guidelines are to initiate therapy with a direct thrombin inhibitor (DTI) based on clinical parameters and to use HIT assays for diagnostic confirmation. Consequently, timely lab data may potentially minimize unnecessary drug exposure, reduce cost, and decrease morbidity. Due to test complexity, the ELISA results consistently precede the SRAs - the “gold standard” for HIT testing. This study examines the predictive value of the optical density (OD) reading and heparin neutralization procedure (100 IU/ml) for determining positive SRA. 200 patients with orders for the anti-PF4 ELISA (GTI) were retested with and without 100 IU of unfractionated heparin. Confirmation by heparin neutralization was reported as % inhibition (>50% inhibition = positive) as calculated by manufacturer’s instructions.
| . | Negative SRA . | Positive SRA . |
|---|---|---|
| Negative, OD/0.4 | 34 | 2 |
| Positive, OD/0.4 | 120 | 44 |
| . | Negative SRA . | Positive SRA . |
|---|---|---|
| Negative, OD/0.4 | 34 | 2 |
| Positive, OD/0.4 | 120 | 44 |
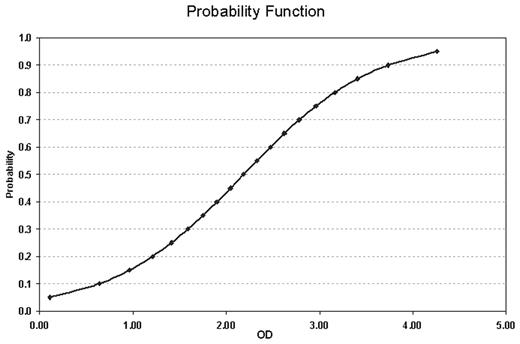
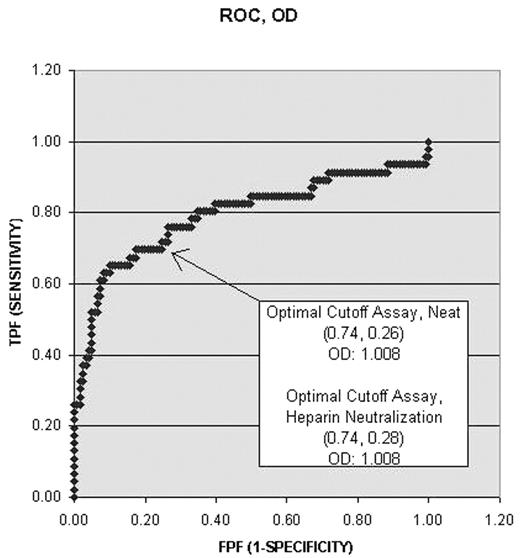
The sensitivity and specificity of the ELISA was 95.6% and 21.6% respectively. The heparin neutralization step improved the specificity to 38.6% and did not alter the sensitivity. Figure 1 shows a single variable binary logistic regression analysis demonstrating the relationship between OD and probability for a positive SRA. An additional binary logistic regression analysis showed no statistical significance for the % neutralization with heparin. A receiver operators curve (ROC) (Figure 2)demonstrating an optimal sensitivity/specificity was generated for both the neat and the heparin neutralized samples. The curves were virtually identical with the same OD cut-off of 1.008. The specificity was nominally improved with the neutralization procedure.
The heparin neutralization step only marginally improves the specificity of the anti-PF4 ELISA and does not correlate with a positive SRA result, and therefore, does not justify the added expense. Higher ELISA OD measurements correlate significantly with the probability of a positive SRA.
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal