Abstract
B cells are not currently known to be capable of producing granzyme B or being cytotoxic. We recently found that human B cells activated with Interleukin 21 (IL-21) and antibodies to the B cell receptor (BCR) or immunostimulatory oligonucleotides (CpG ODN), can produce granzyme B. Further studies were done to assess the biological and potential therapeutic significance of this finding. Granzyme B ELISpot, intracellular staining for granzyme-B, quantitative real time RT-PCR for granzyme B messenger RNA and gene expression array confirmed B cells obtained from the peripheral blood of normal individuals (Fig. 1) and many B cell lines including Namalwa, Daudi, Ramos and EBV-transformed lymphoblasts, can be induced to produce granzyme B. This granzyme B is functional as demonstrated by cleavage of a granzyme B-sensitive colorimetric substrate. IL-21 based treatment also increased the transcription of the gene for perforin and the production of Interferon-γ in select B cell populations. We conclude that IL-21 based therapy can induce B cells to produce functional granzyme B and other components known to be present in the cytotoxic granules of CTL and NK cells. These unexpected findings could have significant implications on our understanding of the role of B cells in immune regulation and for a variety of immune phenomena including auto-, cancer and infectious immunity.
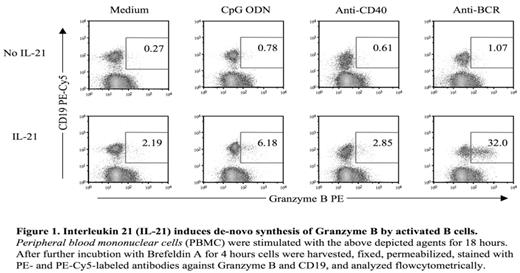
Interleukin 21 (IL-21) induces de-novo synthesis of Granzyme B by activated B cells.Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were stimulated with the above depicted agents for 18 hours. After further incubtion with Brefeldin A for 4 hours cells were harvested, fixed, permeabilized, stained with PE- and PE-Cy5-labeled antibodies against Granzyme B and CD19, and analyzed flowcytometrically.
Interleukin 21 (IL-21) induces de-novo synthesis of Granzyme B by activated B cells.Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were stimulated with the above depicted agents for 18 hours. After further incubtion with Brefeldin A for 4 hours cells were harvested, fixed, permeabilized, stained with PE- and PE-Cy5-labeled antibodies against Granzyme B and CD19, and analyzed flowcytometrically.
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal