Abstract
Objective: The aim of the study was to ascertain the feasibility of cord blood screening to determine the prevalence of haemoglobinopathies by a cost-effective method.
Background: High rate of consanguinity and intercousin marraiges are prevalent in the Sultanate of Oman, leading to an increase in haemoglobinopathies, which is of growing importance as knowledge of a population structure can be a unique aid in planning genetic services.
Methods: 1864 consecutive cord blood samples were screened by HPLC using Biorad Variant II program between April 2005 & March 2006. Complete blood counts [CBC] were also obtained on Cell Dyn 4000 automated blood cell counter. All samples were then processed to isolate and store mononuclear leukocytes for subsequent molecular diagnostics.
Results: We observed a 46.83% incidence of α-thalassaemia, based on significant amounts of Hb Barts on HPLC and low mean cell volume [MCV] & mean cell haemoglobin [MCH] on the CBC.
Neonatal Cord Blood Screening - HPLC and CBC data with Red Cell Indices
| . | Normal . | ATT . | HbS . | HbD . | HbE . | HbC . | ?BTT . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values in parenthesis represent SD | |||||||
| Mean HbF % | 77.4[7.3] | 76.4[8.7] | 89.4[9.4] | 78.1[1.2] | 81.1[4.9] | 80.2[7.8] | 92.1[2.0] |
| Mean HbA % | 22.5[7.3] | 23.6[8.2] | 14.1[6.0] | 13.7[9.9] | 12.7[3.1] | 13.1[4.5] | 8.1[2.1] |
| Mean Haemoglobin g/dl | 15.4[1.8] | 14.4[1.4] | 14.7[1.6] | 14.9[0.7] | 15.6[1.1] | 15.2[0.8] | 13.9[2.5] |
| Mean RBC Count × 1012/L | 4.5[0.6] | 5.0[0.6] | 4.9[0.6] | 4.5[0.4] | 4.8[0.4] | 4.6[0.2] | 4.0[0.6] |
| Mean MCV fl | 105.2[5.4] | 89.9[4.1] | 95.1[9.1] | 100.8[7.0] | 98.1[4.7] | 99.1[5.6] | 104.4[9.5] |
| Mean MCH pg | 34.4[2.1] | 28.5[1.8] | 30.7[3.4] | 33.3[2.7] | 32.6[3.3] | 32.9[1.2] | 34.8[1.0] |
| Mean MCHC g/dL | 32.7[1.1] | 31.7[1.3] | 32.2[1.0] | 33.1[0.9] | 33.6[2.1] | 33.2[1.5] | 33.3[1.0] |
| Mean RDW % | 16.1[1.1] | 17.4[2.1] | 17.1[2.4] | 16.1[1.5] | 17.7[2.4] | 16.5[1.9] | 16.1[2.5] |
| . | Normal . | ATT . | HbS . | HbD . | HbE . | HbC . | ?BTT . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values in parenthesis represent SD | |||||||
| Mean HbF % | 77.4[7.3] | 76.4[8.7] | 89.4[9.4] | 78.1[1.2] | 81.1[4.9] | 80.2[7.8] | 92.1[2.0] |
| Mean HbA % | 22.5[7.3] | 23.6[8.2] | 14.1[6.0] | 13.7[9.9] | 12.7[3.1] | 13.1[4.5] | 8.1[2.1] |
| Mean Haemoglobin g/dl | 15.4[1.8] | 14.4[1.4] | 14.7[1.6] | 14.9[0.7] | 15.6[1.1] | 15.2[0.8] | 13.9[2.5] |
| Mean RBC Count × 1012/L | 4.5[0.6] | 5.0[0.6] | 4.9[0.6] | 4.5[0.4] | 4.8[0.4] | 4.6[0.2] | 4.0[0.6] |
| Mean MCV fl | 105.2[5.4] | 89.9[4.1] | 95.1[9.1] | 100.8[7.0] | 98.1[4.7] | 99.1[5.6] | 104.4[9.5] |
| Mean MCH pg | 34.4[2.1] | 28.5[1.8] | 30.7[3.4] | 33.3[2.7] | 32.6[3.3] | 32.9[1.2] | 34.8[1.0] |
| Mean MCHC g/dL | 32.7[1.1] | 31.7[1.3] | 32.2[1.0] | 33.1[0.9] | 33.6[2.1] | 33.2[1.5] | 33.3[1.0] |
| Mean RDW % | 16.1[1.1] | 17.4[2.1] | 17.1[2.4] | 16.1[1.5] | 17.7[2.4] | 16.5[1.9] | 16.1[2.5] |
Furthermore, the overall incidence of other haemoglobinopathies was 9.39%, with 6.01% incidence of sickle haemoglobin. On HPLC, D-window, E-window and C-window were present in 1.02%, 0.32% and 0.11% of the samples respectively.
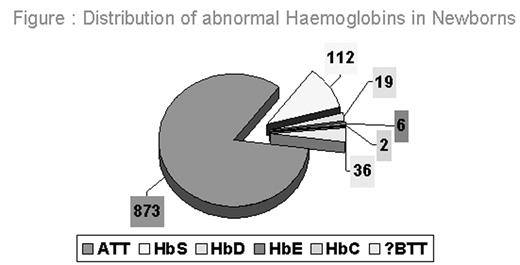
Since HPLC cannot diagnose β-thalassemia major at birth, in samples with HbA below 10%, the beta globin gene was directly sequenced including the promoter, all exons and introns in the abnormal samples. [n=36] Additionally, direct sequencing of abnormal samples with HbS,[n=112] HbD,[n=19], HbE[n=6] and HbC[n=2] were also performed to validate the HPLC results.
Conclusions: It is emphasized that neonatal cord blood screening is an important the first step in the national strategy towards total management of haemoglobinopathies including early diagnosis, comprehensive clinical care and counseling of the affected families. Between group differences were significant for RBC count, MCV, MCH, MCHC and the red cell distribution width (RDW), which along with Hb Barts, and HPLC results can successfully predict the correct underlying diagnosis.
Disclosures: The Research is funded by Institution vide SR/MED/HAEM/06.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal