Abstract
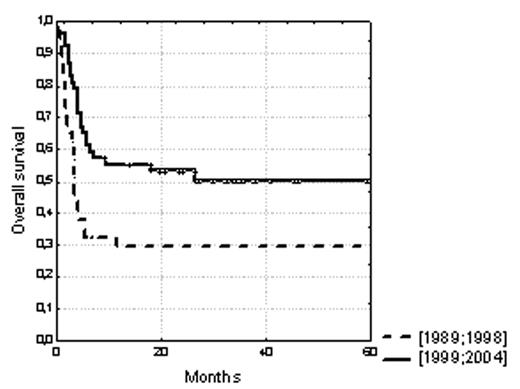
We aimed to determine whether outcome of HSCT from an unrelated donor has improved over time for patients with severe acquired aplastic anemia (SAA) and, if so, to determine whether improvement resulted from changes in patient selection, changes in transplantation technique, or both. We thus analyzed the outcome of 89 patients (median age 17 years, range 0–52) who received such transplantations between 1989 and 2004. We compared two cohorts of patients transplanted within two successive time-periods (1989–1998 and 1999–2004) associated with probabilities (± 95% confidence interval) of 5-year survival significantly different: 29% ± 7% and 50% ± 7%, respectively (P<.01, Figure 1). Significant differences between the two cohorts concerned transplant-related, but not patient- and disease-related variables: the use of ATG and of fludarabine within conditioning and HLA matching at the allelic level for the 10 HLA-A, -B, -C, -DRB1 and -DQB1 loci (P=.0004) were more frequent in the recent 1999–2004 period. In multivariate analysis, the only 2 factors influencing survival were HLA allelic matching (P<.01) and younger age of recipient (<17 years, P<.0001). Of note, the impact of HLA matching disappeared in multivariate analysis when it was considered at the antigenic level for HLA-A, -B and -DR antigens, which underlines the importance of considering HLA matching at the allelic rather than the generic level for these transplantations. Survival reached 78% ± 11% at 5-year for the younger patients fully HLA-matched (n=14), which can be compared with survivals obtained for HLA-identical sibling transplants in similar young patients. Cumulative incidences of graft failure, grade II–IV or grade III–IV acute GVHD, and chronic GVHD were: 14% ± 4 % at 2 years, 50% ± 5 % and 24% ± 4 % at 100 days, and 28% ± 5 % at 2 years after HSCT (limited: 17% ± 4 %, extensive: 11% ± 3 %), respectively. In a competing risk analysis, allelic HLA matching - particularly incorporating HLA-C but not -DQB1 matching - but also a high cell-dose injected (> 2,6.108/kg nucleated cells, the median value of the cohort) and the use of fludarabine and/or ATG in the conditioning regimen were found as protective against graft failure and acute GVHD, respectively. Our results suggest that survival after unrelated transplantation for SAA has improved over the past 15 years, due to a better HLA matching at the allelic level for both HLA class I and class II antigens, but also to other transplant-related factors.
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal