Abstract
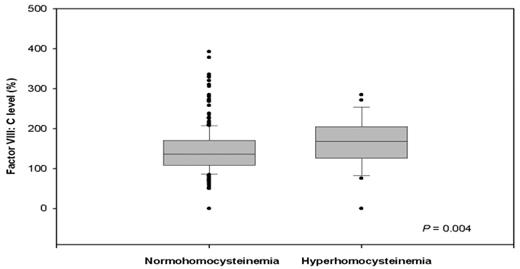
Hyperhomocysteinemia is demonstrated as a risk factor for venous and arterial thrombosis. Experimental evidence suggests that its thrombogenic propensity results from endothelial dysfunction and injury followed by platelet and fibrin formation. However, lowering homocysteine concentrations with vitamin B6, B12 or folic acid has not resulted in a reduced risk of recurrent venous and arterial thrombosis in large prospective clinical trials. This suggests that hyperhomocysteinemia is a surrogate for another thrombophilic related specimen. As high factor VIII:C levels are associated with an increased risk of both venous and arterial thrombosis, and with endothelial injury, we hypothesize that hyperhomocysteinemia and factor VIII:C levels are closely related to each other. Therefore, we performed a study to assess the absolute risk of thrombosis in hyperhomocysteinemia and the effects of elevated factor VIII:C levels on this risk in a large cohort of families with hereditary (index) deficiencies of protein S, protein C or antithrombin. Hyperhomocysteinemia was defined as a fasting plasma homocysteine level above 18.5 μmol/l and factor VIII:C levels were elevated when higher than 150%. A total of 405 relatives were included. Median factor VIII:C levels in hyperhomocysteinemic relatives (n=26, 6%) were 169%, compared to 136% in normohomocysteinemic relatives (P=0.004) (Figure) and were more often elevated (65 vs. 38%, P=0.006). Other thrombophilic defects, including the index deficiencies, factor V Leiden and the prothrombin mutation were equally divided. Hyperhomocysteinemia was associated with an increased risk of venous and arterial thrombosis (relative risk’s 2.6 [1.3–4.8] and 3.7 [1.5–8.4)], respectively). Relatives with elevated factor VIII:C levels were also at risk; relative risk 2.3 (1.4–4.0) for venous thrombosis and 2.3 (1.0–5.1) for arterial thrombosis. After excluding all relatives with elevated factor VIII:C levels, relative risk for venous thrombosis and hyperhomocysteinemia dropped to 1.3 (0.2–9.8) and nil relatives had arterial thrombosis. These results suggest that hyperhomocysteinemia indeed is an epiphenomenon for elevated factor VIII:C levels and therefore homocysteine measurements can be omitted in risk assessment for venous and arterial thrombosis when factor VIII:C measurements are incorporated in thrombophilia screening.
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal