Abstract
The myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are clonal hematopoietic disorders characterized by cytopenia and bone marrow dysplasia. This is the result of proliferation, differentiation and apoptotic processes of hematopoietic precursors and it frequently evolves to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The diagnosis of MDS is essentially morphological and is based on the presence of dysplastic features in peripheral blood and bone marrow. The most reliable features of MDS include the presence of micromegakariocytes in the bone marrow and trilineage dysplasia with a high precentage of blast, or cytogenetic abnormalities (1). One of the morphological features that is easily assessed and therefore often used is the presence of dysgranulopoiesis, such as degranulation of the neutrophil population and/or Pelger-Huët-like anomaly. The Coulter LH750® is an automated hematology analyze, that reports a CBC and a six part WBC differential. The technology of the WBC differential use a combination of three measurements, Volume, Conductivity and Scatter, to measure the WBC in a near native state. The possibility to detect the degranulation with the Mean Conductivity of the Neutrophils (MNEC) and the Mean Scatter of the neutrophils (MNES), measured with the LH750® (2,3) and the difference between degranulated neutrophils and immature netrophils (3) has been published. We were interested to investigate other aspects of these parameters, firstly to determine the variability and the positive predictive value of MNEC and MNES, and secondly to assess the clinical value of measuring them on all routine samples. We determined the reference values for the parameters and applied the lower reference limit (2.5th percentile) for MNEC (<138) and for MNES (<139) to 200 samples from a routine daily worload.
Five sample had both low MNEC and low MNES and the history of these patients were:
Patient 1) NHL in CR after Chemoterapy (CHT) (5 months without treatment).
Patient 2) Hodgkin Disease in CR after 3 year of BEACOOP (dysplasia)
Patient 3) Hodgkin Disease in CR receiving ABVD (2 years without treatment).
Patient 4) Severe Reumathologic disease in treatment with Methotrexate
Patient 5) Vasculitis in treatment with Cyclophosphamid and secondary MDS.
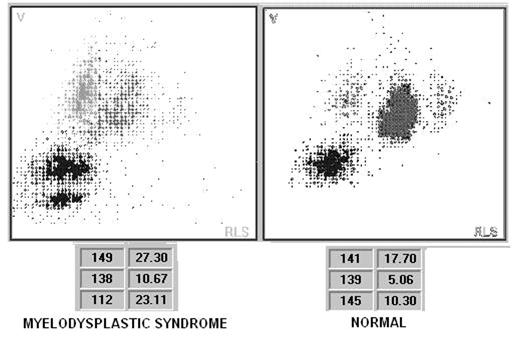
We reviewed the granulation of the netrophils in the 5 positive cases and also in 5 normal controls from the same day, using the same staining procedure. There was a significant decrease of neutrophil granulation with more than 10% of degranulated neutrophils in all of the positive cases compared to the contols. The variability of the two parameters were analyzed in a patient with a myelodysplastic syndrome (see case used for that in he figure enclosed), and the coefficient of variation for the MNEC was 1,5% and for the MNES was 1%.
The Mean Conductivity and the Mean Scatter of the neutrophils, measured using VCS technology, appear to be useful in screening neutrophil dysplasia and their reproducibility suggests that they could be used to screen myelodysplastic syndromes.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal