Abstract
The murine monoclonal antibody R8B12 recognizes the C-terminal region (residues 563–740) of the A2 subunit of factor VIIIa (
Fay et al. J. Biol. Chem. 266:20139, 1991
), as judged by western blotting. The location of the R8B12 epitope within the A2 subunit is not known. In the present study we used affinity-directed mass spectrometry (Zhao et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 93:4020, 1996
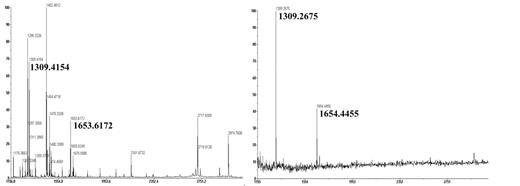
) to map the R8B12 epitope. Purified A2 subunit was subjected to proteolytic digestion with trypsin. The digest was then subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) using R8B12 IgG, in which peptide(s) are selected that bind the antibody. Subsequently the masses of the affinity-selected peptides were determined directly from the immune complex by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Proteolysis of A2 with trypsin generated a pre-IP peptide fingerprint that covered ~40% of the A2 domain sequence (Figure, left). Analysis of the post-IP peptide fingerprint showed two masses, 1309 and 1654, as representing affinity-selected peptide fragments (Figure, right). A theoretical database search identified the 1309 mass peak as A2 domain residues 584–593 and the 1654 mass peak as A2 domain residues 497–510. Direct sequencing of both mass peaks confirmed the results of the theoretical database search. These residues mapped to regions on the A2 domain of the factor VIII A domain homology model that are surface exposed and proximal to each other. Taken together, the above results suggest that A2 domain residues 497–510 and 584–593 represent a discontinous epitope for R8B12. Furthermore, based upon blotting specificity of R8B12 to the C-terminal portion of A2, we speculate that the latter sequence that forms this epitope makes a substantially greater contribution to the binding energy.Author notes
Corresponding author
2005, The American Society of Hematology
2005

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal