Abstract
Introduction: The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib has demonstrated clinical activity in pts with MM. Its adverse effects including thrombocytopenia and peripheral neuropathy affected 30% to 60% of patients overall, and interrupted the therapy in 10% to 20%. There were no toxicity data in Asian pts using bortezomib for MM.
Methods: We reviewed the clinical records of MM pts from 24 centers in Korea using NCI Common Toxicity Criteria version 3.0. They were treated with bortezomib alone or in combination with other agents including thalidomide.
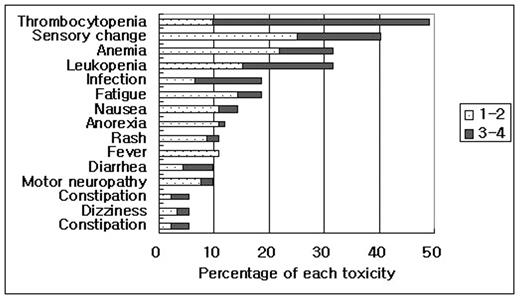
Results: 92 pts with MM were treated with a median age of 60yrs (range: 42–77). Median number of previous treatments was 3 (range: 1–10), 73% had been treated with three or more of the major classes of agents including thalidomide (67%) and autologous stem cell transplantation (51%). Regimens were bortezomib only in 36 (39%), bortezomib plus dexamethasone in 33 (36%), and bortezomib plus thalidomide-containing regimen in 23 (25%) pts. Analysis of response revealed CR +nCR in 31 (34%) and PR in 27 (30%), for an ORR of 64% in 90 evaluable pts. The most commonly reported adverse events were thrombocytopenia, sensory neuropathy, infection and fatigue (figure 1). Six therapy-related mortality (7%) were reported within 20 days after the last dose of bortezomib. Causes of death were infection in 3, disease progression in 2 and suicide in 1 patient. Twelve pts (13%) ceased the therapy due to toxicity; neuropathy in 7, infection in 4 and diarrhea in 1 pt. Neuropathy more than grade 2 were more frequent in pts who received thalidomide (11/23) when compared with those without thalidomide (17/69) (p=0.036). But preexisting neuropathy and number of prior regimens did not affect the neuropathy.
Conclusion: The incidence of thrombocytopenia and neurotoxicity were similar but the gastrointestinal toxicities were relatively low in Korean pts compared to that in western studies. Significant neuropathy was associated with the combination of thalidomide to bortezomib. This finding will give a useful message for the development of safe salvage regimen including bortezomib.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal