Abstract
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia (CLL) remains largely incurable despite recent advances in therapy, and therefore alternative strategies are of interest in treating this disease. One such alternative is the use of gene therapy, but this relies on developing efficient gene transfer technologies. We have compared several viral vectors coding for green fluorescent protein (GFP) for their ability to transduce CLL cells. Three serotypes of adeno-associated virus (AAV) were used, AAV-2, AAV-5 and a relatively new isolate AAV-8, an EI-EIII deleted adenoviral 5 based vector, AV-5, all with GFP regulated by the CMV promoter, and a VSVG pseudotyped lentiviral vector in which GFP expression is controlled by EF1a promotor/enhancer complex. AV-5 resulted in variable GFP expression, 24.1±3.4%, n=10 but caused cell death at high multiplicities of infection (MOI). The lentiviral vector resulted in GFP expression of 23.5±2.6%, n=12, at the highest titre used, and expression declined in a distinct dose-dependent manner as titres were reduced. Of the AAV vectors, AAV-8 was the most efficient with GFP expression at 41.3±1.0% n=14. We conclude that AAV-8 is a promising viral vector for efficient transduction of CLL cells.
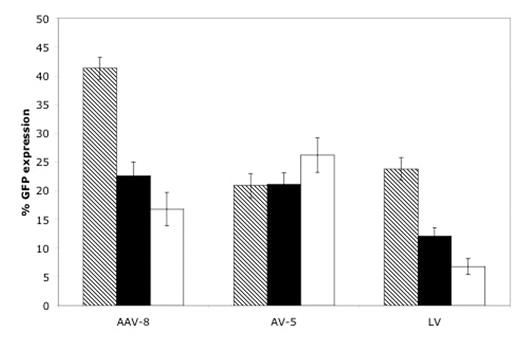
Percentage GFP expression for three viral vectors. Three different MOI’s were used at log dilutions.
Percentage GFP expression for three viral vectors. Three different MOI’s were used at log dilutions.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal