Abstract
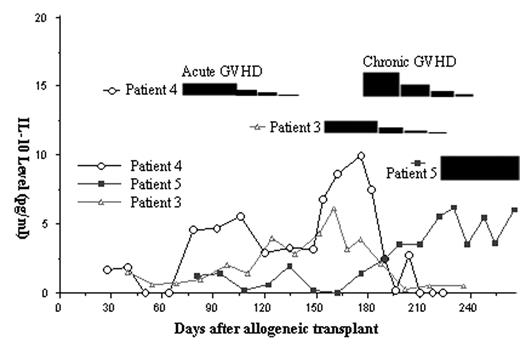
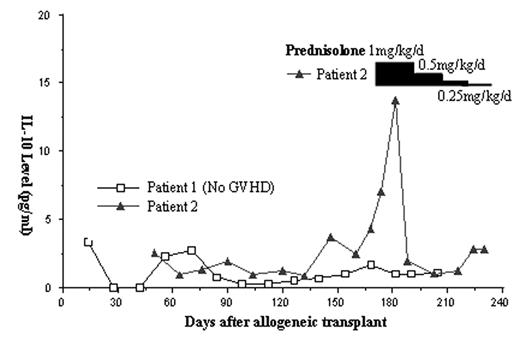
Current evidence suggest the interaction between subset of T cells, the T help1 (Th1) and T help2 (Th2), plays an important role in the pathogenesis of GVHD. Cytokines, either produced by Th1/Th2 or other cells, are important regulators in the whole process and will define the polarization of Th1 or Th2 from naïve T cell. In this study, we used ELISA (R&D, Minneapolis, MN, US) to monitor the serum level of Interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-10, IL-12, and interferon-γ (INF-γ) in patients receiving allogeneic transplant weekly from day 0 to at least day 200. From Jan. 2003, consecutive 20 patients were enrolled. The GVHD prophylaxis consisted of Cyclosporine-A and short course Methotrexate. Of the 20 patients, 2 had grade 3/4 acute GVHD (aGVHD) and 7 had extensive chronic GVHD (cGVHD). The serum levels of IL-4 and IL-12 were below the detectable level (0.13pg/ml and 0.5pg/ml respectively) in most occasions, even during the period of GVHD. Nevertheless, the serum level of IL-10 correlated well with the activity of cGVHD and we used data gathered from 5 patients to demonstrate this good correlation in figure 1 and 2. Patient 1 (open square, figure 1) had no GVHD and the IL-10 levels were below 5pg/ml during the whole period of follow-up. Patient 2 (solid triangle, figure 1) and 3 (open triangle, figure 2) had de novo cGVHD. The IL-10 level increased gradually when cGVHD developed, however, both clinical manifestations of cGVHD and serum IL-10 level decreased rapidly after the administration of Prednisolone (black bar on figure 1 and 2, with the thickness indicating the relative dosage of Prednisolone). Patient 4 (open circle, figure 2) had grade 2 aGVHD that resolved quickly after Prednisolone treatment. However, IL-10 level increased gradually after discontinuing Prednisolone and cGVHD developed subsequently. After adding Prednisolone again, cGVHD improved and IL-10 decreased to undetectable level rapidly. Patient 5 (solid square, figure 2) had steroid-refractory cGVHD. The IL-10 level kept above 5pg/ml for more than 1 month despite Prednisolone 1mg/kg/day giving at the same time and the patient eventually needed further salvage treatment (thalidomide). The serum INF-γ were undetectable in most occasions. It became detectable during period of cGVHD in patients 3, 4 and 5 but not patient 2. In conclusion, post-transplant serum IL-10 level correlates well with the clinical activity of cGVHD as well as the responsiveness to corticosteroid treatment. This novel finding will allow the functional evaluation of individuals’ immune system after allogeneic transplant and should give insight for the adjustment of immunosuppression necessary for cGVHD control.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal