Abstract
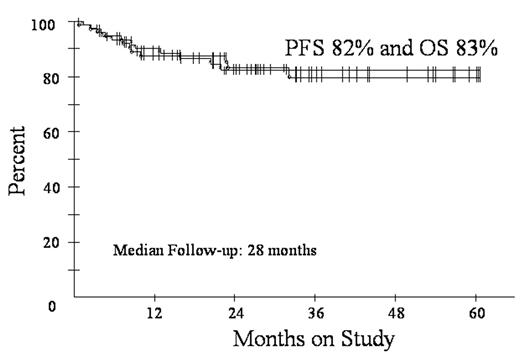
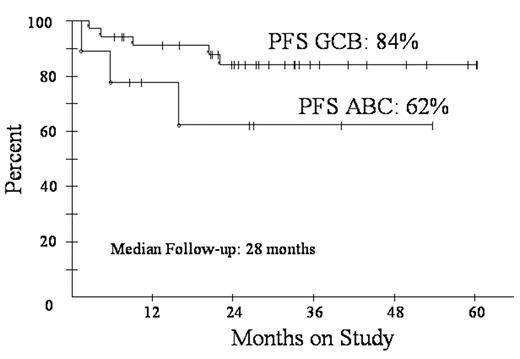
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is subdivided by microarray into germinal center B-cell (GCB) and activated B-cell (ABC) subtypes. These subtypes have distinct pathways of lymphomagenesis and outcome with 5-year survival of 59% and 31%, respectively, using CHOP. A molecular predictor showed high tumor proliferation and the ABC subtype are associated with a poor outcome. We showed DA-EPOCH overcomes the adverse effects of high tumor proliferation (BLOOD 99:2685, 2002) and rituximab overcomes the adverse effects of BCL-2, which is associated with the ABC subtype (Proc Am Soc Heme 102:abstr 356, 2003). To assess DA-EPOCH-R with G-CSF in GCB and ABC subtypes, we employed a validated immunohistochemistry (IHC) algorithm (BLOOD: 103:275, 2004). GCB was defined as CD10+ or BCL-6+ and MUM1-. ABC was defined as CD10- and BCL-6- or CD10-, BCL-6+ and MUM1+. Eligibility includes de novo DLBCL, no prior chemotherapy, any PS, HIV- and stage I thymic DLBCL > 5 cm and all stage II-IV. Characteristics of 77 enrolled pts include median (range) age 48 (12-85) and PS 1 (0-3); stage III/IV 48 (62%); and LDH > nl 42 (55%); extranodal sites >1 27 (35%); and HI/H IPI 26 (34%). Including all 77 pts, response is CR/CRu 72 (94%). At the median (range) follow-up of 28 (4-60) mos, PFS is 82% and OS is 83% (Fig 1). DFS is 87% at 28 mos with no relapses beyond 18 mos. PFS at 28 mos according to IPI risk is 95% for 0-2 factors and 54% for 3-5 factors. Using IHC, 44 pts were subdivided in GCB (35) and ABC (9) subtypes. The proportion of the ABC subtype vs. GCS is low and likely due to incomplete IHC for the ABC subtype. Specifically, 16 cases that were CD10- did not have adequate BCL-6 and/or MUM1 IHC for categorization. PFS at 28 mos for the GCB and ABC subgroups were 84% and 62%, respectively (Fig 2). DA-EPOCH-R employs a pharmacodynamic design where doses of doxorubicin, etoposide and cyclophosphamide are adjusted (i.e. normalized) to achieve neutrophil nadirs < 500/mm3. PK analysis shows that clearance of doxorubicin and etoposide varies by up to 1 log and that dose-adjustment compensates for these differences. This approach increases dose intensity in pts with high drug clearance while limiting toxicity. Based on 451 cycles, the target nadir ANC < 500/mm3 was achieved on 277 (61%) cycles but with 67 (15%) episodes of fever/neutropenia. Non-hematological toxicity was low and there were 2 treatment related deaths. These results suggest DA-EPOCH-R is highly effective in all subtypes of de novo DLBCL. A phase III study comparing R-CHOP and DA-EPOCH-R with microarray analysis of tumor biopsies is under development.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal