Abstract
The optimal induction for older adults with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is unknown. Several anthracyclines have been proposed, but the data remain equivocal. Additionally, few prospective trials of priming with hematopoietic growth factors to cycle leukemia cells prior to induction chemotherapy have been conducted. Three hundred and sixty-two older adults with previously untreated AML were randomized to either daunorubicin, idarubicin or mitoxantrone with a standard dose of cytarabine as induction therapy. In addition, 245 patients were also randomized to receive granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) or placebo beginning 2 days prior to induction chemotherapy and continuing until marrow aplasia. No difference was observed in the disease-free overall survival or in toxicity among patients receiving any of the 3 induction regimens or among those receiving growth factor or placebo for priming. However, the complete remission rate for the first 113 analyzable patients, who did not participate in the priming study and started induction therapy 3 to 5 days earlier than those who did, was significantly higher (50% versus 38%; P = .03). None of the anthracyclines is associated with improved outcome in older adults. Priming with hematopoietic growth factor did not improve response when compared with placebo. Furthermore, delaying induction therapy in older adults may lead to a lower complete remission rate.
Introduction
A combination of an anthracycline and a cytarabine is the most commonly used induction regimen in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). However, neither the best anthracycline nor the optimal dose has been established. Classic studies 2 decades ago established a standard induction regimen of 45 mg/m2 daunorubicin intravenously for 3 days and 100 mg/m2 cytarabine intravenously by continuous infusion for 7 days.1-5 For patients younger than 55 to 60 years, multiple prospective randomized studies compared daunorubicin at a dose of 45 mg/m2 with idarubicin, amsacrine, aclacinomycin A, and mitoxantrone, while keeping the dose of cytarabine constant.6-14 Virtually all of these agents were at least as effective as, if not better than, daunorubicin at a dose of 45 mg/m2. However, the results for patients older than 55 to 60 years are equivocal and do not confirm the superiority of any anthracycline when compared with 45 mg/m2 daunorubicin.9,15 In this prospective randomized study, older adults received either daunorubicin, idarubicin, or mitoxantrone, each combined with the identical dose of cytarabine.
Priming with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) or granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) may modulate cell cycle kinetics of leukemic blasts and render them more susceptible to phase-specific agents such as cytarabine.16 In this prospective trial, patients were also randomized to receive GM-CSF or placebo prior to induction therapy to determine the effect that induction therapy for AML had on efficacy and toxicity. Correlative laboratory studies were also performed to identify in vivo changes that may explain the clinical observations.
Patients, materials, and methods
Eligibility
Eligibility requirements were as follows: (1) age older than 55 years, with no upper age limit; (2) morphologic diagnosis of AML by institution and central review; (3) no prior cytotoxic chemotherapy for malignant conditions; (4) normal cardiac left ventricular ejection fraction; (5) no evidence of severe concurrent cardiac disease; and (6) serum bilirubin level of 34.2 μM (2.0 mg/dL) or lower and serum creatinine level of 176.8 μM (2.0 mg/dL) or lower. Samples of bone marrow aspirate were sent for immunophenotyping, and karyotypes were to be submitted for review.
Treatment
Between April 1993 and February 1997, patients were randomized to either 45 mg/m2 daunorubicin per day intravenously on days 1, 2, and 3 (DA); 12 mg/m2 mitoxantrone per day on days 1, 2, and 3 (MA); or 12 mg/m2 idarubicin per day on days 1, 2, and 3 (IA). Each patient was given 100 mg/m2 cytarabine intravenously per day by continuous infusion for 7 days.
On days 10 to 14, a bone marrow evaluation was performed, and a second induction cycle, identical to the first, was given if there was unequivocal evidence of residual leukemia (greater than 5% blast cells) in a bone marrow aspirate that was not markedly hypocellular.
Beginning in June 1994, patients were also randomized to priming with GM-CSF or placebo. GM-CSF was given at a dose of 250 μg/m2 per day, subcutaneously administered 48 hours prior to the initiation of induction therapy and continued until the bone marrow was free of residual leukemia on day 10 from start of the first or second course of induction chemotherapy. If the marrow was free of residual leukemia, the study medication was discontinued, and patients received open-labeled 250 μg/m2 GM-CSF per day subcutaneously until the absolute neutrophil count (ANC) was 1500/μL for 3 consecutive days.
Patients who achieved complete remission (CR) received 1.5 g/m2 cytarabine intravenously over the course of 1 hour every 12 hours for 12 consecutive doses.17 Patients 70 years of age or older received the identical dose and schedule, but for only 6 doses. At 5 days after completion of the consolidation therapy, all patients were given 250 μg/m2 GM-CSF per day subcutaneously until neutrophils recovered to 1500/μL for 3 consecutive days.
GM-CSF laboratory study
DNA synthesis was assessed by bromodeoxyuridine (BRDU) incorporation at baseline and after 48 hours of in vivo exposure to GM-CSF or placebo. Blood and/or marrow cells were incubated with BRDU at a 1:20 dilution in RPMI medium with 10% fetal bovine serum for 60 minutes at 37°C to label cells in S-phase of cell cycle.18 Fluorescence intensity was collected on a Coulter Epics flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter, Hialeah, FL). If insufficient cells were present in the specimens received for performance of flow cytometry, cells were fixed on glass slides; BRDU/anti-BRDU staining was performed; and cells were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. CFU-GM (leukemia colony-forming unit [CFU-L]) assays for the presence of clonogenic cells were performed with appropriate positive and negative controls or with GM-CSF at 10, 20, and 50 ng/mL. Plates were incubated at 5% CO2 and 37°C for 14 days before scoring for colony growth (defined as clusters of 20 cells or more).19
Statistical analysis
The primary objective of this study was to compare the CR rates of the 3 induction regimens and to compare the CR rates of priming with GM-CSF versus placebo. A secondary objective of this study was to evaluate the duration of CR and overall survival in older adults with previously untreated AML who were treated in these induction arms followed by a single course of consolidation therapy with high-dose cytarabine. The objective of the laboratory study was to examine the effects of GM-CSF on cell cycle markers and cell cycle traverse.
Initially, patients were randomized among the 3 anthracyclines in a balanced design using permuted blocks. To balance treatment assignment across known risk factors, patients were stratified by age (younger than 70 years versus age 70 or older) and by clinical history of myelodysplasia. With the addition of the priming study, the randomization was altered to include blinded assignment to a priming agent.
The study was designed to have 84% power to detect an improvement in CR rate from 55% among patients receiving DA to 75% among patients receiving either IA or MA, with each test conducted at the P = .025 one-sided level of significance. The Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test was used to permit stratification by priming (none, placebo, or GM-CSF). Among patients participating in the priming randomization, the study had 92% power to detect a 20% improvement in the CR rate with GM-CSF priming over placebo, testing at the one-sided P = .05 level of significance and stratifying by induction anthracycline. The study was designed to have 82% power to detect an improvement in disease-free survival by means of a cure rate model, with cure rate improving from 25% to 40% and median time to failure improving from 6 to 12 months among patients experiencing relapse.
Disease-free survival for patients achieving CR is measured from date of CR to date of relapse, death in remission, or date when patient was last known to be in remission. Overall survival is measured from date of randomization to date of death or date last known alive. Plots are constructed according to the method of Kaplan and Meier.20 Differences in disease-free and overall survival are assessed by the log rank test. Association between categorical variables is assessed by the Fisher exact test, and the Kruskal-Wallis test is used for ordered categorical variables. The Wilcoxon rank-sum test is used to compare laboratory values among groups of patients.21 The study was reviewed by the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Data Monitoring Committee, in accordance with the protocol design, for both efficacy and safety endpoints. An O'Brien-Fleming boundary provided guidance on efficacy endpoints; a Pocock boundary was used for safety endpoints. The Institutional Review Board of each participating institution gave approval for this study, and informed consent was provided according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Results
There were 122 patients randomized to DA, 121 to IA, and 119 to MA. Of these, 117 were randomized prior to the introduction of the priming randomization. Of the 362 randomized patients, 348 were medically eligible with a centrally reviewed diagnosis and submitted data; these patients were included in the primary efficacy comparison of these treatment arms (116 on DA, 118 on IA, and 114 on MA). There were no statistically significant differences in the patient characteristics between these 3 arms (Table 1).
Patient characteristics: induction chemotherapy (N = 348)
. | DA, n = 116 . | IA, n = 118 . | MA, n = 114 . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, no. | |||
| Male | 65 | 63 | 65 |
| Female | 50 | 55 | 49 |
| Performance status, no. | |||
| 0-1 | 94 | 98 | 95 |
| 2-4 | 19 | 20 | 17 |
| Age | |||
| Median (range), y | 67 (56-82) | 67.5 (56-86) | 69 (56-84) |
| 56 y-60 y, n | 20 | 20 | 18 |
| 61 y-65 y, n | 29 | 30 | 14 |
| 66 y-70 y, n | 26 | 31 | 40 |
| 71 y-75 y, n | 24 | 24 | 25 |
| 76+ y, n | 17 | 13 | 17 |
| WBC count × 109/L, median (range) | 112.5 (7-12.88) | 65.5 (.6-2000) | 72 (6-2070) |
| Platelet count × 109/L, median (range) | 52 (6-346) | 61 (7-351) | 51 (2-261) |
. | DA, n = 116 . | IA, n = 118 . | MA, n = 114 . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, no. | |||
| Male | 65 | 63 | 65 |
| Female | 50 | 55 | 49 |
| Performance status, no. | |||
| 0-1 | 94 | 98 | 95 |
| 2-4 | 19 | 20 | 17 |
| Age | |||
| Median (range), y | 67 (56-82) | 67.5 (56-86) | 69 (56-84) |
| 56 y-60 y, n | 20 | 20 | 18 |
| 61 y-65 y, n | 29 | 30 | 14 |
| 66 y-70 y, n | 26 | 31 | 40 |
| 71 y-75 y, n | 24 | 24 | 25 |
| 76+ y, n | 17 | 13 | 17 |
| WBC count × 109/L, median (range) | 112.5 (7-12.88) | 65.5 (.6-2000) | 72 (6-2070) |
| Platelet count × 109/L, median (range) | 52 (6-346) | 61 (7-351) | 51 (2-261) |
WBC indicates white blood cell.
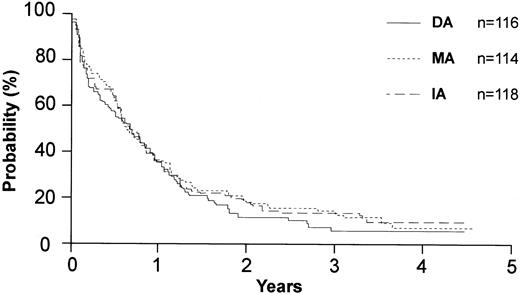
Among the 348 patients, 150 patients (42%) achieved a CR. There were 57 CRs among 113 patients who entered prior to the priming randomization (50%) and 93 CRs among the 235 analyzable patients who entered after priming was incorporated into the study (38%). Of the 150 CRs, 47 were achieved on DA (41% of patients on DA), 51 on IA (43%), and 52 on MA (46%). There were no statistically significant differences between any of these arms (Table 2; Figures 1, 2).
Survival and other results of induction therapy
. | DA . | IA . | MA . | AII . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR, % | ||||
| All patients, N = 348 | 40 | 43 | 46 | 42 |
| Younger than 70 y, n = 209* | 46 | 55 | 51 | 51 |
| 70 y or older, n = 139† | 30 | 24 | 33 | 29 |
| Therapy-related mortality in induction, all patients, %‡ | 16 | 22 | 14 | 17∥ |
| Overall survival, median mo | 7.7 | 7.5 | 7.2 | 7.5 |
| Disease-free survival, median mo§ | 5.7 | 9.4 | 7.1 | 7 |
. | DA . | IA . | MA . | AII . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR, % | ||||
| All patients, N = 348 | 40 | 43 | 46 | 42 |
| Younger than 70 y, n = 209* | 46 | 55 | 51 | 51 |
| 70 y or older, n = 139† | 30 | 24 | 33 | 29 |
| Therapy-related mortality in induction, all patients, %‡ | 16 | 22 | 14 | 17∥ |
| Overall survival, median mo | 7.7 | 7.5 | 7.2 | 7.5 |
| Disease-free survival, median mo§ | 5.7 | 9.4 | 7.1 | 7 |
P = .04 for DA versus IA.
P = .37 for IA versus MA.
P = .31 for DA versus IA; P = .12 for IA versus MA.
There were 125 patients in CR; §P = .68 for DA versus IA.
By age, 13% of all patients younger than 70 years had therapy-related mortality in induction versus 22% age 70 or older; P = .04.
Priming study
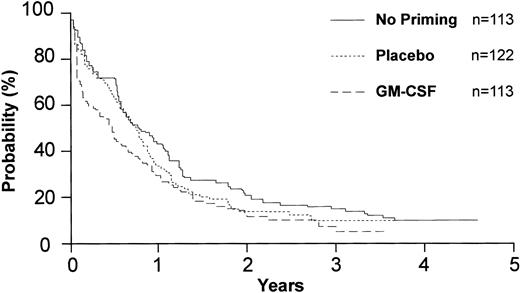
Of the 235 patients included in the primary analysis of this study, 125 were randomized to placebo and 113 were randomized to GM-CSF. There was no difference in the number of patients requiring reinduction in the 2 groups. Ninety-three patients entered CR: 52 of 122 patients receiving placebo and 41 of 113 receiving GM-CSF. Priming with GM-CSF was not superior to priming with placebo with respect to CR rate or survival (Table 3; Figure 3).
Survival and other results of induction in priming randomization
. | GM-CSF . | Placebo . | All . |
|---|---|---|---|
| CR, % | |||
| All patients, n = 235 | 38 | 40 | 30 |
| Younger than 70 y* | 42 | 51 | 46 |
| 70 y or older | 28 | 26 | 27 |
| Therapy-related mortality in induction, %† | 26 | 17 | 22 |
| Overall survival, median mo† | 5.3 | 8.5 | 6.7 |
| Disease-free survival, median mo‡ | 6.9 | 5.1 | 6.1 |
. | GM-CSF . | Placebo . | All . |
|---|---|---|---|
| CR, % | |||
| All patients, n = 235 | 38 | 40 | 30 |
| Younger than 70 y* | 42 | 51 | 46 |
| 70 y or older | 28 | 26 | 27 |
| Therapy-related mortality in induction, %† | 26 | 17 | 22 |
| Overall survival, median mo† | 5.3 | 8.5 | 6.7 |
| Disease-free survival, median mo‡ | 6.9 | 5.1 | 6.1 |
P = .31 for GM-CSF versus placebo.
P = .11 for GM-CSF versus placebo.
There were 77 patients in CR; P = .73 for GM-CSF versus placebo.
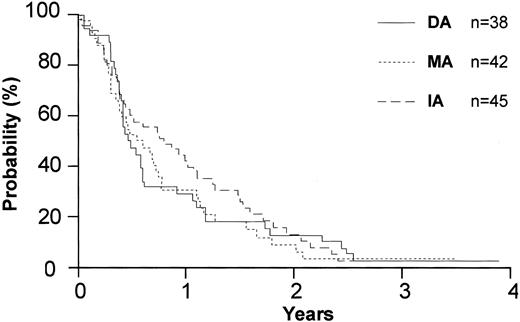
Disease-free survival by anthracycline type for the 125 patients in complete remission.
Disease-free survival by anthracycline type for the 125 patients in complete remission.
Consolidation therapy
A total of 125 patients in CR registered and were included in the primary analysis of disease-free survival. The median disease-free survival (DFS) for patients who received DA, IA, or MA was 5.7 months, 9.4 months, and 7.1 months, respectively (P = .68) (Figure 4). Among the patients in the priming study, the median DFS was 6.9 months with GM-CSF and 5.1 months with placebo (P = .73) (Figure 5). The overall mortality from consolidation was 4%.
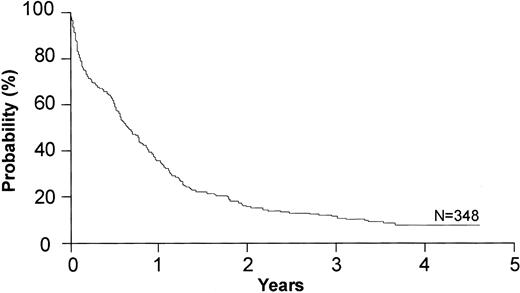
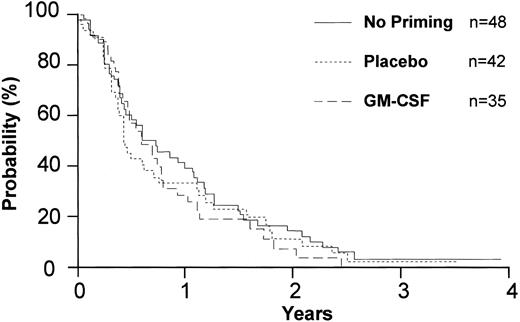
Overall survival of 348 eligible patients by priming. “No priming” represents the cohort of patients who entered the study before initiation of the priming randomization.
Overall survival of 348 eligible patients by priming. “No priming” represents the cohort of patients who entered the study before initiation of the priming randomization.
Disease-free survival by priming for the 125 patients in complete remission. “No priming” represents the cohort of patients who entered the study before initiation of the priming randomization.
Disease-free survival by priming for the 125 patients in complete remission. “No priming” represents the cohort of patients who entered the study before initiation of the priming randomization.
Response rate before and after initiation of the priming randomization
Fifty-seven (50%) of the 113 prepriming patients achieved CR compared with 93 (38%) of 235 patients who also participated in the priming randomization (P = .03) (Table 4). There was no difference in presenting features, such as WBC count, among the 2 groups of patients. The only difference between the 2 groups is the delay from diagnosis to induction therapy in the group who entered the priming randomization. Among the 113 patients who were treated before priming, therapy could be initiated immediately upon randomization as there was no blinded component. Following the second priming randomization, the need to obtain blinded study medication, often with an intervening weekend and the inherent delay due to the 48-hour administration of priming therapy, frequently led to a delay of 4 to 5 days in the initiation of the induction therapy compared with the group receiving this same therapy prior to the priming randomization. Thus, the mean time between randomization in the priming study and initiation of chemotherapy was 83 hours.
Response rate for randomization before and after priming
CR . | All, N = 348 . | Before priming, n = 113 . | After priming, n = 235 . |
|---|---|---|---|
| All patients, % | 42 | 50 | 38* |
| Younger than 70 y, % | 51 | 59 | 46* |
| 70 y or older, % | 29 | 36 | 27† |
CR . | All, N = 348 . | Before priming, n = 113 . | After priming, n = 235 . |
|---|---|---|---|
| All patients, % | 42 | 50 | 38* |
| Younger than 70 y, % | 51 | 59 | 46* |
| 70 y or older, % | 29 | 36 | 27† |
P = .03 for before priming versus after priming.
P = .31 for before priming versus after priming.
Cytogenetics
Cytogenetic analyses were performed by the respective institutions on all patients. The ECOG Cytogenetics Committee reviewed data on 328 patients, and 232 patients (67%) considered acceptable for analysis are reported here (Table 5). On the basis of the SWOG classification, 1% had favorable cytogenetics; 53% had intermediate cytogenetics; 38% had unfavorable cytogenetics; and the cytogenetics of 8% were unknown. Of note, 45% had normal karyotypes, and 13% had deletions of whole or part of chromosomes 7 or 5. The data for CR rate and overall survival by cytogenetics are shown in Table 6. Both demonstrate a statistically significant decrease as the cytogenetic risk group becomes more unfavorable (P = .003). The distribution of patients by risk category for the initial patient group (n = 113) was similar to those patients enrolled in the randomized priming study (n = 245). The Fisher exact test suggests that there was no association between risk category and enrollment in the priming study (P = .52).
Results of cytogenetics analysis*(n = 232)
. | Frequency . |
|---|---|
| Favorable | |
| t(15;17)(q22;q11-12) | 2 |
| inv(16)(p13q22) | 1 |
| Intermediate | |
| Normal* | 104 |
| + 8† | 13 |
| Others | 5 |
| Unfavorable | |
| del(5)(q12-31-q31-35)‡ | 10 |
| del(5)(q13q33)‡ | 9 |
| - 7‡ | 9 |
| del(7)(q22)‡ | 2 |
| del(7)(q32)‡ | 1 |
| del(20)(q11-13) | 4 |
| del(20)(q11) | 2 |
| + 8§ | 6 |
| Others | 45 |
| Unknown | 19 |
. | Frequency . |
|---|---|
| Favorable | |
| t(15;17)(q22;q11-12) | 2 |
| inv(16)(p13q22) | 1 |
| Intermediate | |
| Normal* | 104 |
| + 8† | 13 |
| Others | 5 |
| Unfavorable | |
| del(5)(q12-31-q31-35)‡ | 10 |
| del(5)(q13q33)‡ | 9 |
| - 7‡ | 9 |
| del(7)(q22)‡ | 2 |
| del(7)(q32)‡ | 1 |
| del(20)(q11-13) | 4 |
| del(20)(q11) | 2 |
| + 8§ | 6 |
| Others | 45 |
| Unknown | 19 |
Percentage of patients in each grouping are as follows: favorable, 1%; intermediate, 53%; unfavorable, 38%; and unknown, 8%. Results are based on Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) classification.22
45% of all patients analyzed for cytogenetics.
6% of all patients analyzed for cytogenetics.
Patients with these 5 unfavorable cytogenetics (deletions of whole or part of chromosomes 7 or 5) compose 13% of all patients analyzed for cytogenetics.
Associated with del(7).
Results by cytogenetics (n = 232)
. | Favorable, n = 3 . | Intermediate, n = 122 . | Unfavorable, n = 88 . | All . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR, % | 67 | 50* | 30 | 42 |
| Overall survival, median mo | 15.1 | 10.1† | 5.1 | NA |
. | Favorable, n = 3 . | Intermediate, n = 122 . | Unfavorable, n = 88 . | All . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR, % | 67 | 50* | 30 | 42 |
| Overall survival, median mo | 15.1 | 10.1† | 5.1 | NA |
Results are based on SWOG classification.22 NA indicates unavailable.
P = .003 for intermediate versus unfavorable.
P = .002 for intermediate versus unfavorable.
GM-CSF laboratory study
Of the 245 patients enrolled in the priming study, 180 (73%) had samples sent for laboratory analysis. Of these, 106 (43%) had day-0 and day-2 samples available. Of these 106, 53 patients received priming with placebo, and 53 received GM-CSF. The mean change in S-phase percentage for placebo patients was 0.25%, and the mean change with GM-CSF was 2.05% (P = .003; Wilcoxon rank sum test). This suggests that GM-CSF priming did result in larger changes in the S-phase percentage. Of the GM-CSF–primed patients, 34 (64%) showed an increase in S-phase over the 2-day priming period, compared with 19 (36%) of the placebo-primed patients (P = .006; Fisher exact test). Among the patients enrolled in the priming study, the WBC count increased an average of 3 × 109/L (300/μL) from day 1 of priming to day 3 (day 1 of chemotherapy) in the placebo-primed patients and 8900/μL among those primed with GM-CSF (P = .0003). There was no significant correlation between the increase in CFU-GM with GM-CSF exposure and the change in S-phase percentage between day 0 and day 2 as measured by BRDU uptake for the GM-CSF–primed patients, the placebo-primed patients, or the study population as a whole. In both groups, 25 of 53 patients achieved a CR. Among the 53 placebo-primed patients, the mean change in S-phase among the 30 non-CR patients was 0.15% and mean change among the 23 CR patients was 0.40%. For the 53 GM-CSF–primed patients, the mean change in S-phase among the 30 non-CR patients was 1.9% and the median among the 23 CR patients was 2.3% (Table 7).
Change in percentage of cells in S-phase between day 0 and day 2
. | Placebo, n = 53 . | GM-CSF, n = 53 . |
|---|---|---|
| Total, % | 0.25 | 2.05 |
| CR obtained, % | 0.4 | 2.3 |
| CR not obtained, % | 0.15 | 1.9 |
. | Placebo, n = 53 . | GM-CSF, n = 53 . |
|---|---|---|
| Total, % | 0.25 | 2.05 |
| CR obtained, % | 0.4 | 2.3 |
| CR not obtained, % | 0.15 | 1.9 |
Range of S-phase percentage at day 0 was 0% to 33%, and at day 2, 0% to 44%. NA indicates not available.
Discussion
Induction chemotherapy for AML with the use of 45 mg/m2 daunorubicin and 100 mg/m2 cytarabine is widely established as the gold standard. However, in adults younger than 55 or 60 years of age, improved CR can be obtained with a variety of other anthracyclines.6-12 However, among older adults with AML, induction toxicity is greater, and significantly more patients have unfavorable cytogenetics and, thus, more resistant disease compared with younger patients.23,24 In this study, differences in efficacy or toxicity between any of the 3 regimens were identified. However, this does not exclude the possibility that a higher dose of anthracycline or an alternative schedule might have yielded different results.
The Medical Research Council in the United Kingdom prospectively compared the combination of 45 mg/m2 daunorubicin for 3 days, 200 mg/m2 cytarabine for 10 days, and 200 mg/m2 6-thioguanine for 10 days (DAT) versus 50 mg/m2 daunorubicin for 3 days, 200 mg/m2 cytarabine for 10 days, and 100 mg/m2 etoposide (VP16) for 5 days (ADE) versus 12 mg/m2 mitoxantrone for 3 days and 200 mg/m2 cytarabine for 5 days (MAC).25 Patients receiving DAT had a better overall response rate than those receiving either ADE or MAC. However, the treatment arms were not comparable; since the protocol design did not permit a direct comparison of daunorubicin and mitoxantrone, the MAC arm included only half of the cytarabine dose and 6-thioguanine was omitted.25 Similarly, comparisons cannot be made in a recent SWOG study of induction therapy in older adults, as mitoxantrone and etoposide were compared with cytarabine and daunorubicin.26
Over the past decade, several groups have investigated whether hematopoietic growth factors can prime leukemic blasts by increasing the proportion in the active phase of the cell cycle, thereby, theoretically, increasing their susceptibility to S-phase–active agents such as cytarabine. In vitro studies have shown that growth factors such as GM-CSF, G-CSF, stem cell factor (SCF) (c-kit ligand), interleukin-3, and others can increase the fraction of leukemic blasts in the S-phase.16 Hematopoietic growth factors may enhance the cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents in AML by several other mechanisms, including facilitation of intracellular uptake of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl-cytosine 5′-triphosphate (Ara-CTP)27 or, possibly, by altering bcl-2 protein expression after cytarabine-mediated generation of reactive oxygen intermediates.28 Furthermore, it is possible that hematopoietic growth factors may also increase stimulation of leukemic cell metabolism, which may contribute to increased uptake and processing of cytarabine27 ; and finally, hematopoietic growth factors may enhance chemotherapy-induced apoptosis of leukemic blasts.29 Several important phase 2 studies suggested that in vivo blast cells could be recruited into the S-phase with little, if any, detrimental effect on the outcome of treatment.30,31 The results of these studies have been confusing,32-41 but broadly suggested that stimulation of leukemia was not generally a clinical problem. In contrast, only one study showed a beneficial effect of priming with cytokines in patients with AML.38 Two hundred forty patients aged 50 to 75 years with newly diagnosed AML were randomized to receive placebo or Escherichia coli–derived GM-CSF (5 μg/kg per day) by 6-hour intravenous infusion starting 12 hours after initiation of induction therapy on day 1 and continuing through and after chemotherapy until recovery of neutrophils or evidence of regrowth of leukemia. Although there was no difference in the overall CR rate between GM-CSF and placebo patients, the 2-year DFS was significantly improved in the GM-CSF group (48% versus 21%; P = .003). There were no in vitro laboratory correlative studies, and it is difficult to identify the biological factor most important in the improved outcome. However, a fundamental difference between this study and other reports was that the priming cytokine was not administered prior to the administration of chemotherapy, suggesting that some detrimental effect might occur following several days of blast cell stimulation without simultaneous cytotoxic therapy.42
In the present study, after priming with GM-CSF, the percentage of blasts in the S-phase increased as measured by BRDU uptake. However, this increase was minimal (mean, approximately 2%) and did not differ between those patients who attained CR and those patients who did not attain CR. This suggests that priming for 48 hours with GM-CSF, at the dose and timing of this study, did not have a sufficient effect on S-phase percentage to translate into a clinical impact.
Cytogenetics has been shown to be the most important prognostic factor in AML. These data have been rigorously analyzed in 2 major clinical trials.22,43 The best results for initial response and overall survival are for patients with favorable cytogenetics, followed by intermediate cytogenetics, and with unfavorable cytogenetics being the worst. While these data have been established for younger adults, until recently there has been no confirmation of the prognostic value of cytogenetics in older adults.44 The data from this study demonstrate that cytogenetics also remains an important prognostic factor in older patients.
The CR rate among the initial cohort of 113 patients who did not participate in the priming randomization was significantly better than the subsequent cohort of 235 patients who participated, especially among patients younger than 70 years (Table 4). Among the latter group, the actual administration of priming therapy as well as the logistics and inherent delay in randomization to blinded study medication, often entailed a delay of 4 to 5 days in the start of induction therapy. This observation must be interpreted very cautiously as these 2 groups were treated sequentially and were not prospectively compared. Nevertheless, they were treated by the same groups of physicians in the same medical centers, and there were no differences in the biology of the patient populations in these 2 groups and no differences in the therapy or supportive care. Thus, these data suggest, that delaying induction therapy in older adults with AML may have a detrimental effect on the initial response and overall outcome.
Appendix
ECOG is chaired by Robert L. Comis. The following list contains the names of ECOG institutions that were active as of October 27, 2003.TBL8
Active ECOG Institutions as of 10/27/03
Name . | Type of Institution . |
|---|---|
| Albert Einstein College (NY) | MAIN |
| Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center | MAIN |
| Cancer Institute of New Jersey | MAIN |
| Case Western-MetroHealth Medical Center | MAIN |
| Central Illinois CCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| Christiana Care CCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| Colorado Cancer Research Program CCOP | Primary CCOP |
| Columbus CCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| Emory University | MAIN |
| Evanston Hosp. (CCOP) | Primary CCOP |
| Fox Chase Cancer Center | MAIN |
| Indiana Univ Medical Center | MAIN |
| Instituto de Enfermedades Neoplasicas | MAIN |
| John H Stroger Hosp of Cook County | Primary MBCCOP |
| Johns Hopkins University | MAIN |
| LSU Medical Center CCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| Main Line Health CCOP | Primary CCOP |
| Marshfield Clinic | Primary CCOP |
| Mayo Clinic | MAIN |
| Metro-Minnesota CCOP: Abbott-NW | Primary CCOP |
| Moffitt Cancer Center | MAIN |
| New York University Medical Center | MAIN |
| Northern Indiana CRC CCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| Northwestern University | MAIN |
| Ochsner Clinic | Primary CCOP |
| OLM Cancer Center MBCCOP | Primary MBCCOP |
| Penn State Cancer Institute | MAIN |
| University of Pennsylvania | MAIN |
| University of Pittsburgh | MAIN |
| University of Pretoria | MAIN |
| San Juan Minority Based CCOP | Primary MBCCOP |
| Scott & White CCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| Southern NV Cancer Research Foundation CCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| St Francis Hospital: Oklahoma CCOP | Primary CCOP |
| St Vincent Hospital Regional Cancer Center CCOP | Primary CCOP |
| Stanford University | MAIN |
| Tufts/New England Medical Center | MAIN |
| University of New Mexico MBCCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| University of Alabama-Birmingham | MAIN |
| Vanderbilt University | MAIN |
| Medical College of Wisconsin | MAIN |
| University of Wisconsin | MAIN |
Name . | Type of Institution . |
|---|---|
| Albert Einstein College (NY) | MAIN |
| Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center | MAIN |
| Cancer Institute of New Jersey | MAIN |
| Case Western-MetroHealth Medical Center | MAIN |
| Central Illinois CCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| Christiana Care CCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| Colorado Cancer Research Program CCOP | Primary CCOP |
| Columbus CCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| Emory University | MAIN |
| Evanston Hosp. (CCOP) | Primary CCOP |
| Fox Chase Cancer Center | MAIN |
| Indiana Univ Medical Center | MAIN |
| Instituto de Enfermedades Neoplasicas | MAIN |
| John H Stroger Hosp of Cook County | Primary MBCCOP |
| Johns Hopkins University | MAIN |
| LSU Medical Center CCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| Main Line Health CCOP | Primary CCOP |
| Marshfield Clinic | Primary CCOP |
| Mayo Clinic | MAIN |
| Metro-Minnesota CCOP: Abbott-NW | Primary CCOP |
| Moffitt Cancer Center | MAIN |
| New York University Medical Center | MAIN |
| Northern Indiana CRC CCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| Northwestern University | MAIN |
| Ochsner Clinic | Primary CCOP |
| OLM Cancer Center MBCCOP | Primary MBCCOP |
| Penn State Cancer Institute | MAIN |
| University of Pennsylvania | MAIN |
| University of Pittsburgh | MAIN |
| University of Pretoria | MAIN |
| San Juan Minority Based CCOP | Primary MBCCOP |
| Scott & White CCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| Southern NV Cancer Research Foundation CCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| St Francis Hospital: Oklahoma CCOP | Primary CCOP |
| St Vincent Hospital Regional Cancer Center CCOP | Primary CCOP |
| Stanford University | MAIN |
| Tufts/New England Medical Center | MAIN |
| University of New Mexico MBCCOP (EAPP) | CCOP (Expanded Participation Project) |
| University of Alabama-Birmingham | MAIN |
| Vanderbilt University | MAIN |
| Medical College of Wisconsin | MAIN |
| University of Wisconsin | MAIN |
Prepublished online as Blood First Edition Paper, September 25, 2003; DOI 10.1182/blood-2003-05-1686.
Supported in part by Public Health Service grants CA23318, CA66636, CA21115, CA11083, and CA17145 from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, and the Department of Health and Human Services.
F.A.H. was employed by Immunex Corp, whose product (GM-CSF) was studied in the current work.
A complete list of the members of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group appears in the “Appendix.”
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
We are grateful to Ms Sonia Kamenetsky and Ms Rivka Hadomi for assistance in the preparation of this manuscript. The contents of this study are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the National Cancer Institute.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal